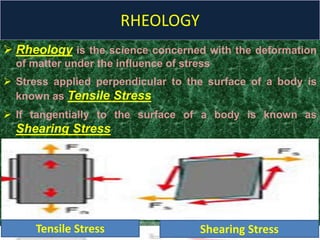
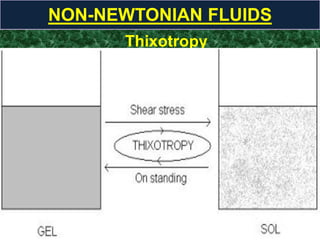
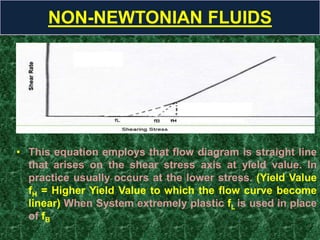
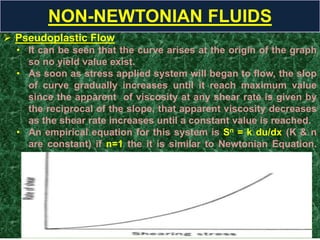
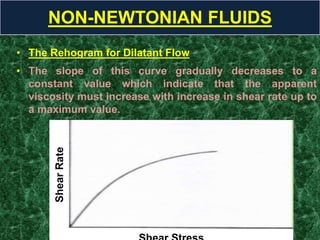
This document discusses rheology, the science of deformation of matter under stress. It defines tensile and shearing stresses and explains reversible and irreversible deformations. Viscosity is introduced as the resistance of fluids to flow, with Newtonian fluids obeying the law of proportionality between stress and shear rate. Non-Newtonian fluids are divided into time-dependent categories like thixotropy and time-independent types including plastic, pseudoplastic and dilatant flows. Specific examples and rheograms are provided to illustrate different fluid behaviors.