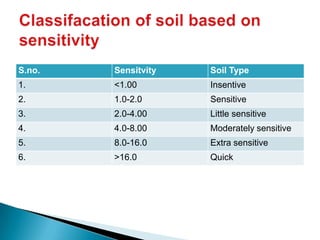
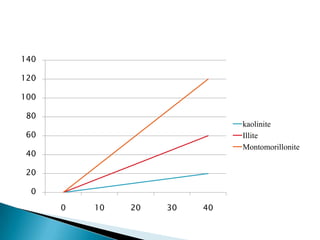
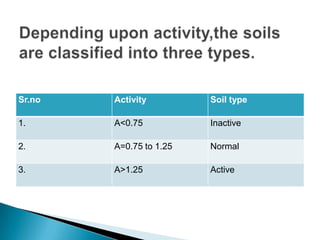
The document discusses thixotropy, sensitivity, and activity in soils. Thixotropy refers to the regain of shear strength in soils over time after being remolded such as during pile driving. Sensitivity indicates the loss of strength from remolding and is measured as the ratio of undisturbed to remolded strength. Activity is measured as the ratio of plasticity index to clay fraction and indicates the water holding capacity of clayey soils.