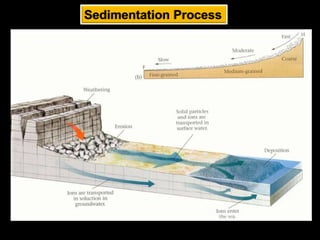
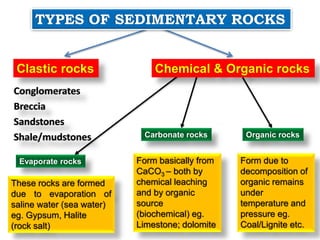
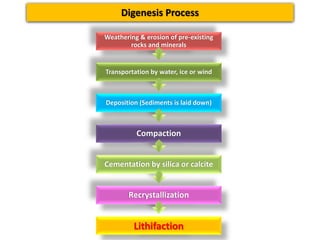
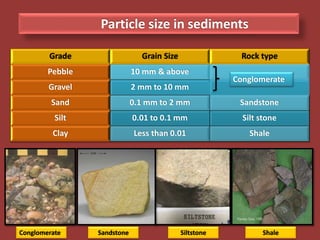
Sedimentary rocks are formed by the consolidation and cementation of sediments. Sediments are deposited under water by processes like weathering and erosion of pre-existing rocks. They are then transported by agents such as water, ice, or wind before being deposited. Over time and with sufficient pressure and cementation, sediments lithify to form sedimentary rocks. Sedimentary rocks can be clastic rocks composed of fragments, or non-clastic chemical and organic rocks formed through precipitation or organic processes. Common sedimentary rock types include conglomerates, sandstones, shales, limestones, dolomites, gypsum, halite, and coal.