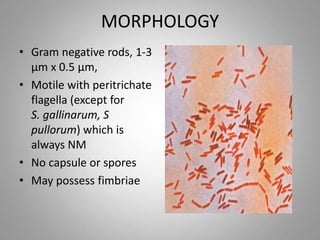
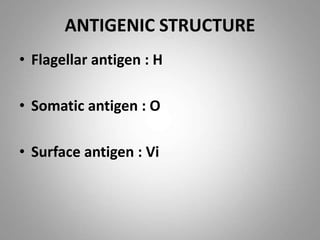
Salmonella is a gram-negative rod-shaped bacteria. There are over 2400 serotypes, with some causing typhoid fever in humans (Salmonella enterica serotypes Typhi, Paratyphi A, B, C) and others causing food poisoning (Salmonella enteritidis, S. typhimurium). Salmonella has flagella, is facultatively anaerobic, and grows well at 37°C. Identification involves culture, biochemical testing, and serotyping. Salmonella can cause typhoid fever through ingestion, initially infecting the intestines before spreading systemically. Left untreated, typhoid fever can last weeks and cause complications. Vaccines and improved sanitation help control typh