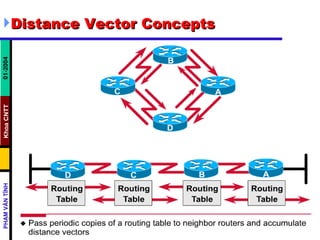
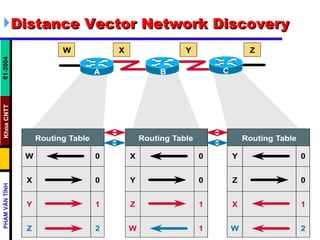
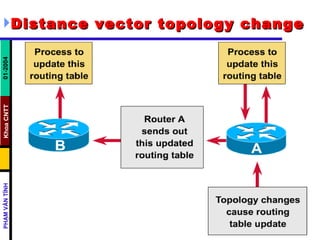
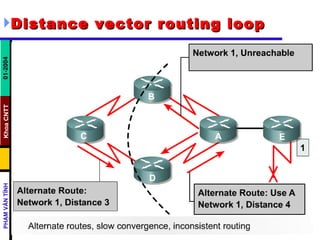
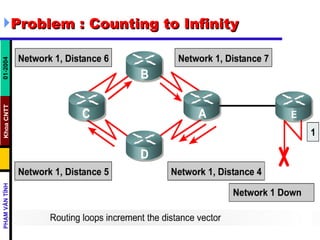
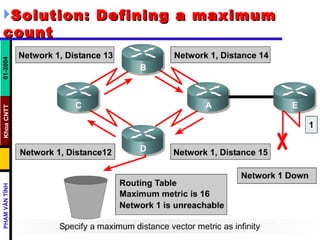
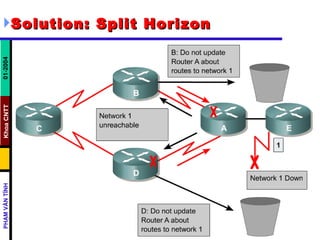
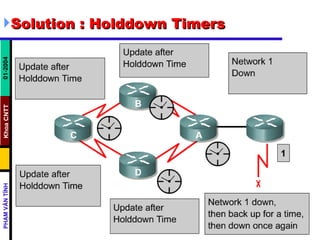
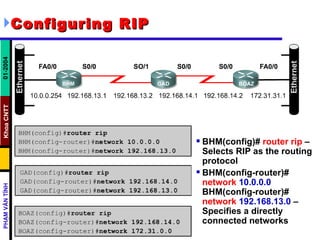
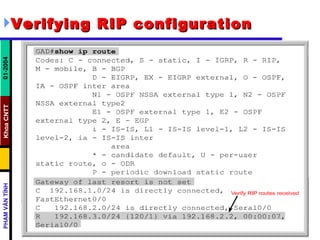
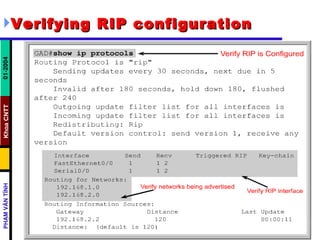
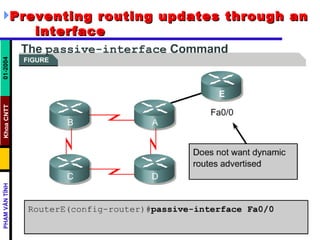
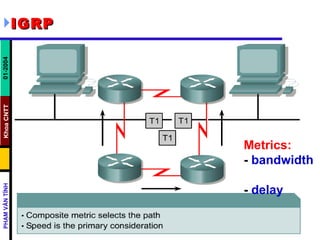
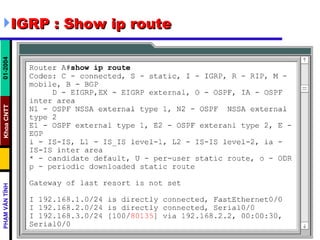
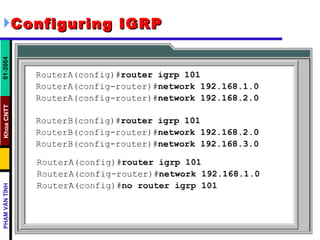
Distance vector routing protocols like RIP use hop count as the metric to determine the best path. This can lead to routing loops when routers continuously update each other with increasing hop counts, a problem known as "counting to infinity". RIP implements techniques like split horizon, holddown timers, and triggered updates to prevent this. The document goes on to describe how to configure and verify RIP, troubleshoot routing issues, and integrate static routes. It also provides an overview of IGRP configuration and verification.