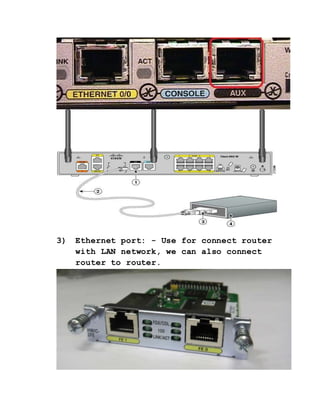
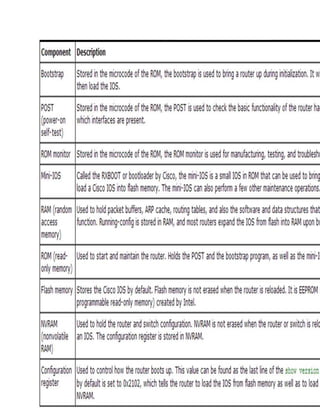
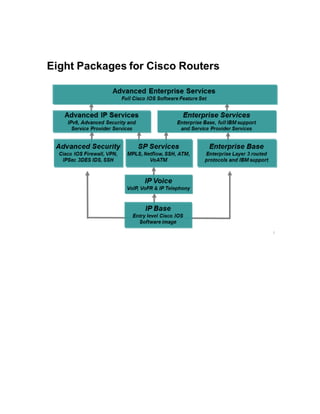
A router is a networking device that operates at the network layer and connects different networks. It selects the best and shortest path for packet forwarding based on its routing table, and can filter traffic using access control lists. Routers have various ports including console, auxiliary, Ethernet LAN ports, and serial WAN ports used to connect to other routers and modems. The Cisco IOS software controls router functions and is loaded during bootup from flash memory or a TFTP server.