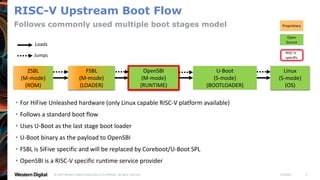
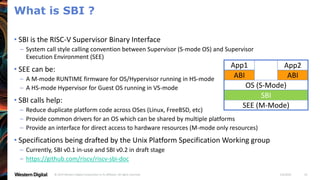
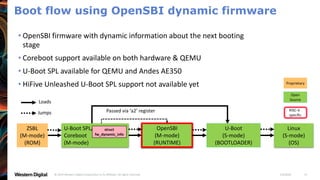
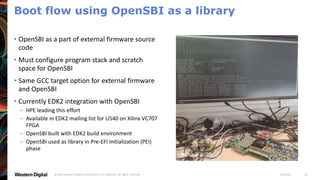
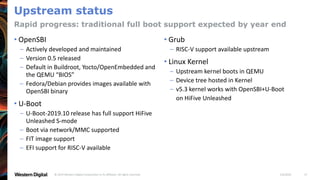
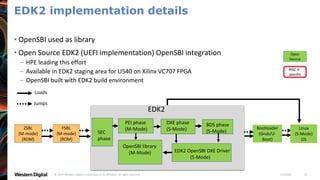
- OpenSBI is an open-source implementation of the RISC-V Supervisor Binary Interface (SBI) specifications. It provides runtime services in M-mode to facilitate booting of operating systems.
- OpenSBI supports various RISC-V platforms including SiFive boards, QEMU, and is integrated with projects like U-Boot and EDK2. It provides a standardized way for operating systems to interface with the underlying hardware.
- Future work includes supporting more platforms, implementing the SBI v0.2 specification, and enabling features like sequential CPU boot and hypervisor support. OpenSBI aims to establish a stable boot ecosystem for RISC-V.