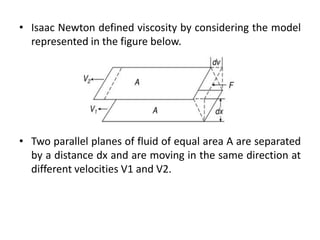
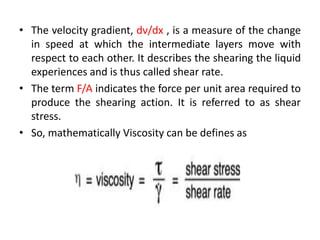
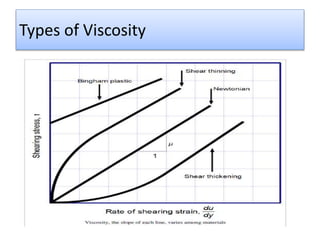
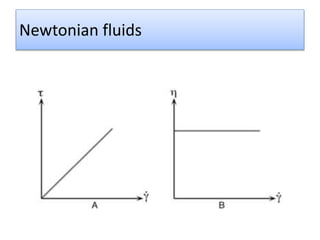
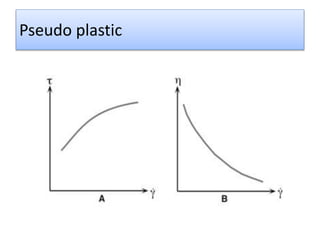
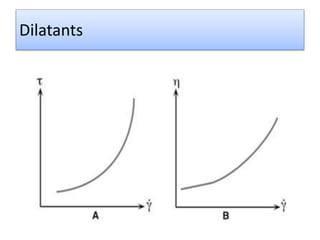
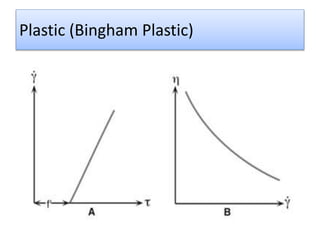
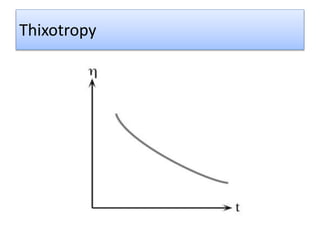
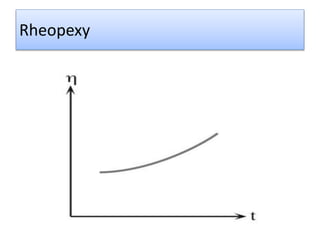
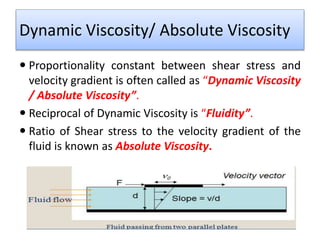
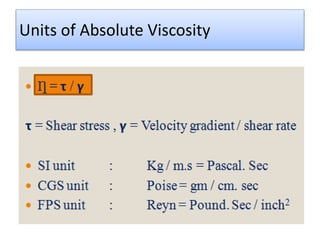
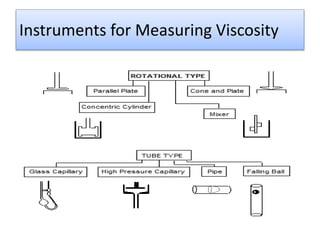
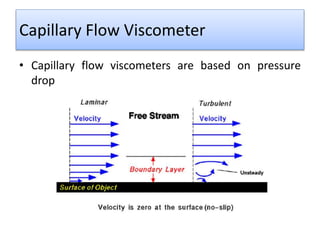
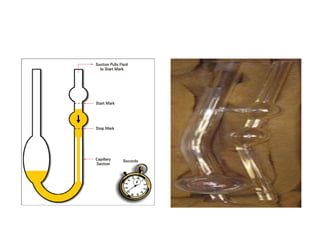
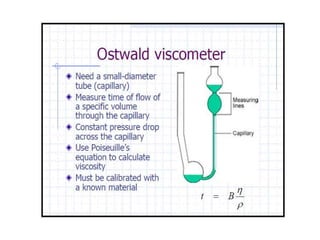
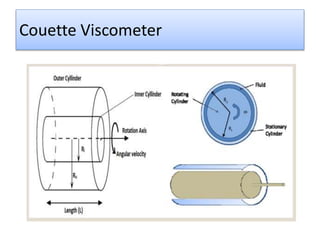
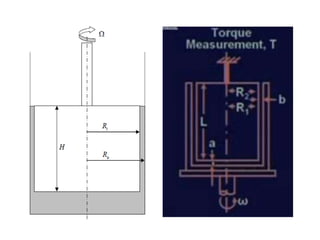
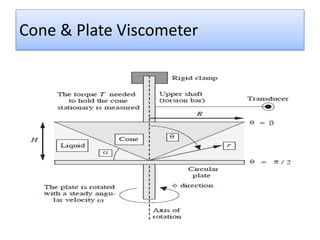
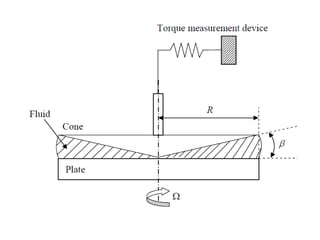
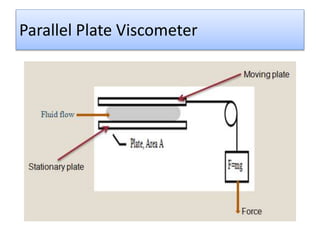
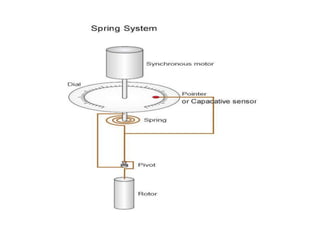
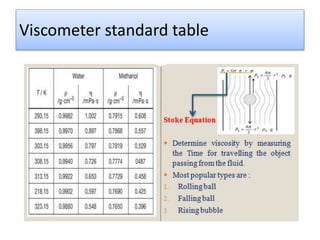
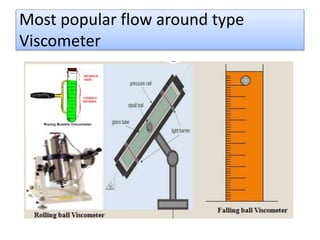
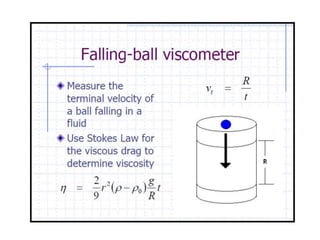
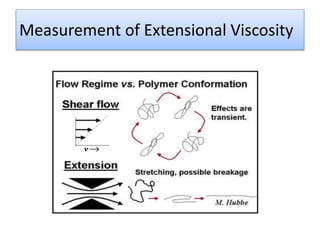
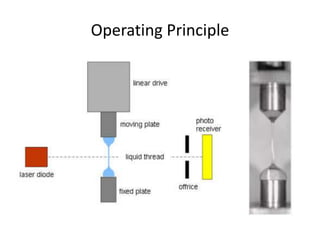
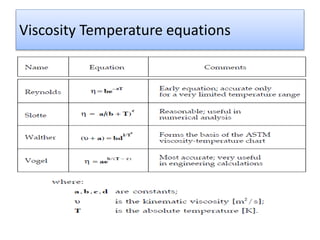
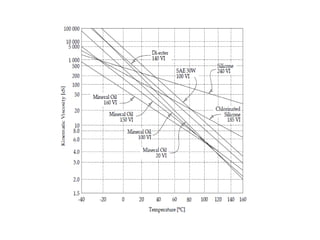
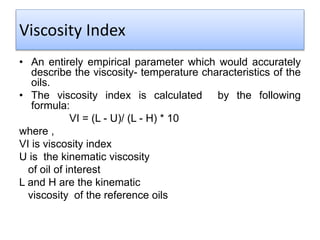
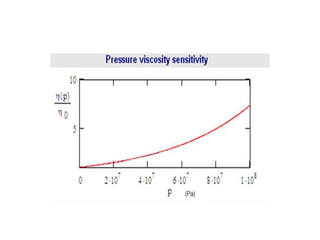
The document provides a comprehensive overview of viscosity, including its definition, measurement methods, and behavior of different fluid types. It distinguishes between Newtonian and non-Newtonian fluids, describing various categories such as pseudoplastic and dilatant fluids, along with the principles of viscosity measurement using instruments like viscometers. Additionally, it discusses how viscosity is affected by temperature and pressure, and outlines the importance of viscosity measurement in various practical applications.