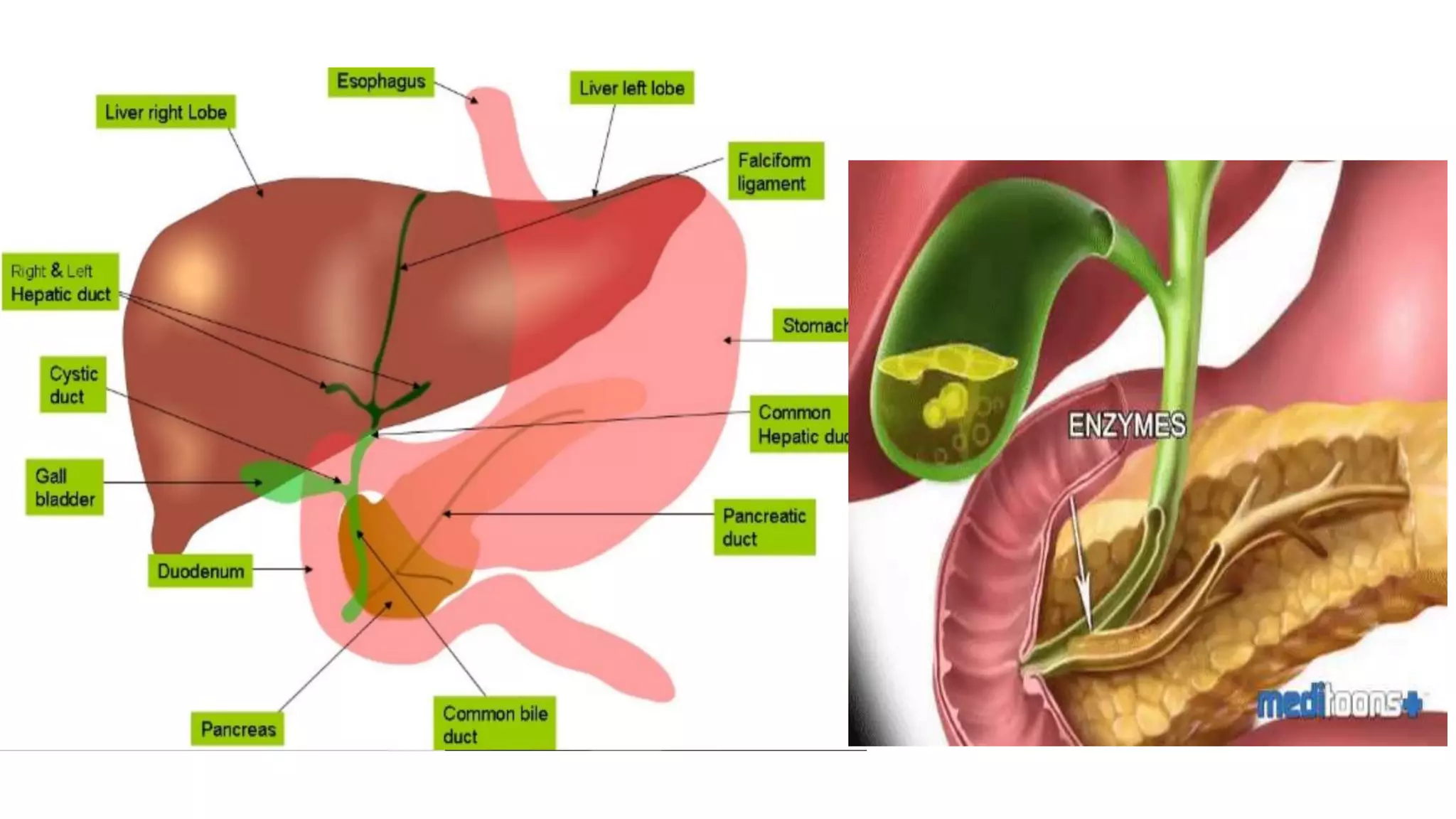
MRI can be used for hepatobiliary and pancreatic imaging to detect and characterize lesions. It provides T1-weighted, T2-weighted, diffusion-weighted, and post-contrast images. Specific sequences like MRCP and fat-suppressed T2-weighted images aid in visualization of the biliary tree and distinguishing lesions from liver and fat tissue. Common benign lesions like hemangiomas and FNH have characteristic enhancement patterns while malignant lesions like HCC and metastases often appear hypovascular and demonstrate washout on delayed phases. MRI is thus an important tool for pre-operative evaluation and detection of recurrence in hepatobiliary surgery.