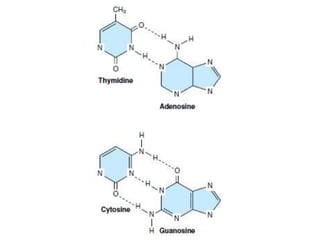
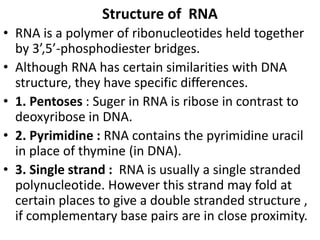
Nucleotides are the monomer units that make up nucleic acids like DNA and RNA. They consist of a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar, and a phosphate group. Nucleotides join together via phosphodiester bridges between the 3' carbon of one sugar and the 5' carbon of the next, forming polynucleotide chains. There are two main types of nucleic acids: DNA contains the sugar deoxyribose and is usually double-stranded, while RNA contains the sugar ribose and is generally single-stranded. The structures and functions of DNA, RNA, and their components are essential for genetic inheritance and protein synthesis.