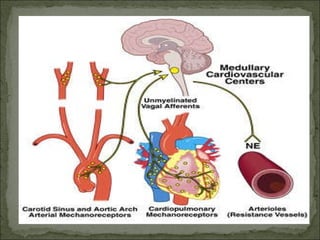
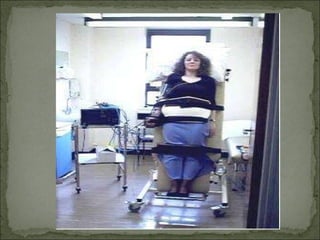
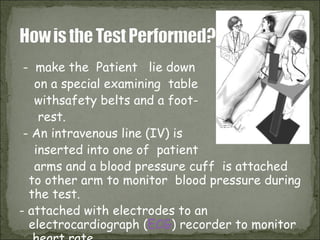
The Tilt Table Test is used to evaluate causes of syncope (fainting) by reproducing symptoms while closely monitoring the patient. During the test, the patient lies on a table that is tilted to 60-80 degrees for up to 45 minutes. Electrodes monitor heart rate and a blood pressure cuff measures pressure. If no symptoms occur, medication may be administered to increase heart rate and tilt continued. Fainting during the test confirms vasovagal or neurocardiogenic syncope caused by abnormal nervous system reflexes lowering blood pressure and heart rate. The test aims to safely reproduce symptoms to identify causes of fainting.