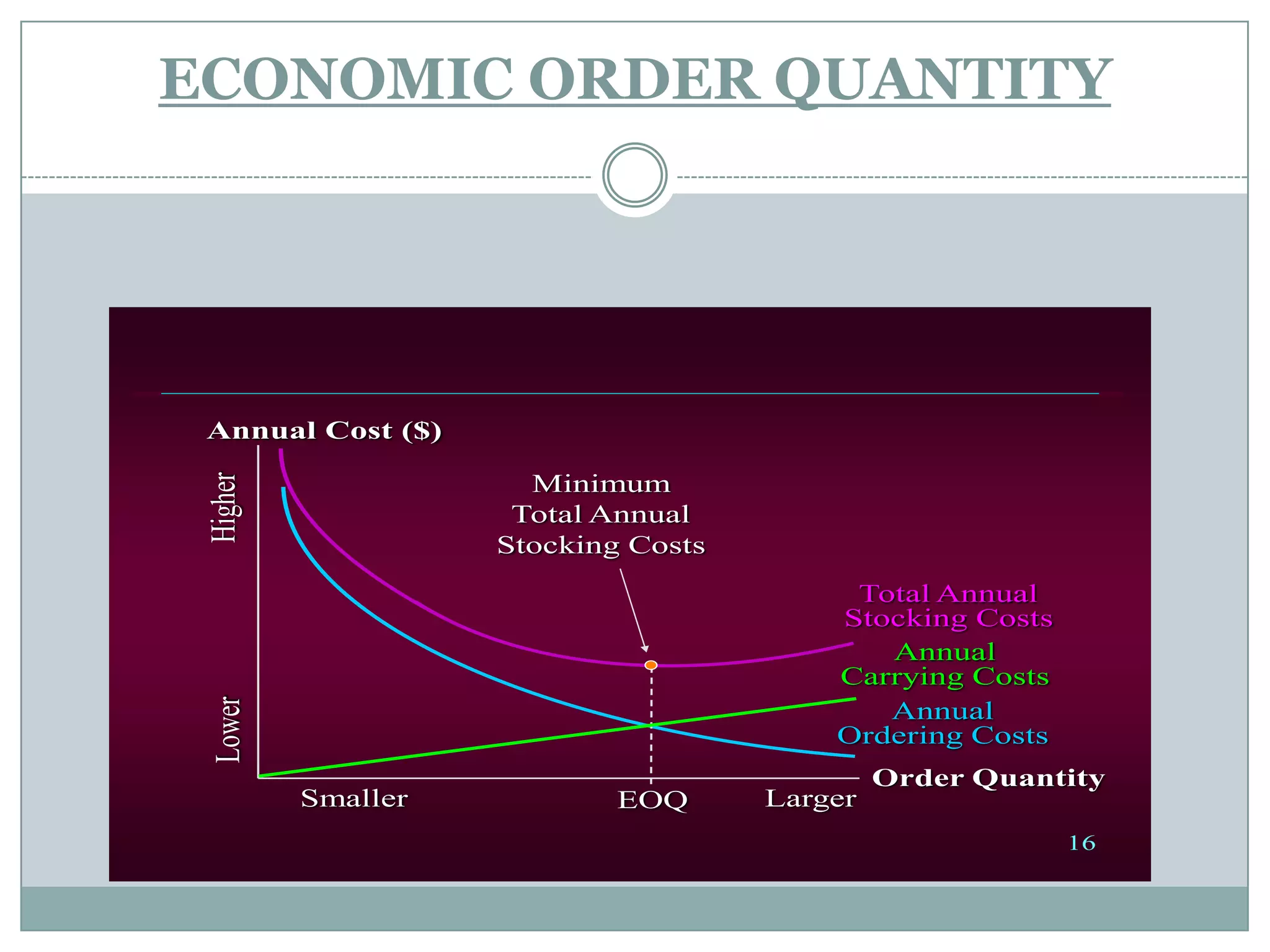
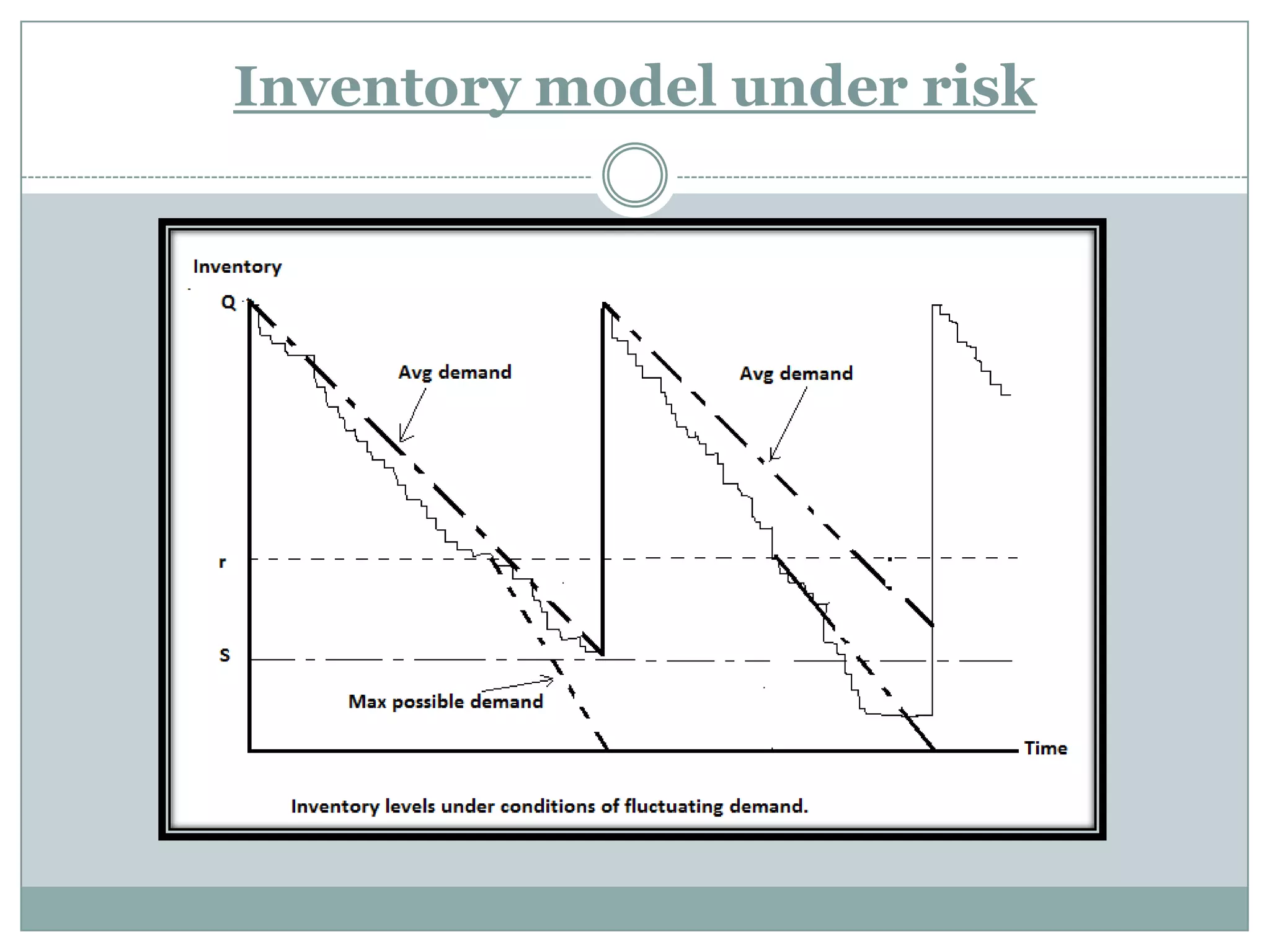
This document discusses inventory control and management. It defines inventory as physical resources held for sale or transformation, and inventory systems as policies that monitor levels and determine replenishment needs. Reasons for holding inventory include stabilizing production, taking advantage of discounts, and meeting demand during replenishment periods. The objectives of inventory control are to track inventory levels of the right quality and quantity. Costs associated with inventory include purchase, capital, ordering, carrying, and shortage costs. Decisions around inventory planning include determining order quantities and timing.