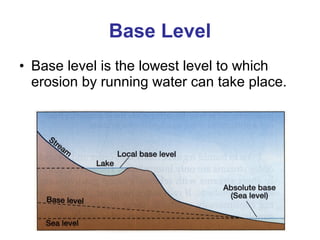
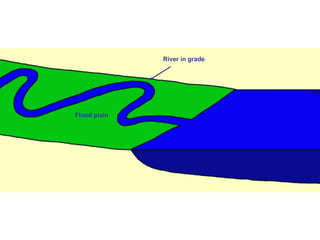
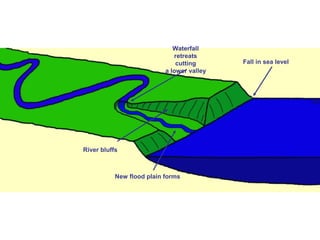
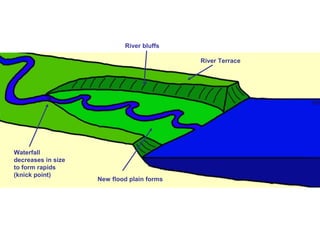
This document discusses river rejuvenation and the landforms it produces. River rejuvenation occurs when a river's base level changes, such as due to sea level change or glacial isostatic adjustment. This decreases the river's gradient, increasing its erosional power. Key landforms produced include waterfalls, incised meanders, river terraces, and knickpoints as the river grade is adjusted to the new base level.