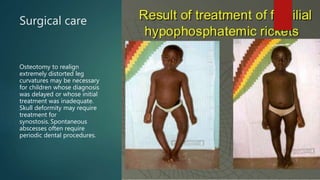
This document summarizes hypophosphatemic rickets, a form of rickets characterized by low serum phosphate levels that are resistant to treatment with vitamin D. It describes X-linked hypophosphatemia, which accounts for 80% of cases and results from a mutation causing increased fibroblast growth factor 23 levels and phosphaturia. Clinical signs include slow growth, bowed legs, and joint abnormalities. Diagnosis involves lab tests showing low phosphate and imaging showing widened growth plates. Treatment includes the monoclonal antibody burosumab to block fibroblast growth factor 23 and phosphate/vitamin D supplements.






![Diagnoses
Imaging studies;
• Radiography of the wrists, knees, ankles, and long bones shows no
pathognomonic sign.
• MRI reveals maximum physial widening and transverse degree of
widening—that correlate with alkaline phosphatase levels.
Renal Tubular Phosphate Reabsorption;To evaluate percentage of
phosphate reabsorbed.
Phosphate Clearance (CPi) / Creatinine Clearance (Ccr)] X 100%
Cpi=[Urine Phosphate (mg/dL) X Volume (mL/min)] / Plasma Phosphate
(mg/dL)
normal TRP >90%
TRP in XLH is 60%;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hypophosphatemicrickets-180705042944/85/Hypophosphatemic-rickets-9-320.jpg)