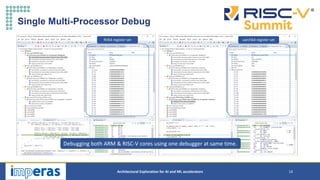
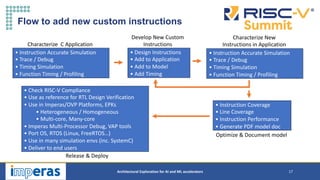
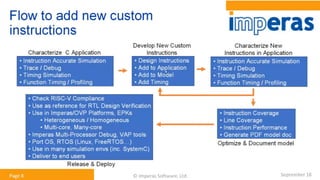
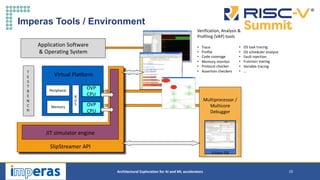
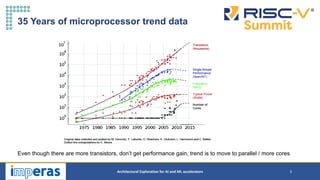
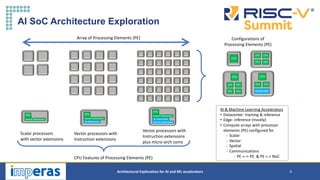
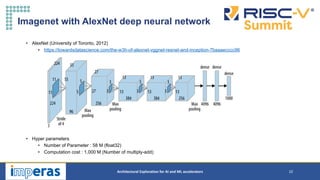
This document discusses architectural exploration for AI and ML accelerators using simulation tools. It notes that current AI/ML applications require custom hardware configurations to achieve performance goals. The Imperas simulation tools allow analyzing performance on different hardware designs by running software on virtual platforms months before RTL implementation. Imperas provides virtual platforms for heterogeneous systems running full operating systems along with detailed analysis, profiling and debugging tools. It also includes a RISC-V reference model that enables developing custom instructions for architectural exploration of AI/ML accelerators.








![Information Classification: General
Architectural Exploration for AI and ML accelerators 12
Simulate a Virtual Platform model
UART0
(for ARM[0])
UART1
(for RV64[0])
UART2
(for RV64[1])
UART3
(for RV64[2])
UART17
(for RV64[16])
RAM
ARM
Cortex-A57 [0]
RISC-V
RV64GC [0]
RISC-V
RV64GC [1]
RISC-V
RV64GC [16]
RAM
RAM Bus bridge
Bus bridge
ARM bus RISC-V bus
shared bus
…
…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/risc-vsocarchitecturalexplorationforaiandmlaccelerators-210317222942/85/RISC-V-SoC-Architectural-Exploration-for-AI-and-ML-Accelerators-12-320.jpg)