This document provides an overview of MATLAB, including:
- MATLAB was developed in 1984 as a technical computing tool for tasks like numerical computation, data analysis, and GUI building.
- It describes basic MATLAB commands, operators, functions, and how to generate GUIs.
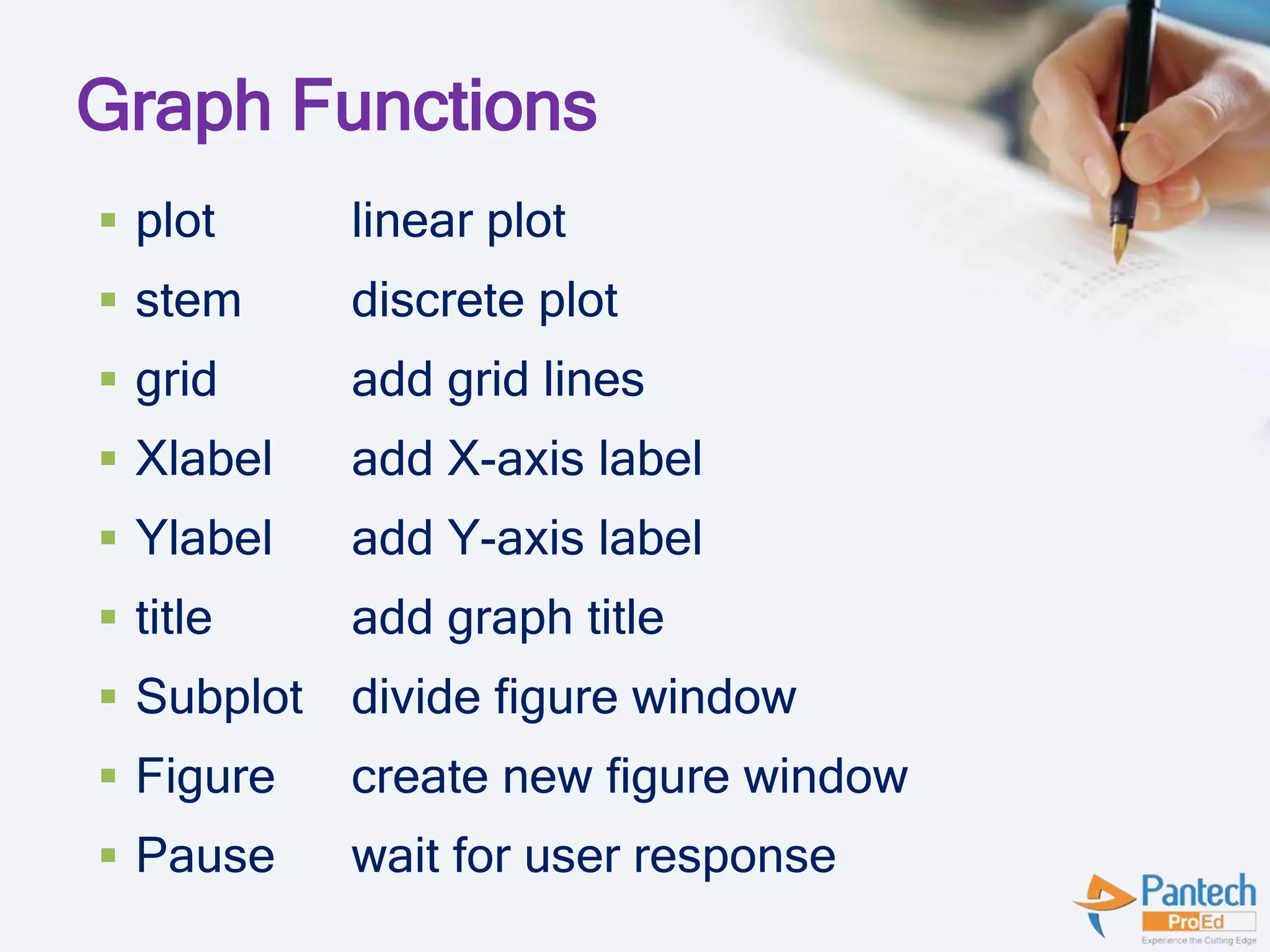
- Graphical functions, arithmetic operators, logical operators, matrices, plots, loops, and basic GUI components are explained.
- The document concludes with contact information for the presenter.










![Matrix Creation
When entering a matrix, separate columns by
spaces or commas; separate rows by semicolons.
For example, typing:
A = [1 2; 3 4]
results in:
A = 1 2
3 4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/matlab-170803065711/75/Matlab-13-2048.jpg)