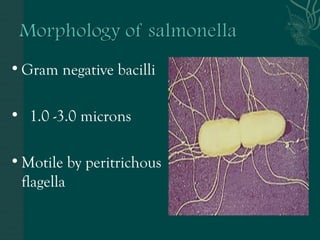
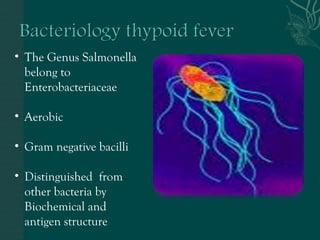
1. Salmonella is a genus of Gram-negative bacteria that can cause two main diseases: typhoid fever and food poisoning.
2. It is divided into over 2,000 serotypes based on antigen structure and species typing. Salmonella typhi causes typhoid fever while Salmonella paratyphi A, B, and C cause paratyphoid fevers.
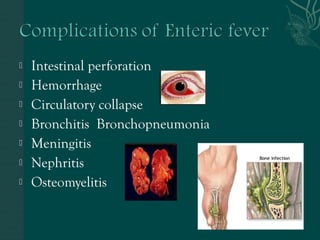
3. Salmonella is typically transmitted via contaminated food or water and causes gastrointestinal symptoms like diarrhea, fever, and abdominal cramps. Proper handwashing and avoiding raw meat and eggs can help prevent transmission.