1. The document discusses sales management, including defining it as the management of a firm's sales operations. It covers the objectives of sales management such as growing revenue, setting sales volumes, and improving production.
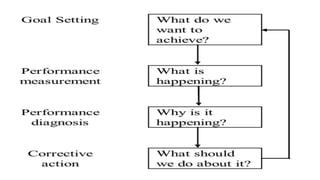
2. Sales forecasting methods are explained, including qualitative methods like expert opinion and quantitative methods like time series analysis. Sales planning and control involves setting goals, analyzing the current situation, preparing action plans, and setting performance metrics.
3. The document provides an overview of key concepts in sales management, forecasting, and planning, outlining definitions, objectives, methods, and the sales planning and control process in 3 sentences or less.