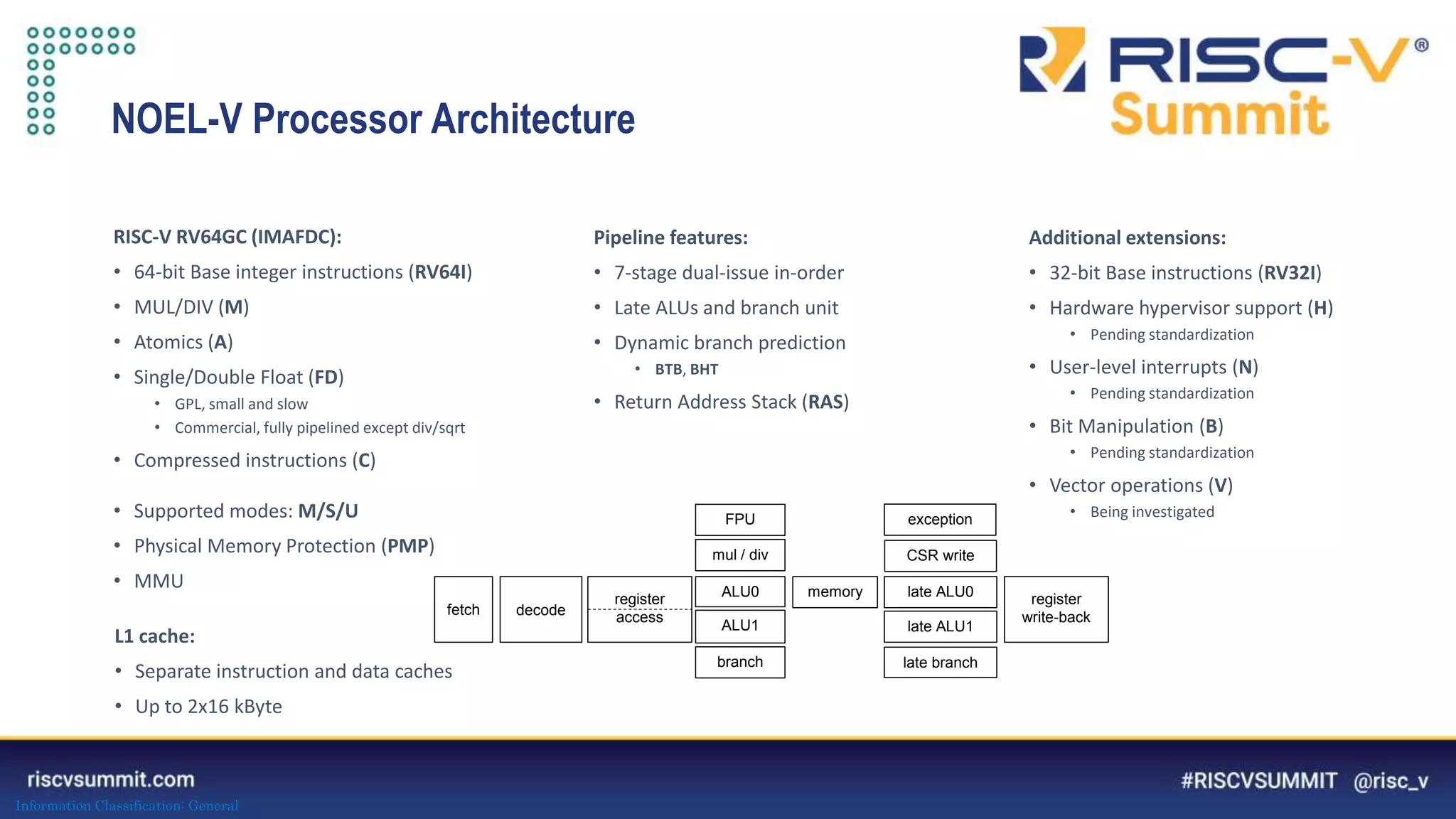
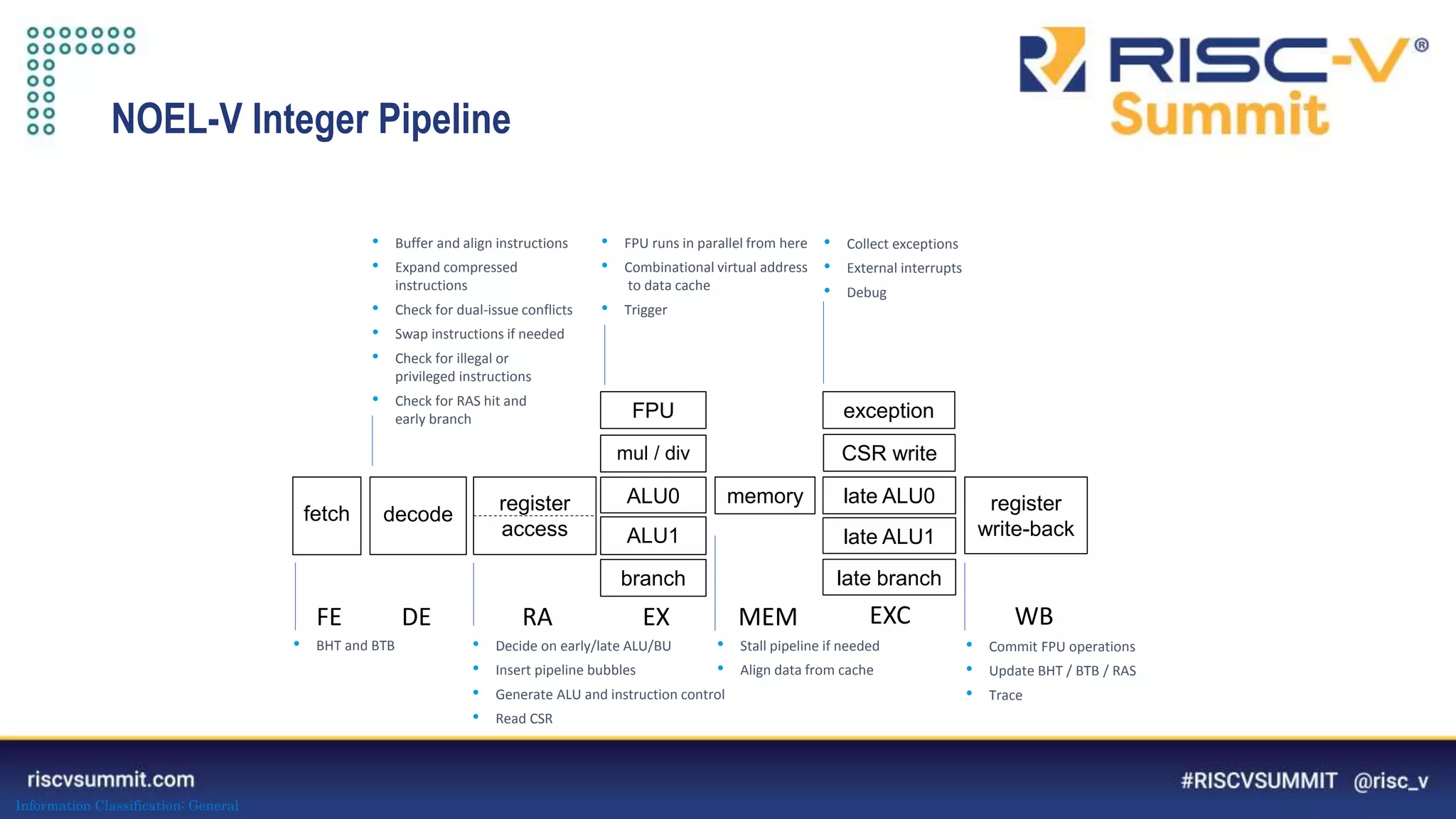
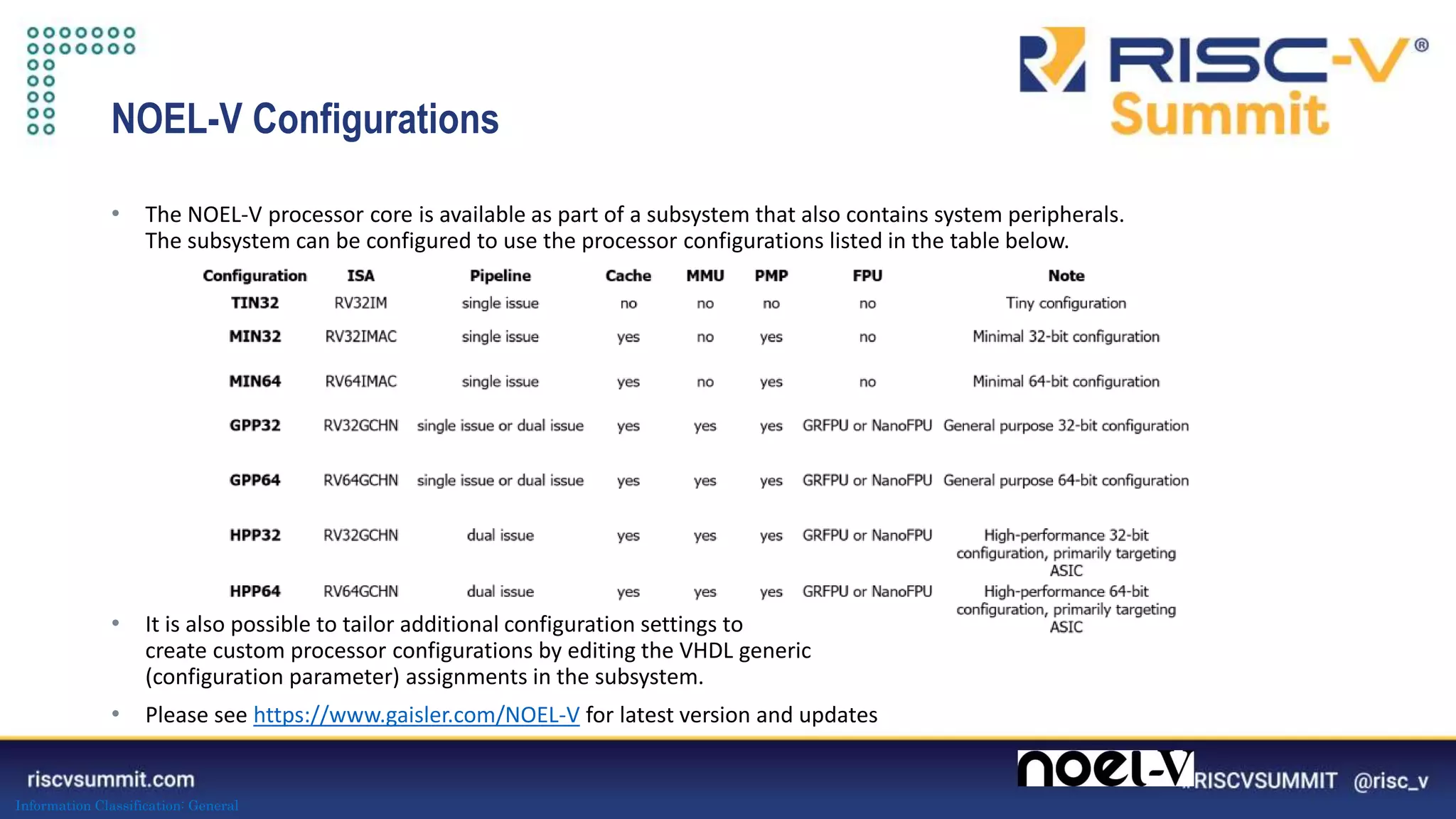
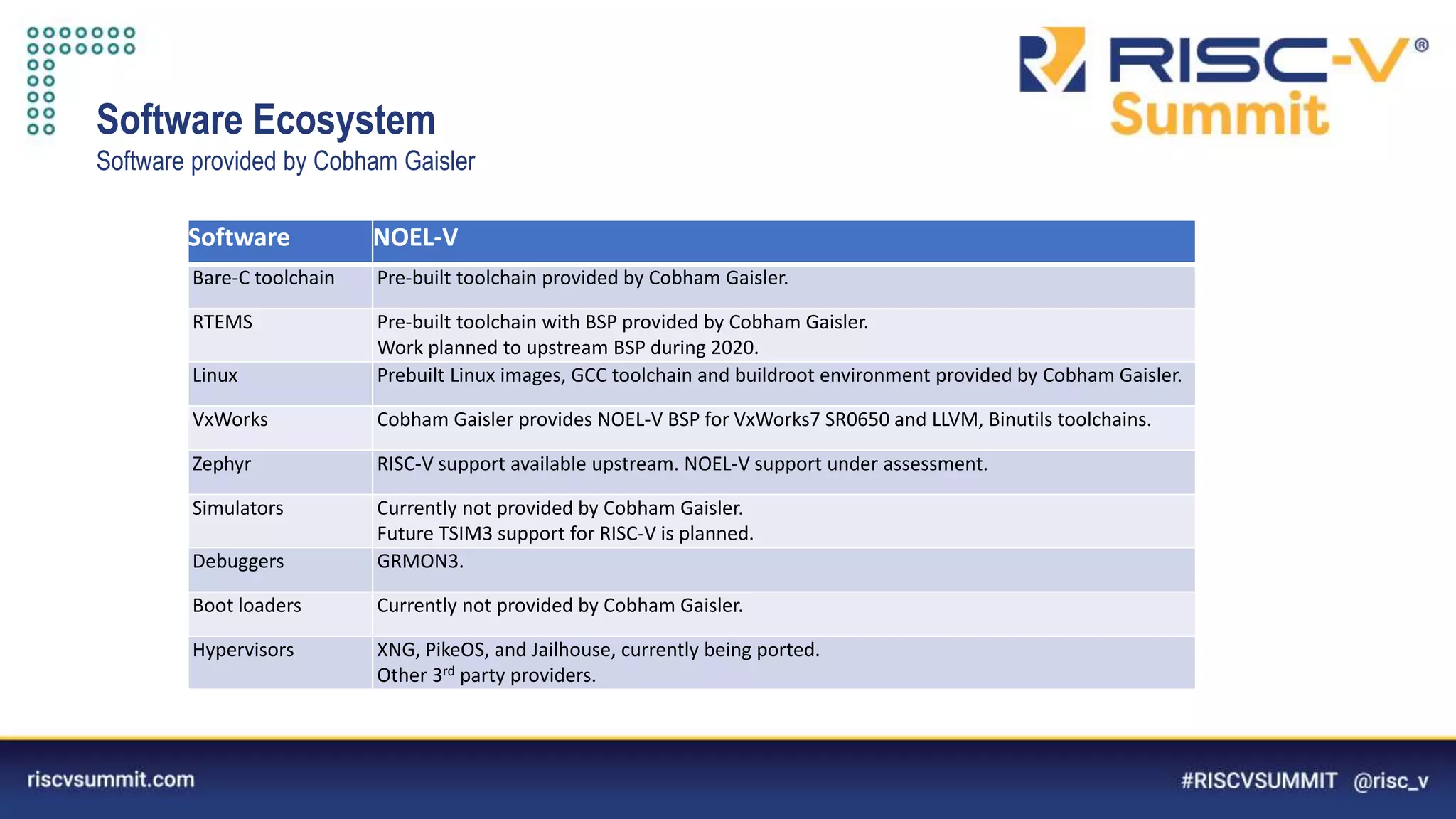
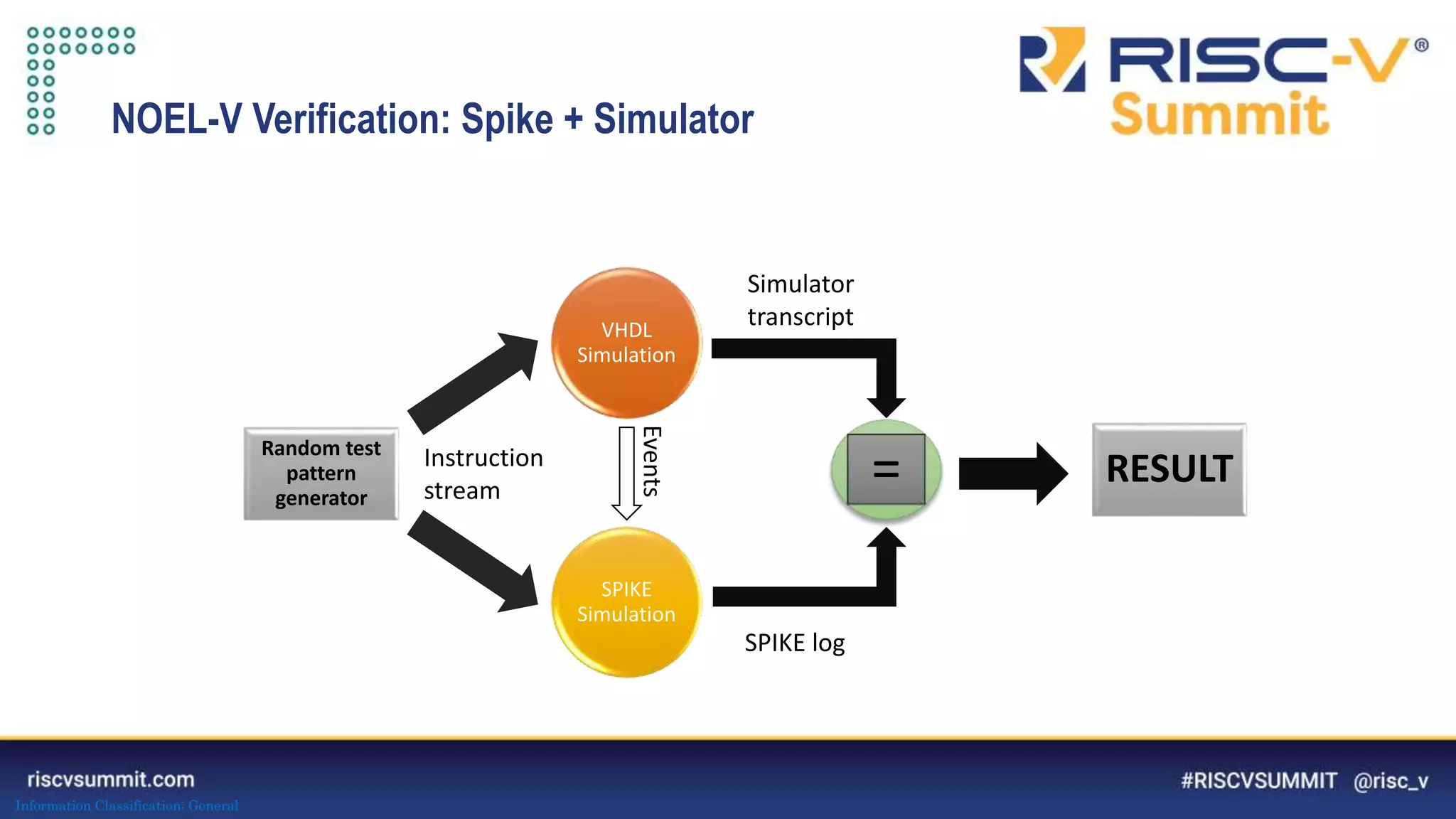
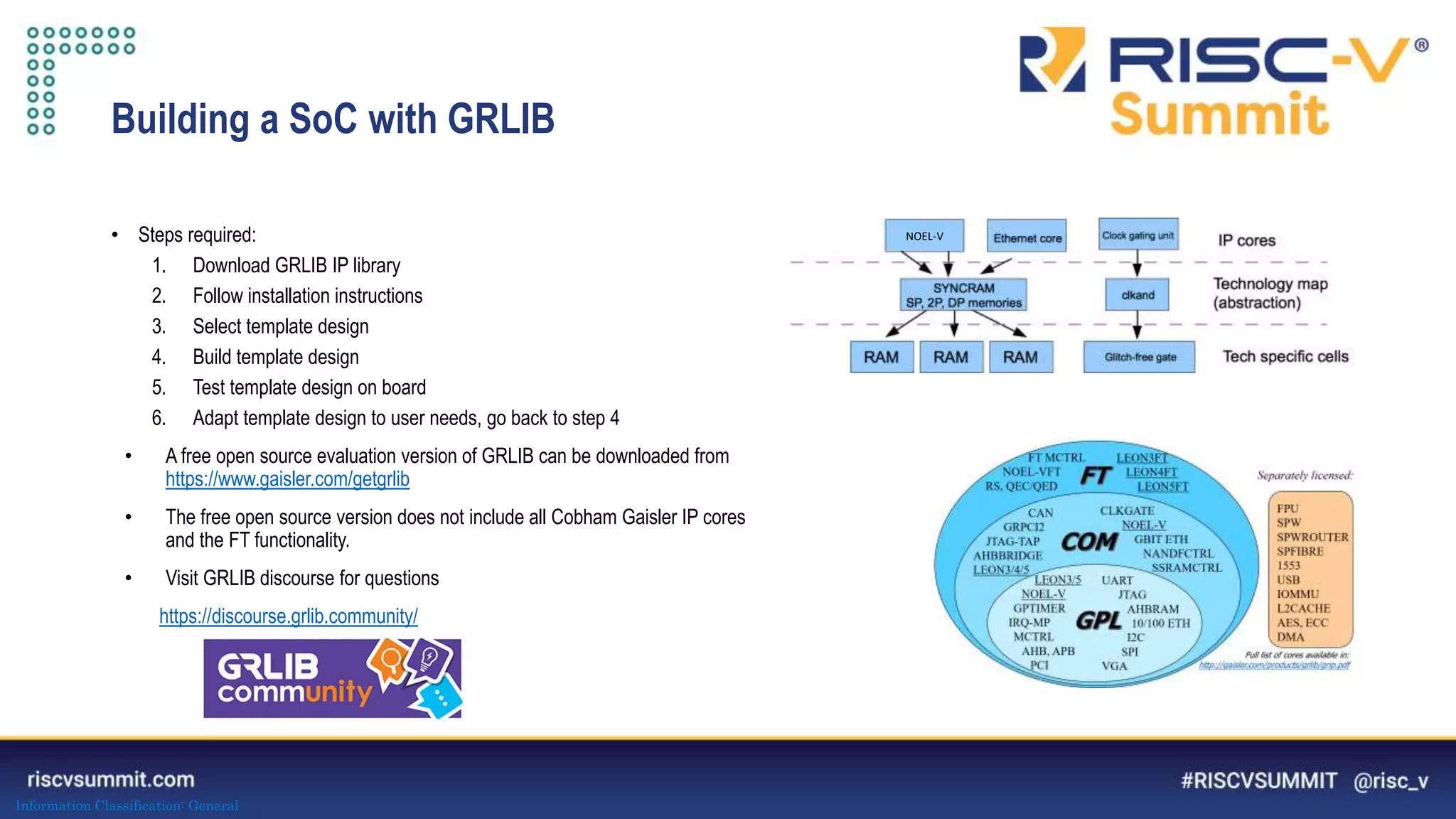
This document summarizes the NOEL-V processor family from Cobham Gaisler. It describes the NOEL-V as a RISC-V compliant 64-bit processor with fault tolerance features. It provides details on the processor architecture, peripherals, software ecosystem, verification process, and commercial and open source availability. Examples of projects adopting the NOEL-V include the European H2020 funded De-RISC and SELENE projects for safety-critical computing.