Embed presentation

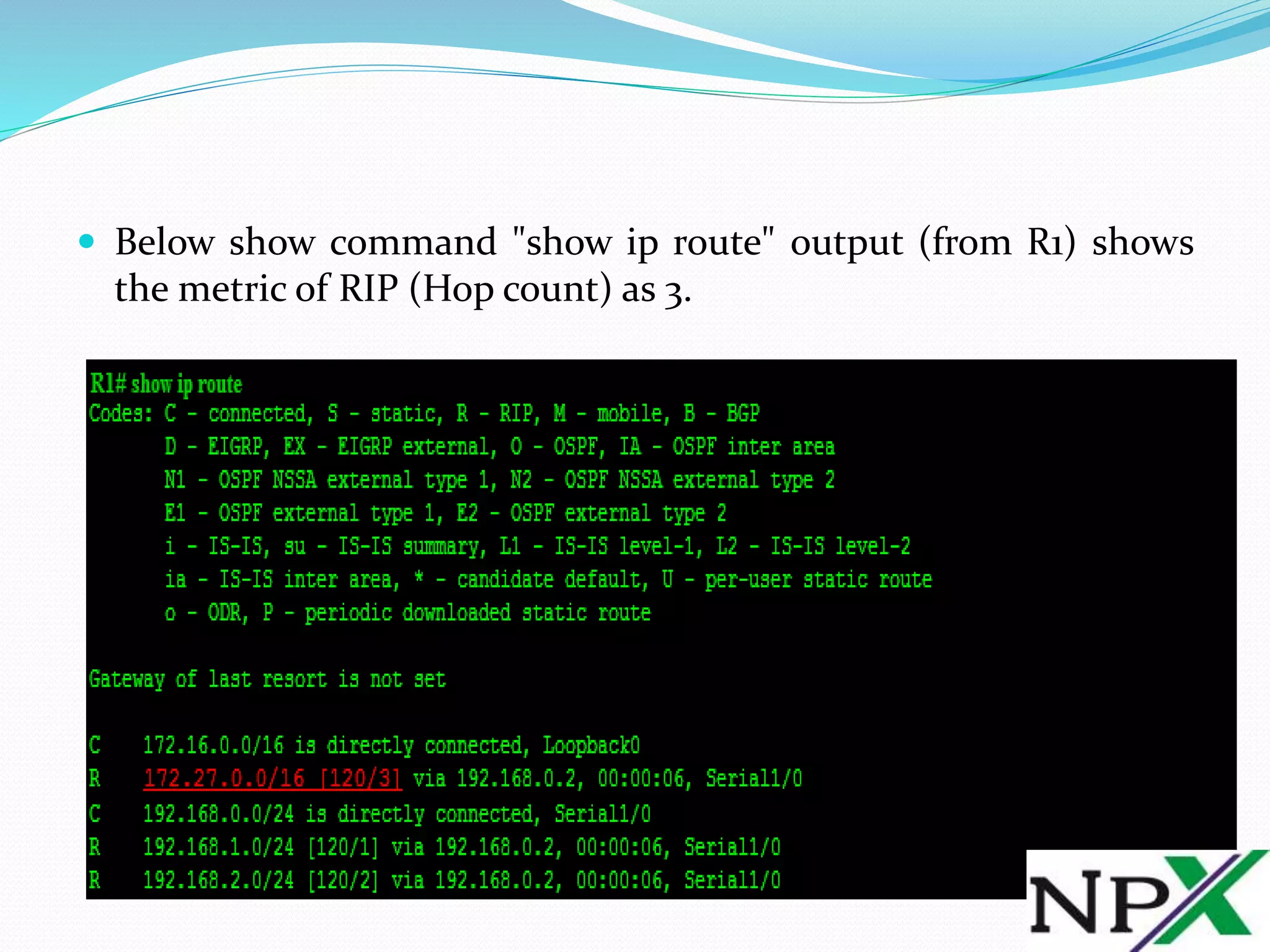
![ From above output, [120/3] shows 120 is the
default Administrative Distance of RIP (Routing Information
Protocol) and 3 is the metric (Hop Count) of RIP (Routing
Information Protocol) for above topology.
RIP (Routing Information Protocol) selects the best path to a
Destination Network based only on the number of hops to the
destination network. If you have multiple paths with different
bandwidth to the destination network, then RIP’s best path
calculation may become wrong.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ripmetrichopecountandhopcountcalculation-160704054916/75/RIP-Metric-Hope-Count-and-Hop-Count-Calculation-5-2048.jpg)

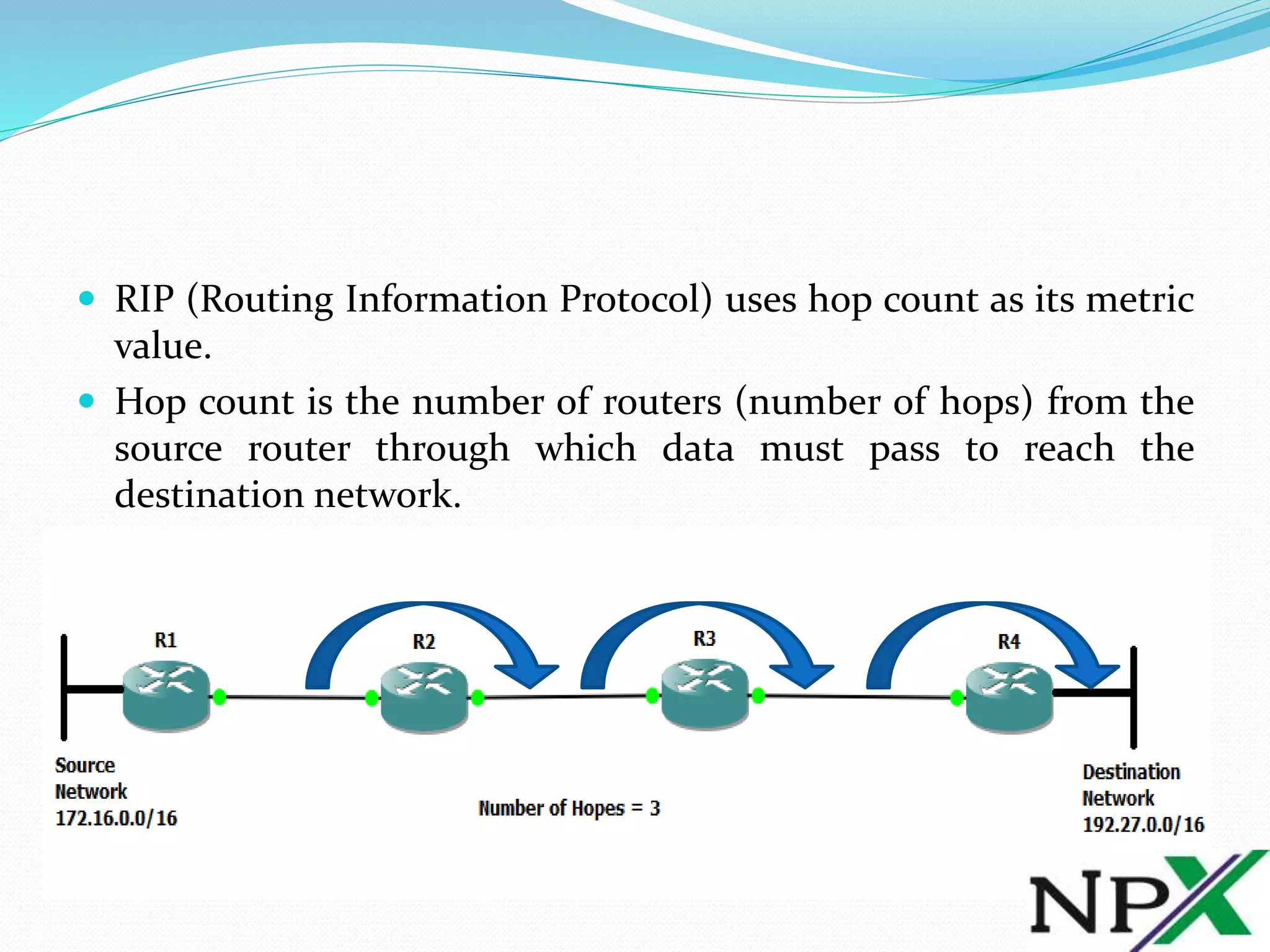
RIP uses hop count as its metric value, which is the number of routers a data packet must pass through to reach its destination network. In the lab topology, it takes 3 hops (R2, R3, R4) for data from the source router R1 to reach the destination network at R4. The show ip route output from R1 displays the metric for the route as 3 hops. RIP selects the best path based solely on the lowest hop count.




![ From above output, [120/3] shows 120 is the
default Administrative Distance of RIP (Routing Information
Protocol) and 3 is the metric (Hop Count) of RIP (Routing
Information Protocol) for above topology.
RIP (Routing Information Protocol) selects the best path to a
Destination Network based only on the number of hops to the
destination network. If you have multiple paths with different
bandwidth to the destination network, then RIP’s best path
calculation may become wrong.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ripmetrichopecountandhopcountcalculation-160704054916/75/RIP-Metric-Hope-Count-and-Hop-Count-Calculation-5-2048.jpg)