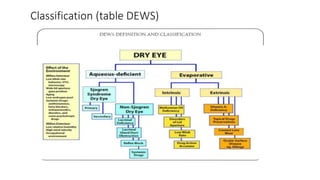
Dry eye, also known as keratoconjunctivitis sicca, is a condition caused by either a deficiency in tear production or abnormalities in the tear film that lead to increased tear evaporation. There are two main types - aqueous deficiency dry eye and evaporative dry eye. Common tests used to diagnose dry eye include tear film break-up time (TBUT), Schirmer test to measure tear production, and rose Bengal staining to detect damage to the ocular surface. Signs and symptoms include irritation, dryness, redness, and punctate erosions seen on fluorescein staining of the cornea. Treatment focuses on managing the underlying cause, supplementing tears, and preventing further tear film evaporation