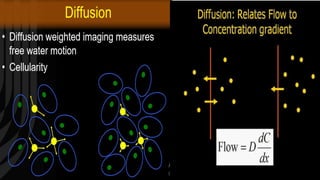
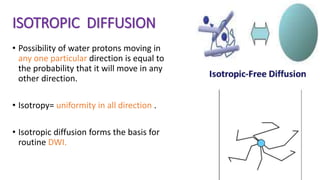
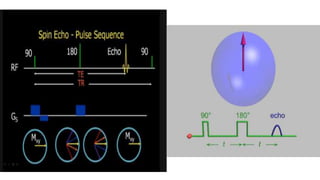
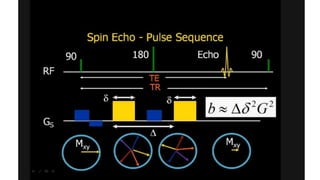
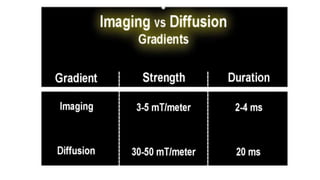
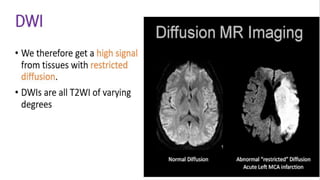
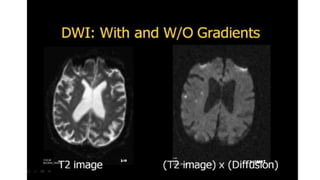
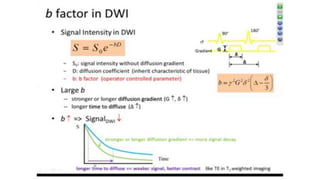
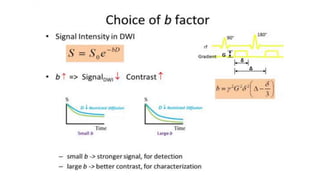
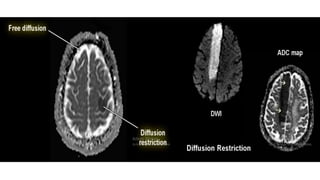
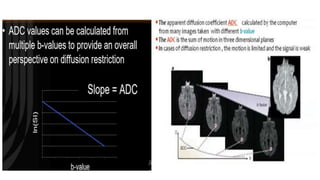
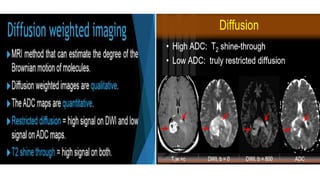
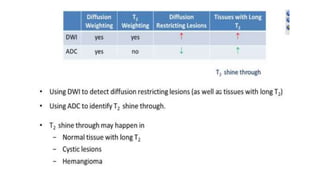
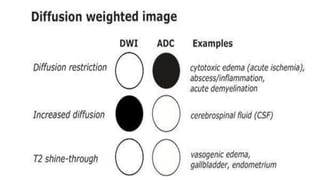
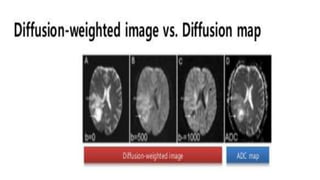
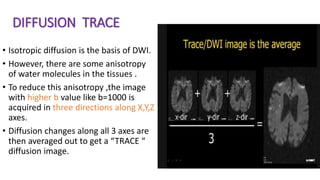
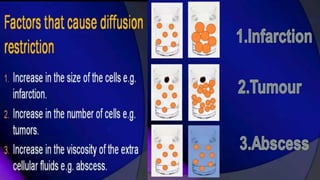
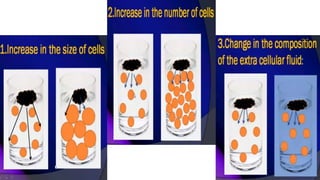
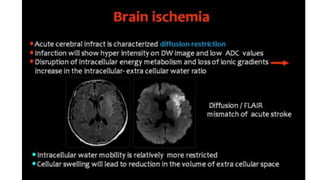
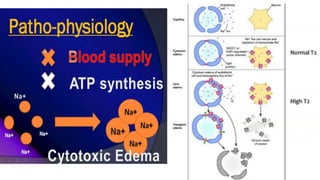
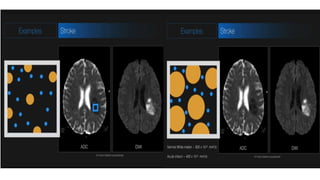
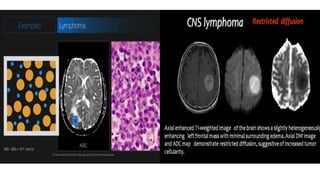
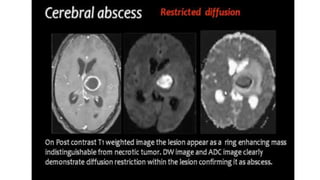
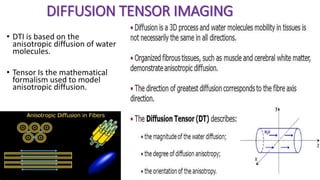
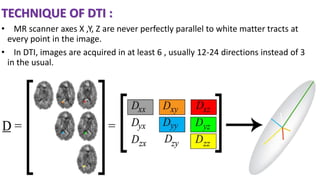
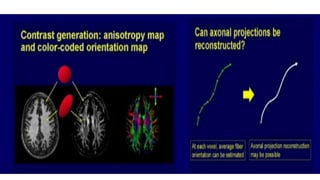
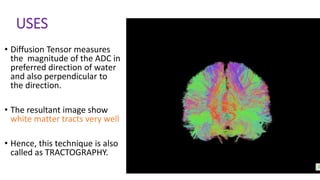
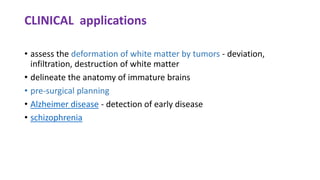
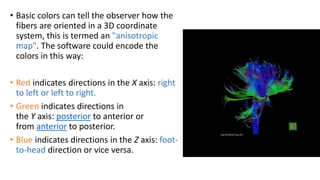
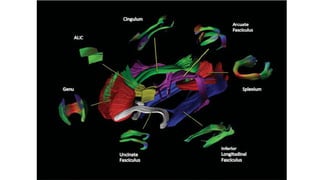
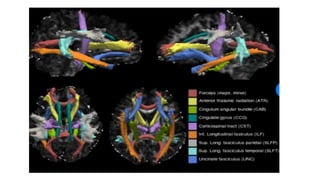
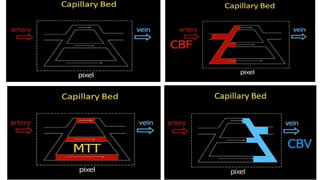
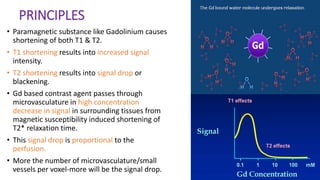
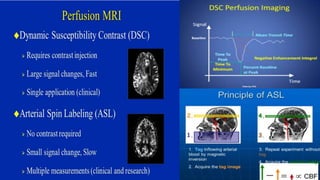
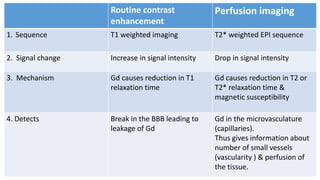
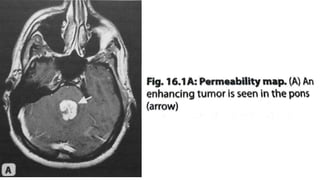
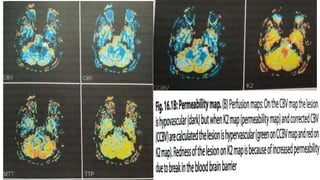
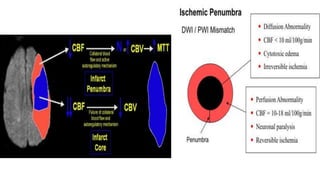
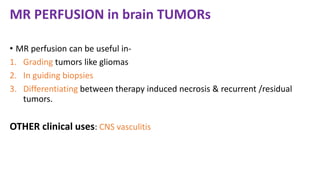
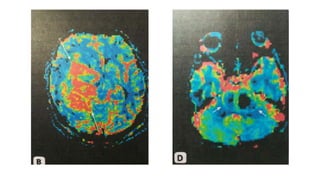
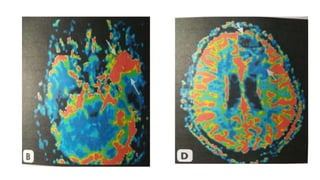
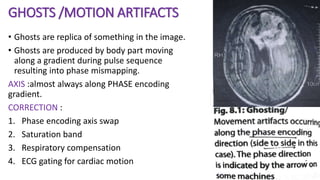
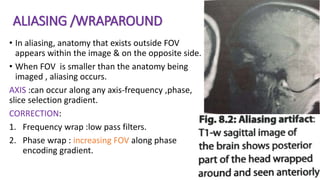
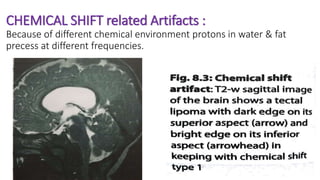
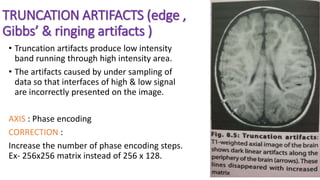
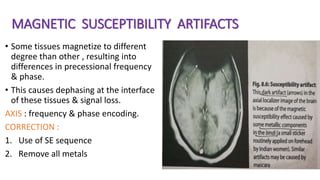
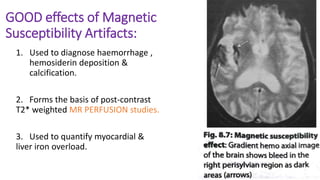
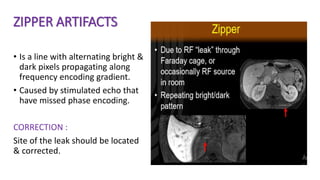
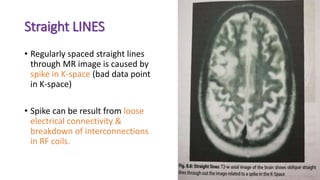
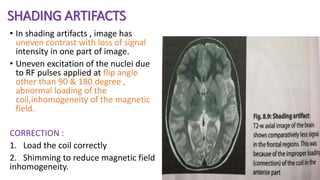
MR diffusion, perfusion, and artifacts are discussed. Diffusion imaging measures water mobility and is used to characterize tissues and pathology. Perfusion imaging measures blood flow and is used to assess diseases like stroke and tumors. Common artifacts include ghosts from motion, aliasing from small fields of view, truncation artifacts at tissue interfaces, and magnetic susceptibility artifacts at tissue boundaries. Clinical applications of diffusion, perfusion, and other sequences are also outlined.