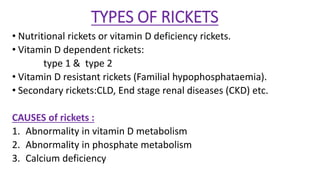
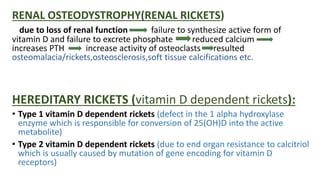
This document provides information on rickets, a metabolic bone disease caused by vitamin D deficiency or impaired mineralization. It discusses the following key points:
- Rickets mainly affects children under 2 years old and causes soft, weak bones and skeletal deformities from imperfect bone mineralization.
- It is most commonly caused by nutritional deficiencies, especially of vitamin D, but can also be caused by genetic or other medical conditions.
- Symptoms include bone pain, softening of the skull and ribs, bowed legs, fractures, and delayed growth. Radiographs show widened growth plates and fraying of the metaphysis.
- Treatment involves high-dose vitamin D and calcium supplementation to promote bone mineralization and




















![CRANIOTABES
• Occurs due to thinning of
outer table of occipital or
parietal bone.
[CLINICALLY , detected by
gentle pressure by thumbs
over the occipital or posterior
parietal bones , pingpong
sensation will be felt.
**EARLIEST clinical sign of
rickets.]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rickets-180522174721/85/Rickets-23-320.jpg)




![IN LONG STANDING CASES:
• Bowing of the long bones.
• Fracture of weight bearing bones.
• Looser’s zones [less than osteomalacia]
• Triangular pelvic cavity.
• Stunted growth.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rickets-180522174721/85/Rickets-28-320.jpg)









![CLINICAL FEATURES
ROSARY FORMATION
• Rickets can present
within 2 months of age.
• Bone pain,short
strature,fracture,tooth
deformities etc.
• Knobby and nodular
appearance.
• Rare before 6 months.
• Progressive
irritability,pseudoparaly
sis,haemorrhage into
gum and mucous
membranes etc.
• Angular costochondral
junction with sharper
step-off
AREA OF INVOLVEMENT Zone of hypertrophy Primary spongiosa
RADIOLOGICAL FEATURES:
1. Epiphysis Epiphyseal centres are
indistinct or invisible .
Epiphysis is small,sharply
marginated by a sclerotic rim
(WIMBERGER’S SIGN)
[termed as signet ring or
ringing of epiphysis]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rickets-180522174721/85/Rickets-38-320.jpg)
![Cont..
2.Metaphysis : (a)
• Loss of zone of provisional
calcification adjacent to
metaphysis,having faint
irregular outline(FRAYING)
• Splaying and cupping of
metaphysis.
Zone of provisional
calcification at metaphysis is
dense,giving a white line
(FRANKEL’S LINE)
(b) Not found. • Beneath this is a lucent
zone,due to lack of
mineralized
osteoid(TRUMERFELD
ZONE)
• Lateral projection of white
line may lead to formation
of spur or marginal cleft
(PELKAN’S SPUR) ( [corner
sign:great diagnostic value]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rickets-180522174721/85/Rickets-39-320.jpg)
![Continue…..
3.Shaft abnormalities Cortical thinning with
course trabeculation.
Cortical thinning with
GROUND GLASS
APPERANCE
[CHARACTERISTIC ]
4.SUBPERIOSTEAL LAYER May be found but Less
marked effect.
Sub-periosteal haemorrhage
due to capillary fragility
giving rise to periosteal
elevation.(affected bone
looks like a dumbbell or a
club)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rickets-180522174721/85/Rickets-40-320.jpg)


