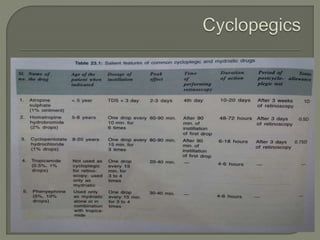
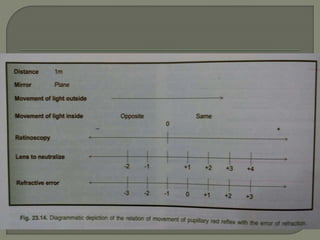
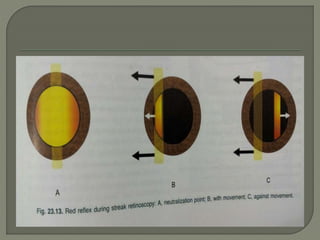
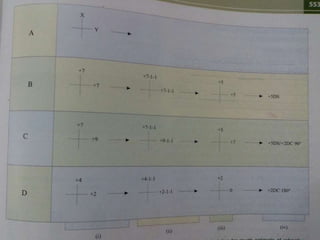
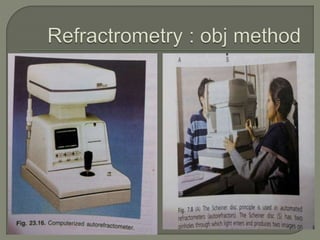
This document discusses the process of determining and correcting refractive errors through objective and subjective refraction methods. It describes retinoscopy and trial frame techniques used in subjective refraction to find the optimal lens prescription. Specifically, it details how Jackson's cross cylinder and fogging techniques are used to refine the cylindrical correction and verify the accuracy of the prescription before the final step of binocular balancing for the patient.