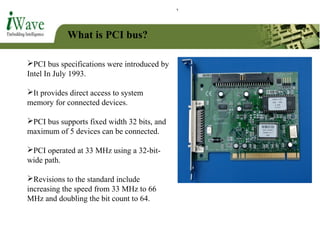
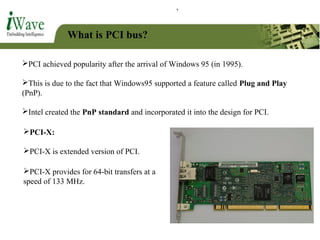
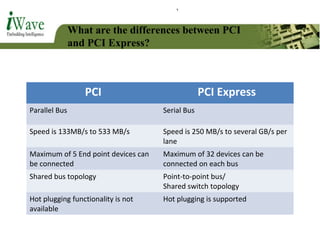
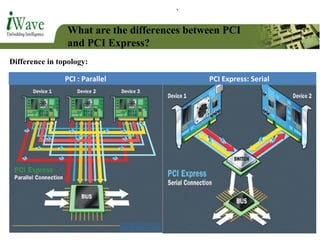
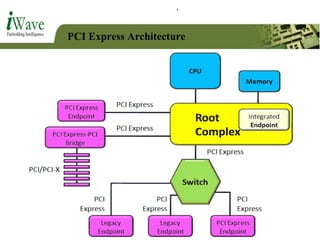
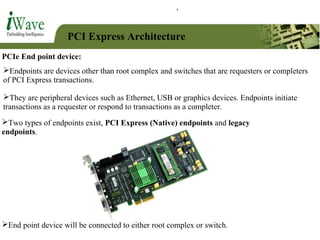
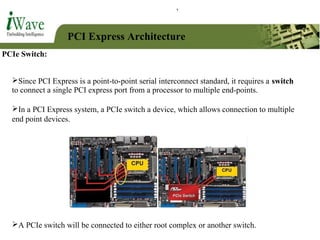
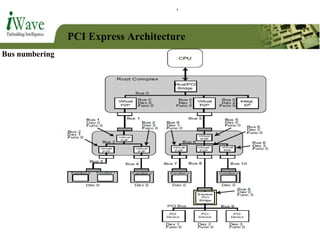
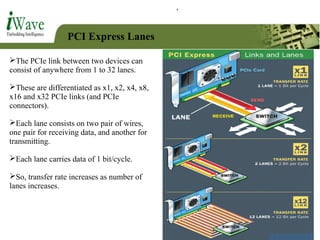
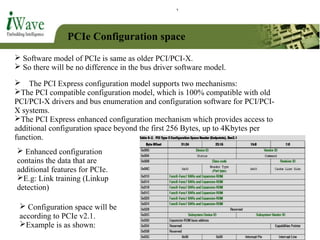
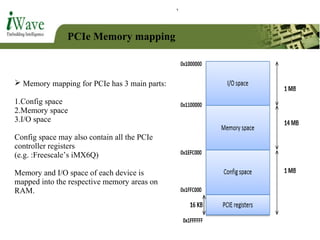
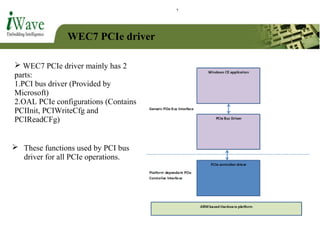
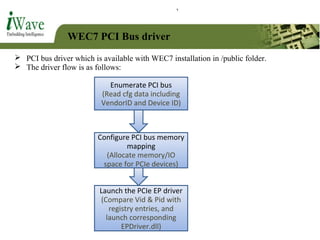
This document provides an overview of PCI and PCI Express buses. It defines PCI as a parallel bus standard introduced in 1993 to connect peripherals to the computer. PCI Express is described as a newer serial standard introduced in 2004 that offers improvements over PCI like higher throughput and hot plugging support. The document outlines key differences between the two standards and provides details on PCI Express architecture including root complexes, endpoints, switches, and bridges. It also covers topics like PCI Express lanes, connectors, configuration space, and memory mapping. In the end it provides a brief introduction to PCI bus drivers in the Windows environment.