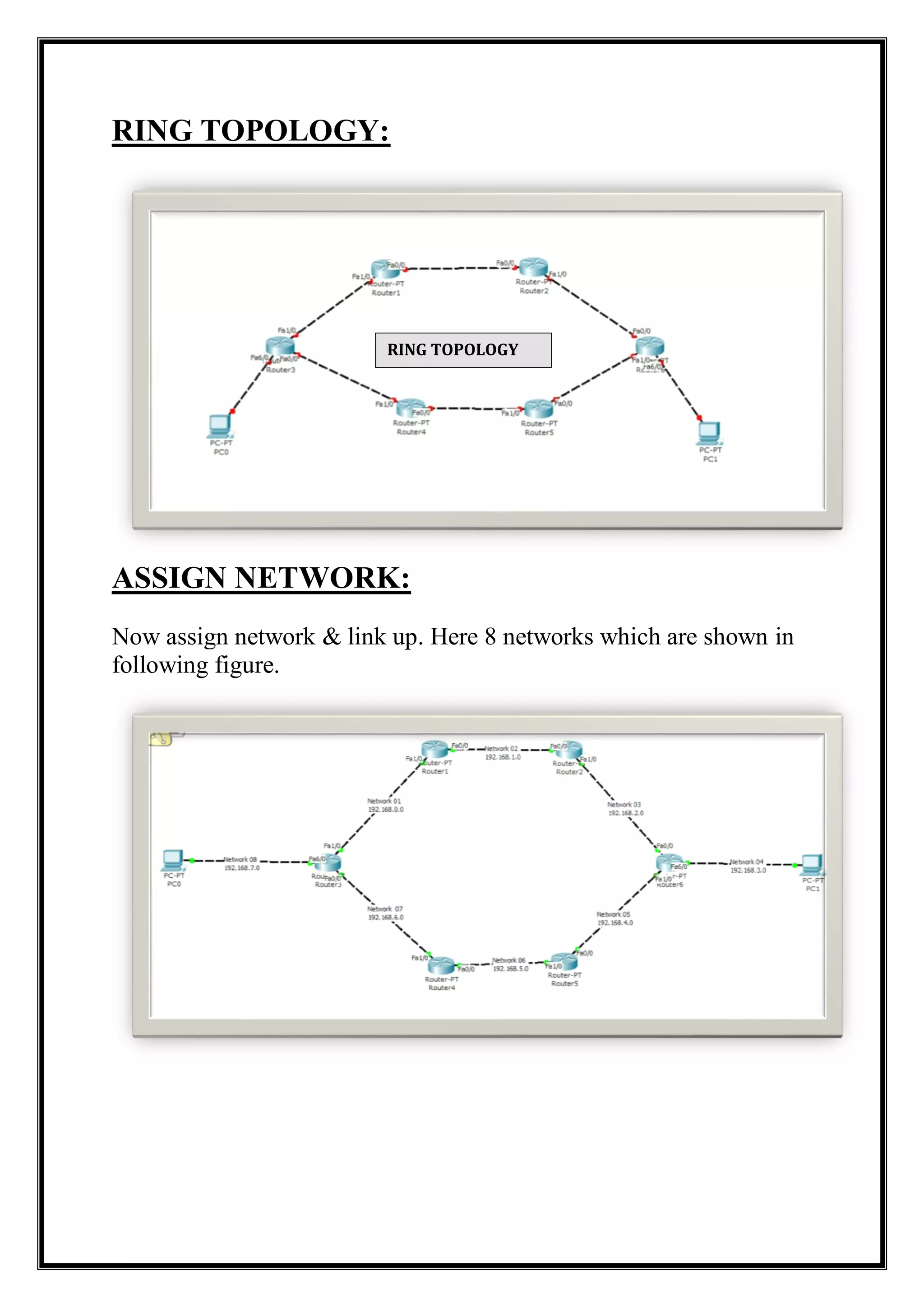
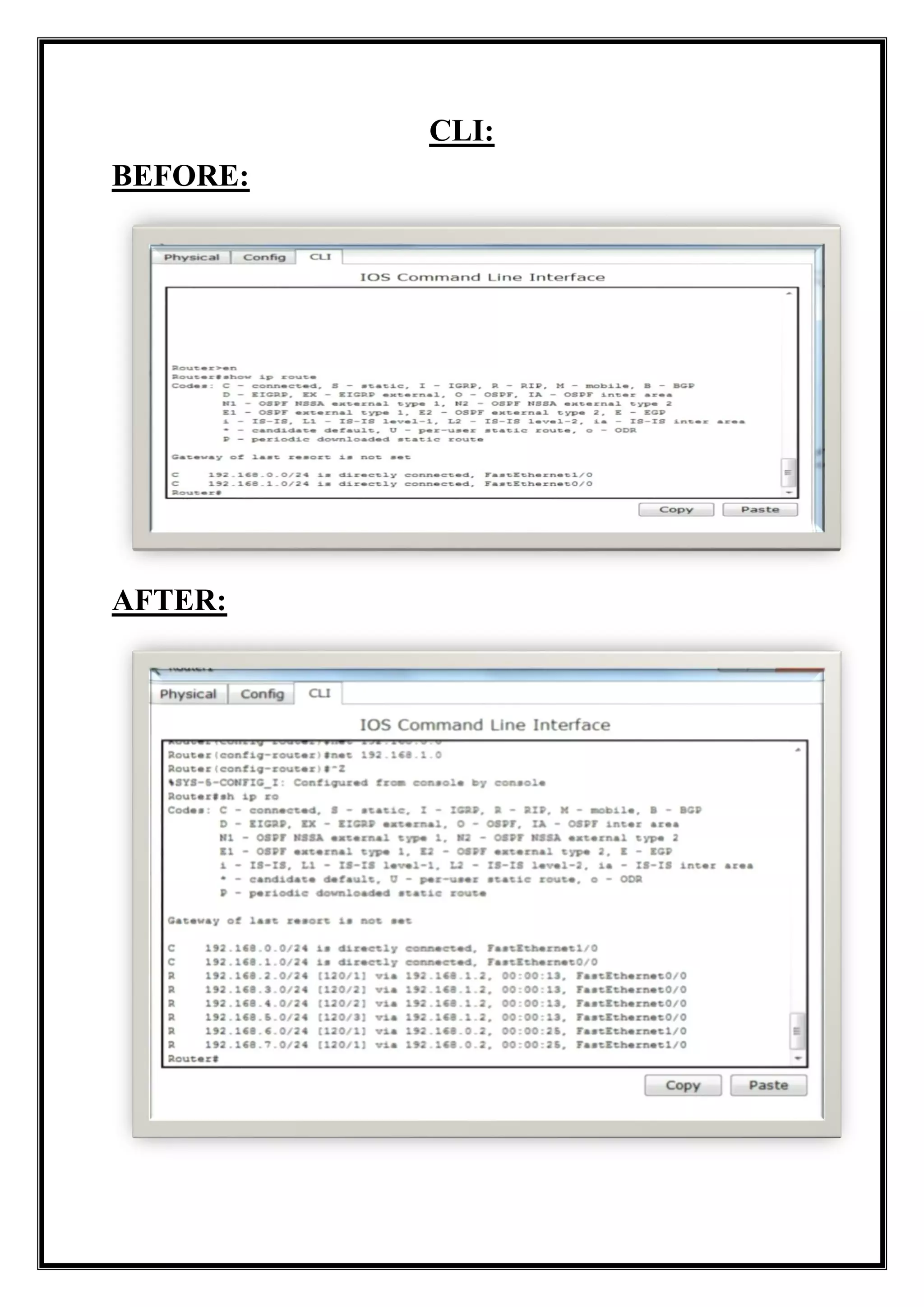
The document provides an overview of the Routing Information Protocol (RIP), detailing both version 1 and version 2, including their definitions, advantages, disadvantages, and operational details. It explains RIP's reliance on hop count as a metric for routing, with version 1 being a classful protocol and version 2 being classless, allowing for subnet information. Additionally, the document describes a ring topology setup using routers and end devices, demonstrating RIP configuration and its effects on network visibility.