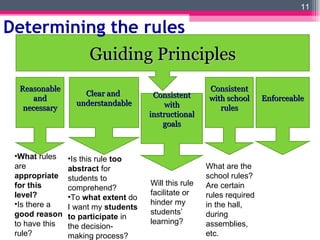
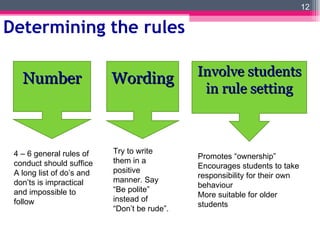
The document discusses establishing an inclusive learning environment in the classroom. It covers establishing rules and routines to create order and maximize learning time. Rules should be clear, consistent, and developed with student input. Routines provide procedures for daily tasks. The document also stresses the importance of building rapport between teachers and students to foster engagement and care. Teachers are advised to greet students warmly, get to know them, and maintain open communication.