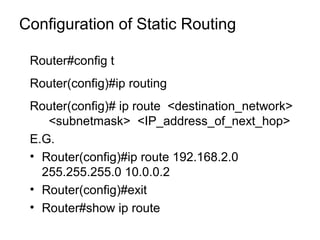
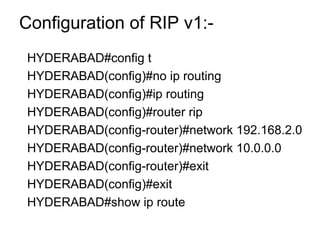
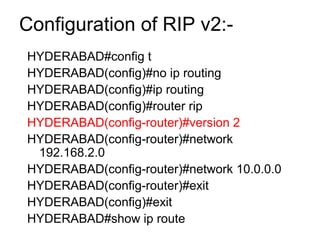
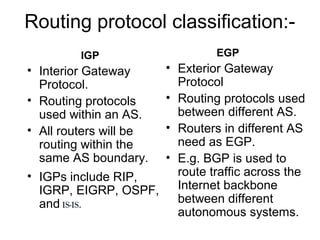
IP routing is the process of moving packets between networks using routers. Routing protocols are used by routers to dynamically find all networks and ensure consistent routing tables. Common routing protocols include RIP, IGRP, OSPF, and EIGRP. Static routing manually configures routes, while dynamic routing automatically adapts to network changes. Dynamic routing includes distance vector protocols like RIP, link state protocols like OSPF, and hybrid protocols like EIGRP. Routing protocols classify interior gateway protocols (IGPs) as intra-AS and exterior gateway protocols (EGPs) like BGP as inter-AS.



![Static Routing
• It is manually configured by administrator.
• Mandatory need of destination network ip.
• It is very secure and fast.
• There is no bandwidth usage between routers.
• Used for small organization with network of 10-15
routers
• Administrative distance for static route is 0 & 1.
[Admin. Distance is ‘trustworthiness’ of routing
information.lesser the AD higher the performance. 0-
very good , 255-very bad]
Disadvantages :-
Used for small network.
Everything to manually
Network change effect complete n/W](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5-routing-140821125344-phpapp01/85/CCNA-part-5-routing-4-320.jpg)