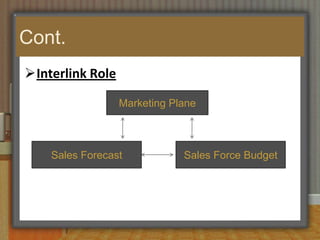
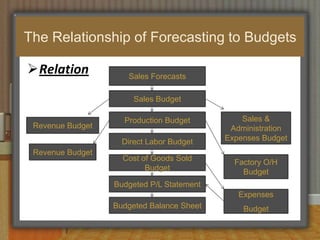
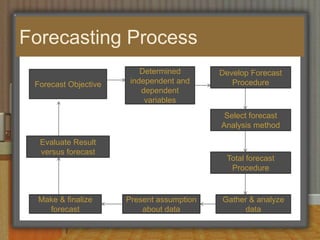
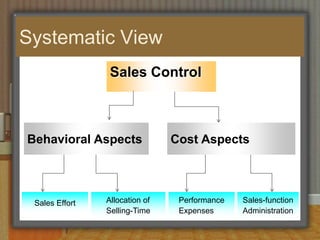
This document discusses sales budgeting, forecasting, and control. It covers developing sales budgets to plan and coordinate sales, types of budgets including sales, selling expense, and administrative budgets. Forecasting methods like macro, micro, qualitative, and quantitative are described. Sales forecasting is used for production scheduling, pricing, promotion, and financial planning. Control involves setting standards, evaluating performance, and correcting deviations to optimize sales, profits, and revenue.