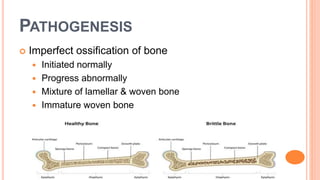
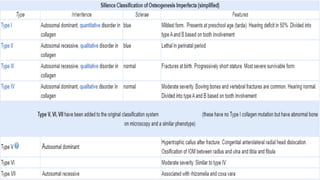
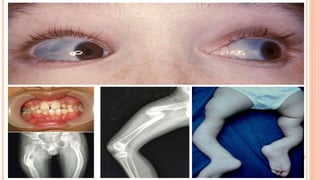
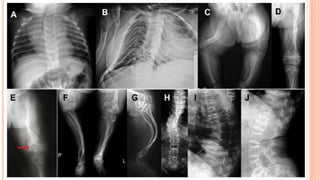
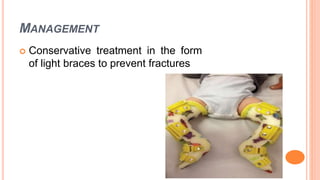
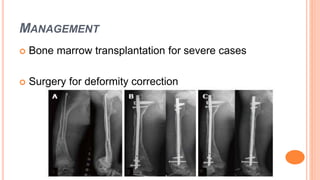
This document discusses osteogenesis imperfecta, a hereditary condition characterized by fragile bones. It is caused by abnormalities in type I collagen production and affects bone formation. The condition ranges in severity and can cause blue sclera, hearing loss, joint laxity, and bone fractures from minor trauma that heal slowly with abnormal bone formation. Management includes braces to prevent fractures, bisphosphonate therapy to increase bone density and reduce fractures, and surgery for deformity correction in severe cases.