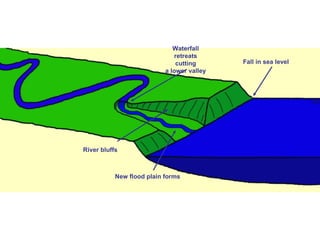
River rejuvenation occurs when a river's base level changes, altering the gradient of the river channel and increasing its erosive power. This causes the river to cut downward into its channel, forming landforms such as waterfalls, incised meanders, and river terraces. Changes in base level are typically caused by isostatic adjustments to sea level from glacial rebound or eustatic sea level changes.