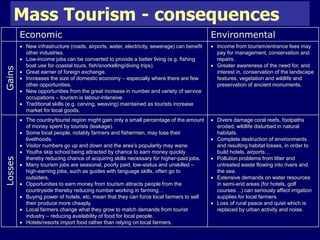
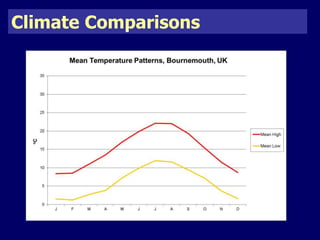
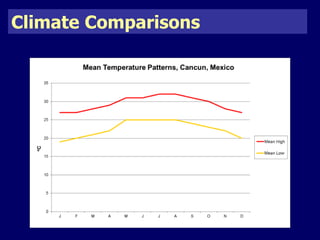
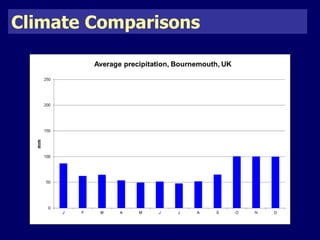
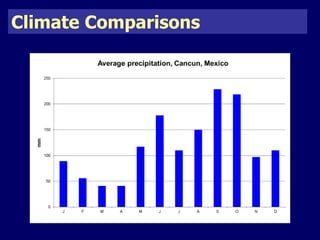
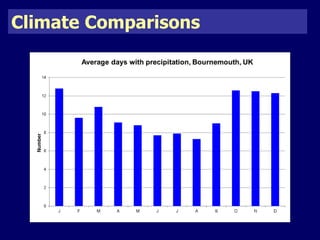
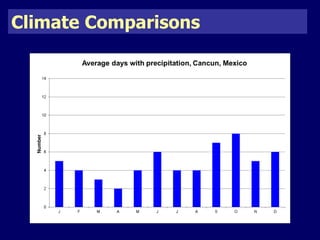
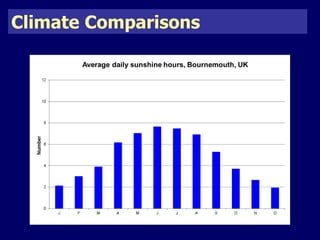
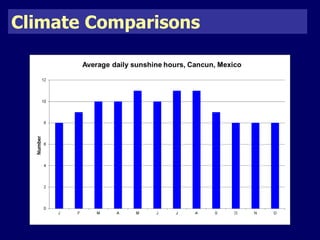
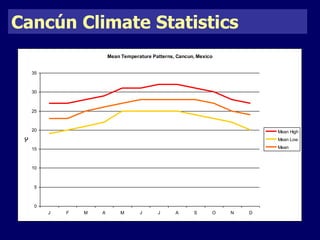
The document discusses mass tourism, providing characteristics and examples of its development. It describes how formerly small fishing villages in Spain were transformed into large resorts catering solely to tourists. A card sorting activity identifies both economic and environmental gains and losses from mass tourism. Gains include job creation and infrastructure development, while losses include damage to environments and local cultures.