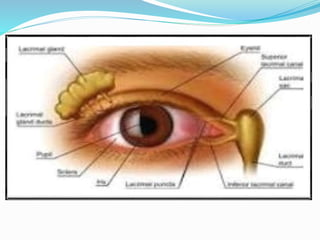
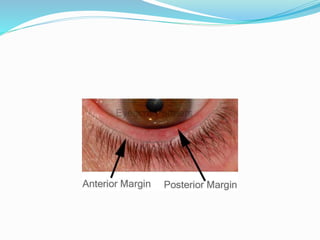
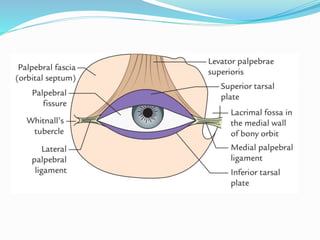
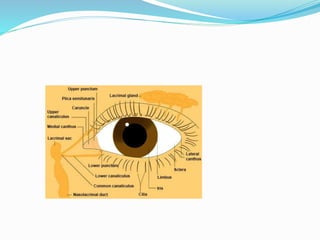
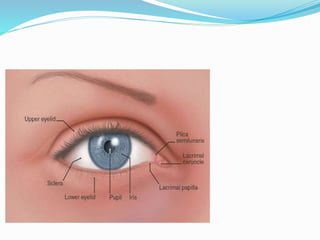
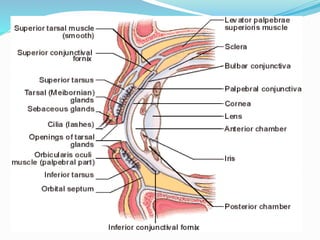
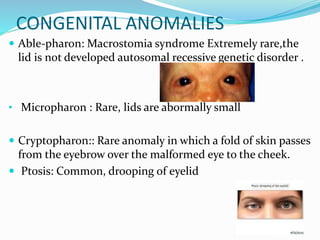
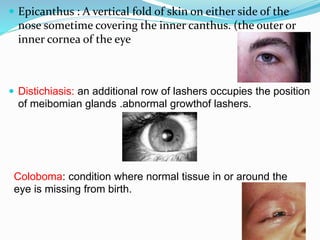
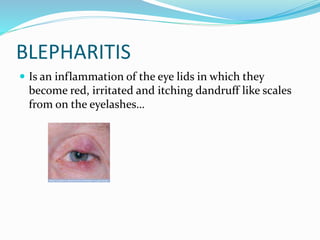
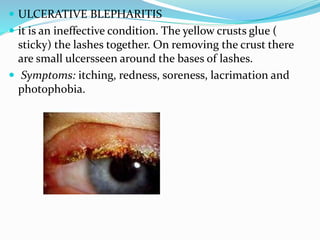
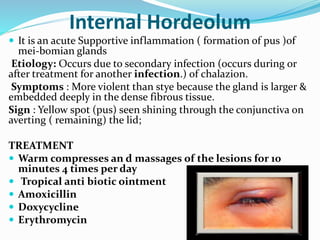
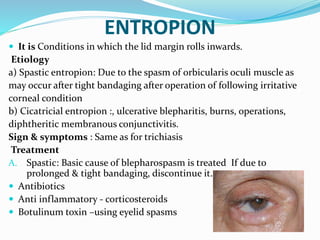
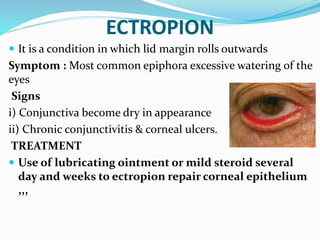
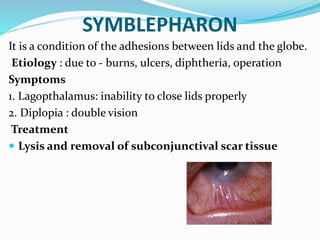
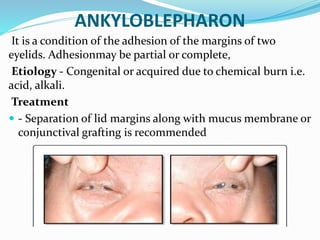
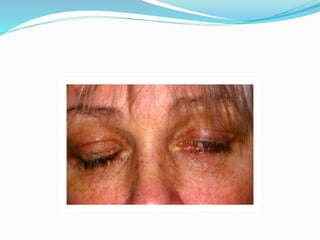
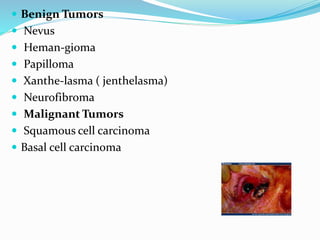
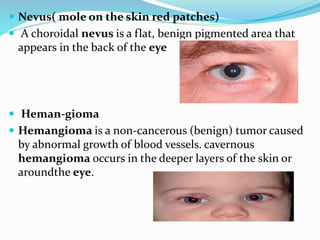
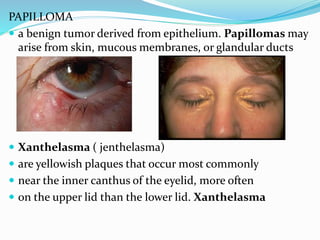
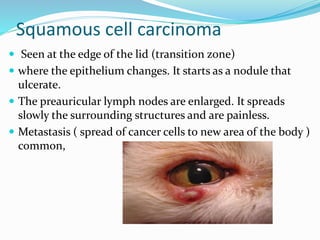
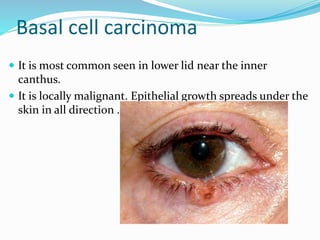
This document provides an overview of eyelid anatomy, infections, tumors, and deformities. It describes the layers of the eyelid, including skin, muscles and glands. Common eyelid infections like blepharitis, hordeolum and chalazion are explained. Eyelid tumors including nevus, hemangioma, papilloma and carcinomas are outlined. Various eyelid deformities such as entropion, ectropion, lagophthalmos and ptosis are also summarized, along with their causes and treatments.