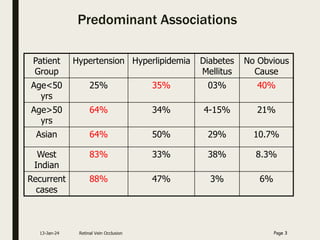
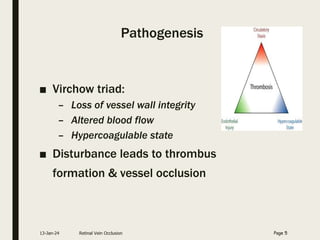
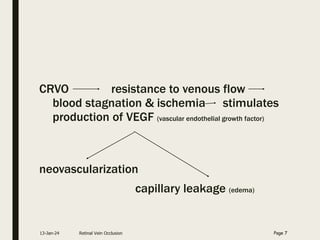
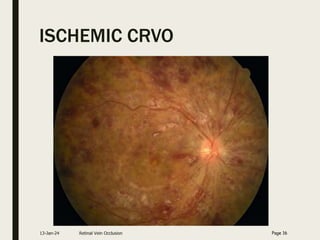
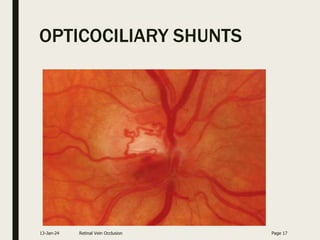
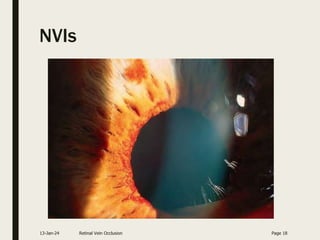
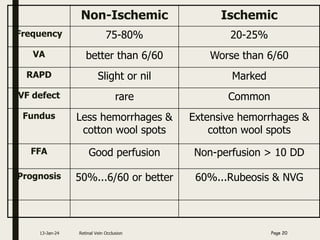
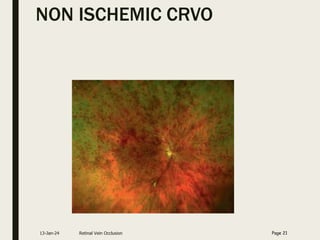
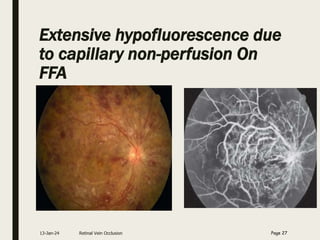
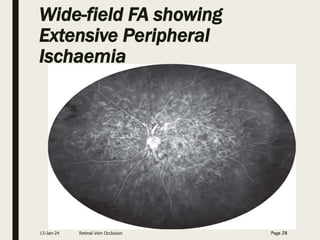
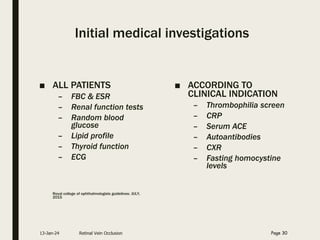
Central retinal vein occlusion (CRVO) occurs when the central retinal vein gets blocked, causing fluid and blood to leak into the retina. It can be either ischemic or non-ischemic depending on the extent of blocked blood flow. Risk factors include hypertension, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, and various hematological disorders. Treatment involves managing underlying conditions, treating macular edema with anti-VEGF injections or steroids, and laser photocoagulation if neovascularization develops. The goal is to preserve vision by reducing edema and preventing complications like glaucoma. Regular follow up is needed to monitor for recurrence or progression.