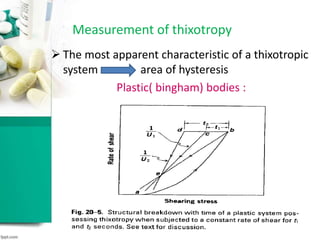
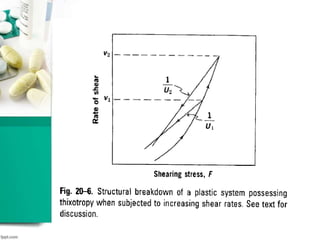
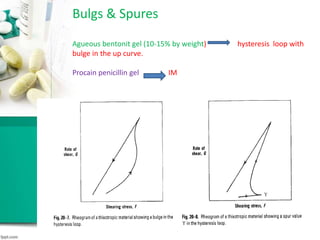
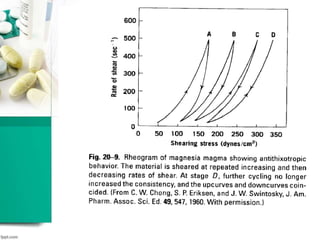
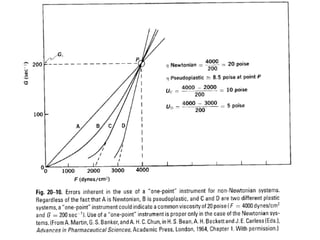
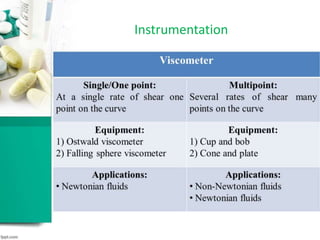
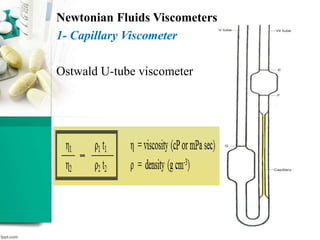
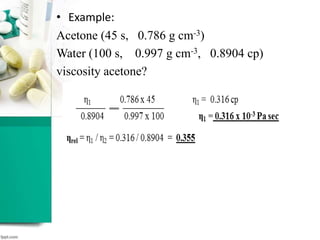
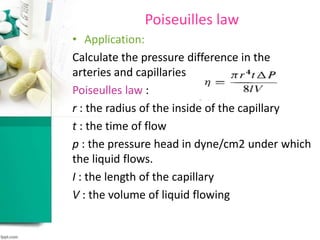
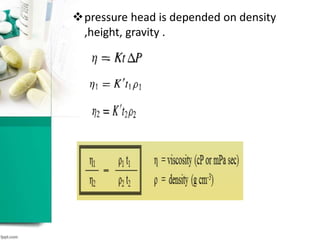
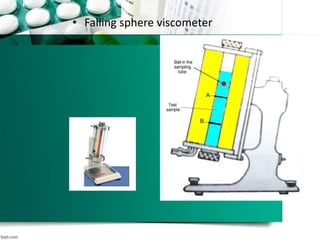
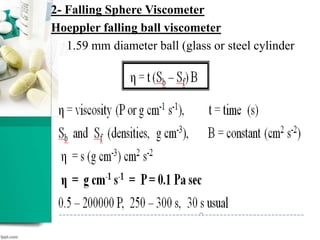
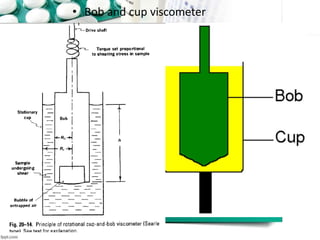
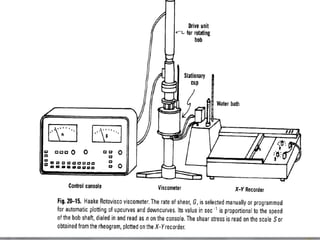
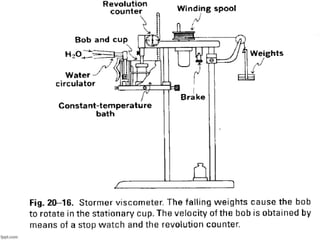
This document discusses various methods for measuring rheological properties such as viscosity and thixotropy. It describes key characteristics of thixotropic systems like hysteresis and how instruments can determine structural breakdown. Common viscometers are described including capillary, falling sphere, and bob-cup designs. The bob-cup viscometer uses concentric cylinders and can measure properties like plastic viscosity and yield value. Thixotropic formulations are desirable in pharmaceuticals as they remain thick in containers but spread easily upon administration. Degree of thixotropy impacts sedimentation rate and can enable drug depots to form after intramuscular injection.