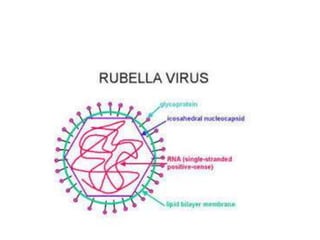
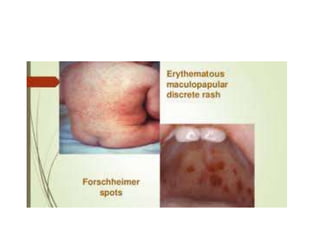
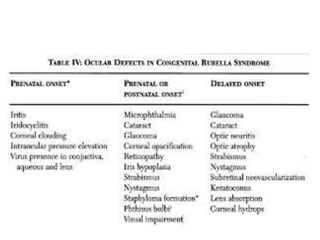
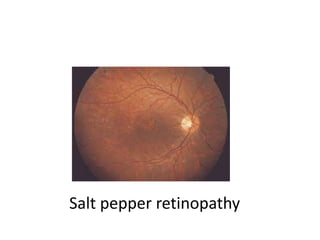
Rubella, also known as German measles, is caused by the rubella virus and can lead to congenital rubella syndrome if transmitted during pregnancy. Symptoms include a maculopapular rash, fever, and respiratory issues, appearing 14-21 days post-infection. Prevention is through vaccination, and while treatment is generally supportive, severe cases can result in serious complications such as deafness and cardiac defects.