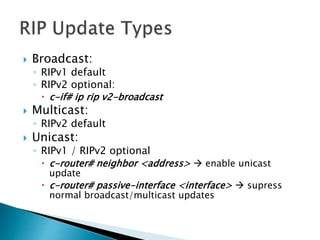
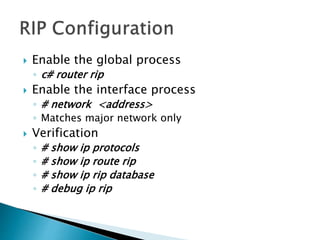
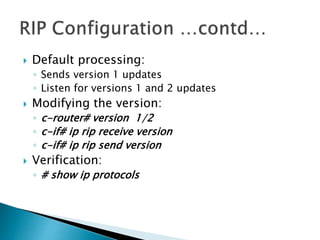
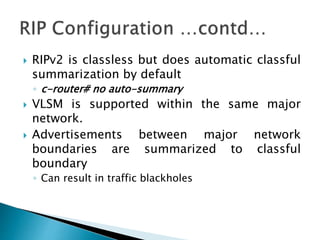
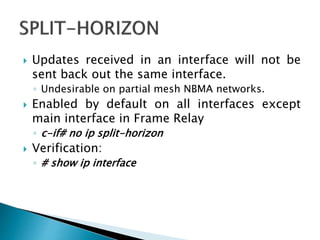
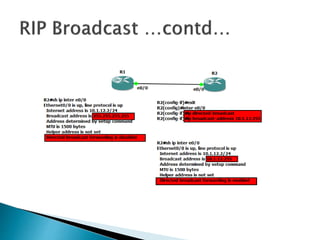
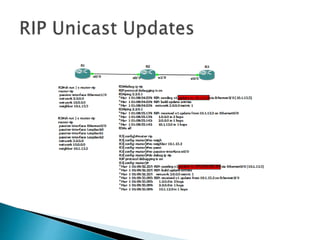
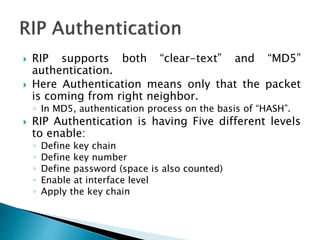
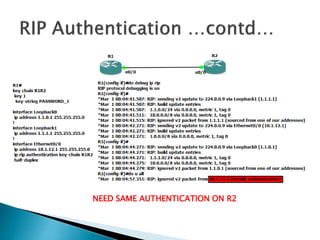
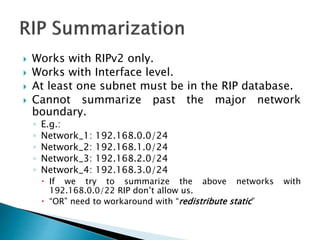
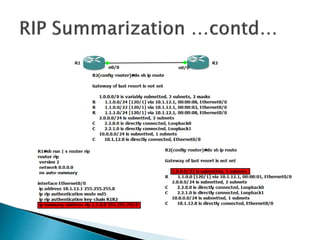
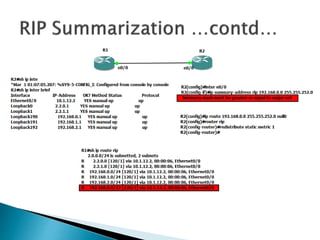
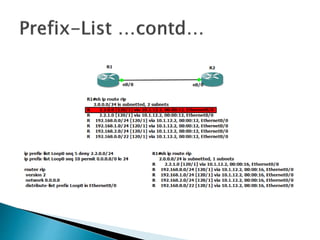
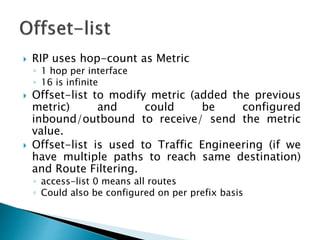
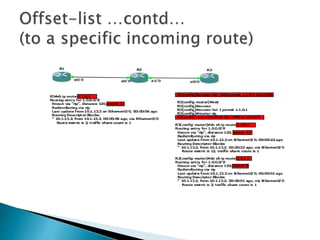
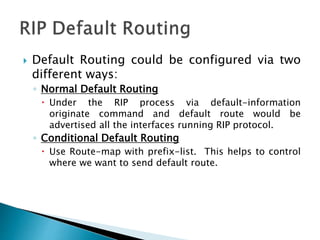
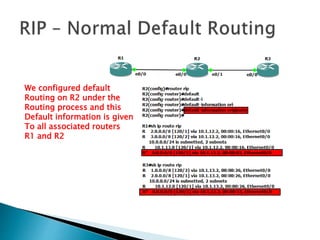
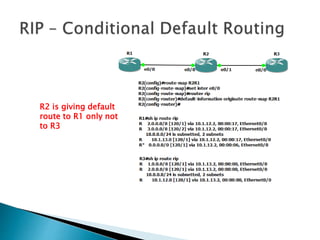
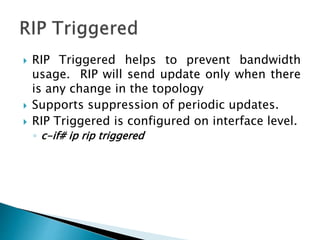
The document discusses the Routing Information Protocol (RIP). It describes that RIP is a distance-vector interior gateway protocol that uses hop count as its routing metric. It discusses the two versions of RIP - RIPv1 and RIPv2, and their differences in areas like classful/classless operation, broadcast/multicast updates. It also covers RIP configuration, operation, timers, authentication, route filtering, and other features.