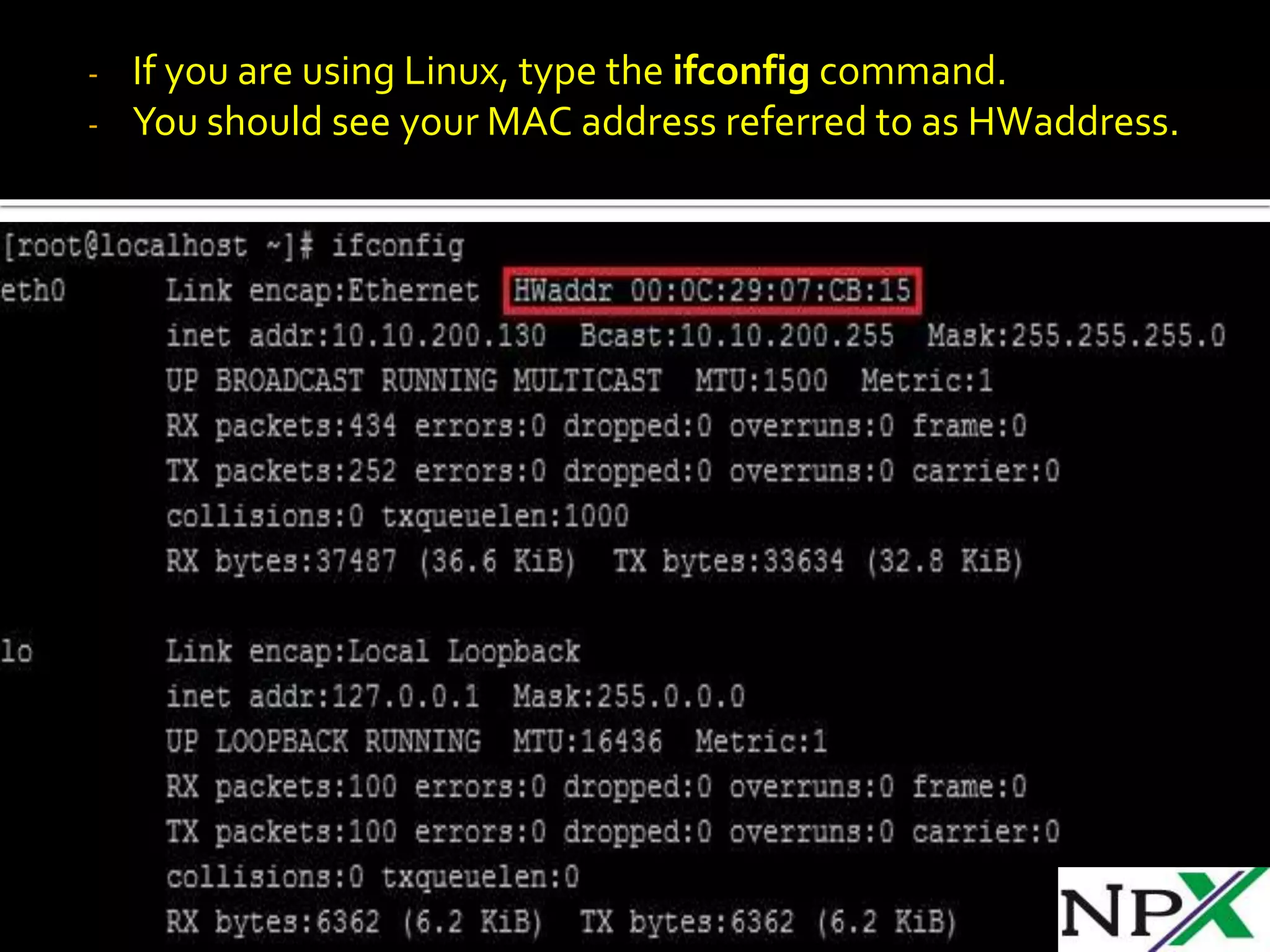
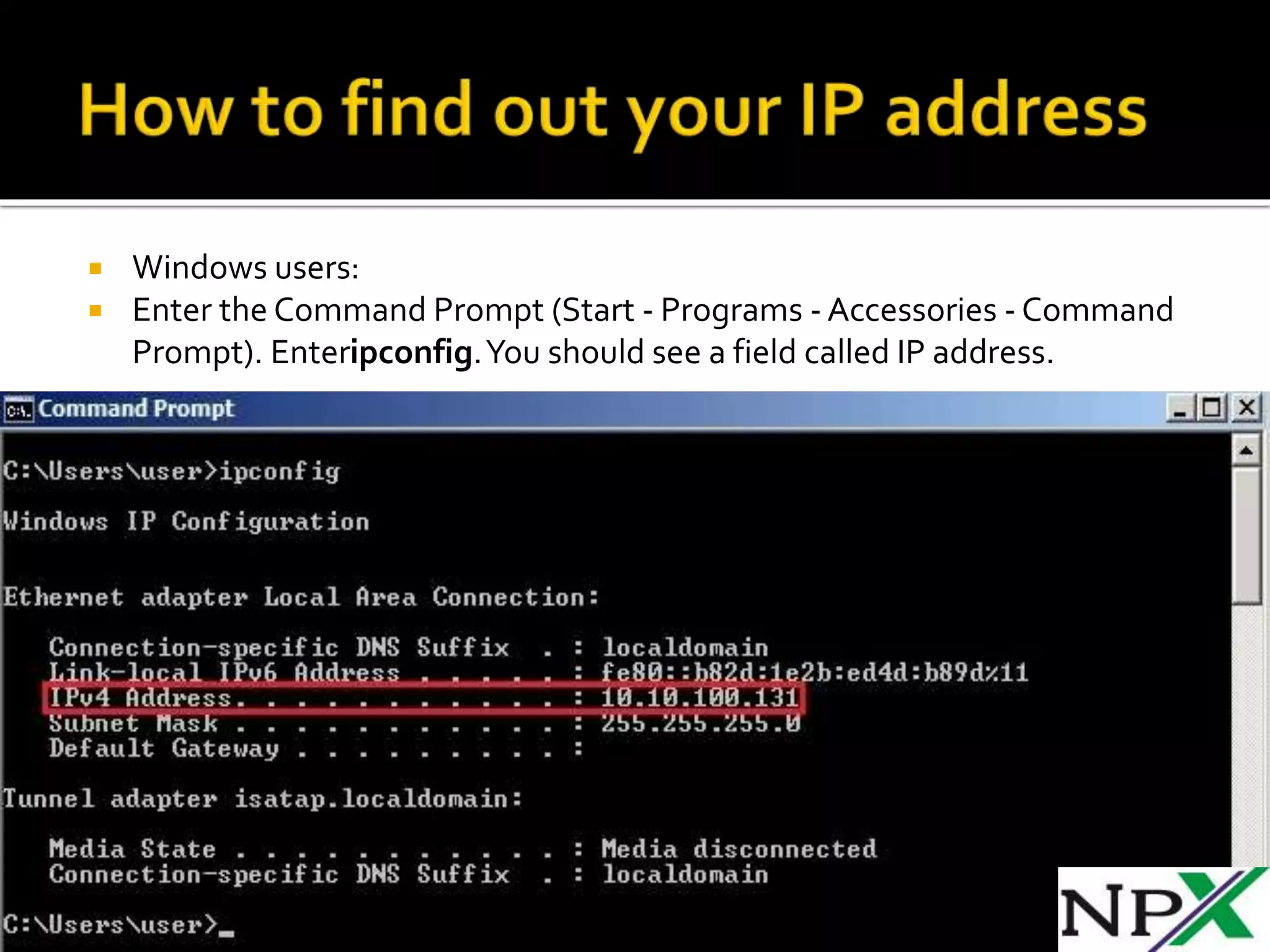
A MAC address is a 48-bit hardware address that uniquely identifies network interfaces for communication in an Ethernet network. It is stored in the network card's firmware and is usually written as 12 hexadecimal digits separated by hyphens. An IP address is a 32-bit logical address that identifies a device on an IP network and can be configured manually or automatically via DHCP. Private IP address ranges like 10.0.0.0/8 and 192.168.0.0/16 are non-routable and used for local area networks.