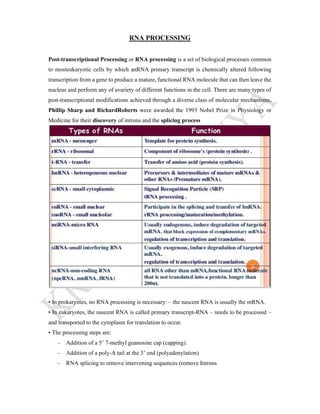
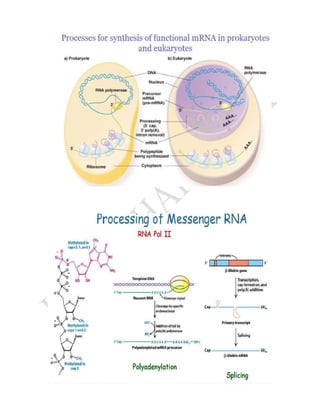
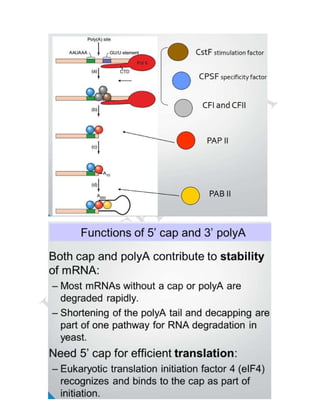
RNA processing is the set of post-transcriptional modifications that produce a mature RNA molecule from a primary transcript in eukaryotic cells. This involves adding a 5' cap, polyadenylating the 3' end, and splicing out introns. Polyadenylation involves cleavage of the nascent RNA downstream of the AAUAAA sequence by ribonuclease, followed by addition of around 200 adenine nucleotides to the 3' end by poly(A) polymerase. The spliceosome, composed of small nuclear RNAs and proteins, facilitates splicing by binding to splice sites on the RNA and catalyzing transesterification reactions to remove introns and ligate exons.