Salmonella is a gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic rod. There are over 2500 serotypes of Salmonella enterica which can cause diseases like typhoid fever and gastroenteritis in humans. S. enterica serovar Typhi causes typhoid fever. It is transmitted through the fecal-oral route. In the body, it infects the intestinal mucosa and spreads to the liver, spleen and bone marrow, causing systemic infection. Clinical features include sustained fever, headache, abdominal pain and rose colored rashes. Complications may include intestinal perforation or hemorrhage. Laboratory diagnosis involves culturing blood, bone marrow or stool to isolate the bacteria. Serological tests like the Widal test detect










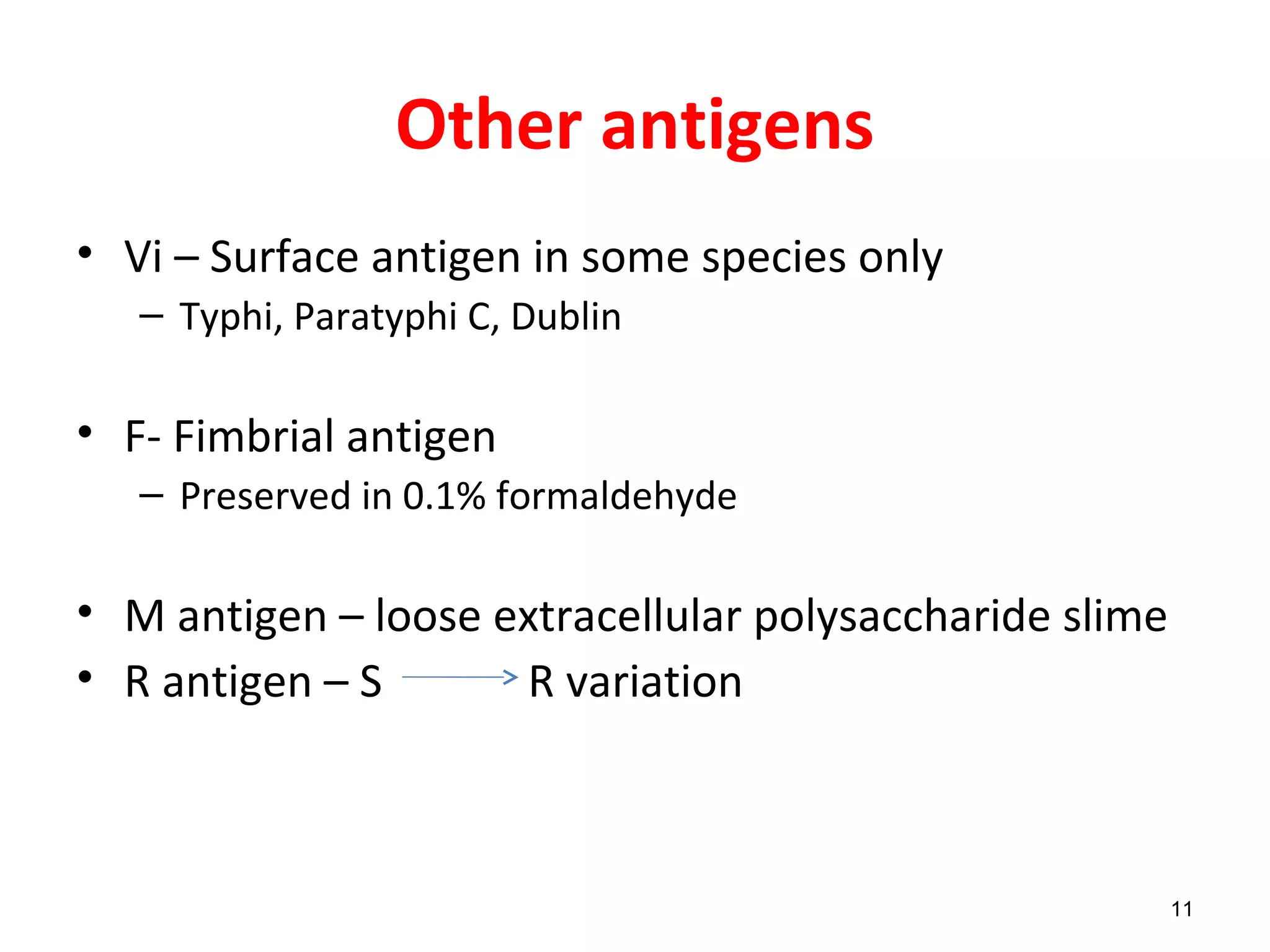
![Kauffmann – White scheme
• Serotype 0 antigens H antigens
Phase 1 2
Typhi 9,12[Vi] d -
Paratyphi A 1,2,12 a [1,5]
12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/salmonellabscnursing-190126182735/75/Salmonella-basics-12-2048.jpg)