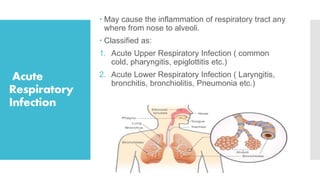
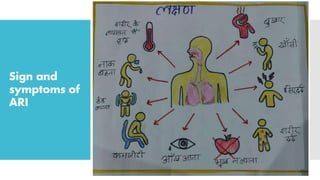
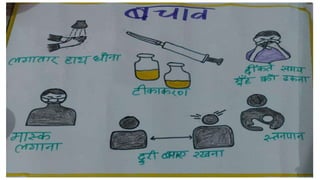
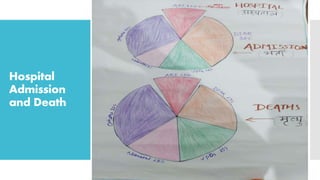
The National Acute Respiratory Infections Control Programme, initiated in 1990, aims to reduce child mortality due to pneumonia through improved treatment practices and early detection. It focuses on training healthcare providers to manage acute respiratory infections effectively, promoting maternal education, and ensuring timely referrals for severe cases. The programme incorporates strategies such as standard care management, vaccination, and community involvement to combat ARIs in children under five.