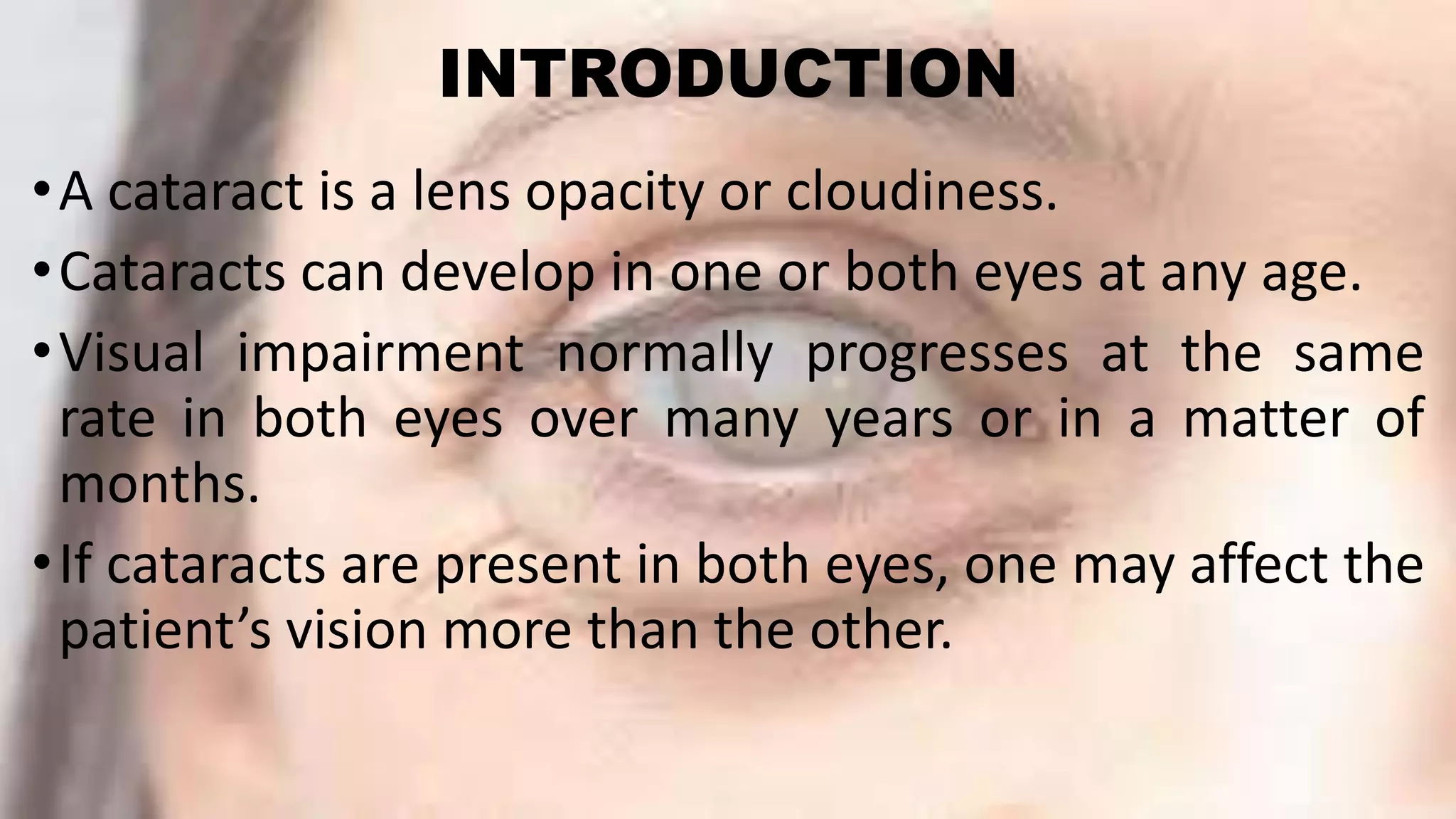
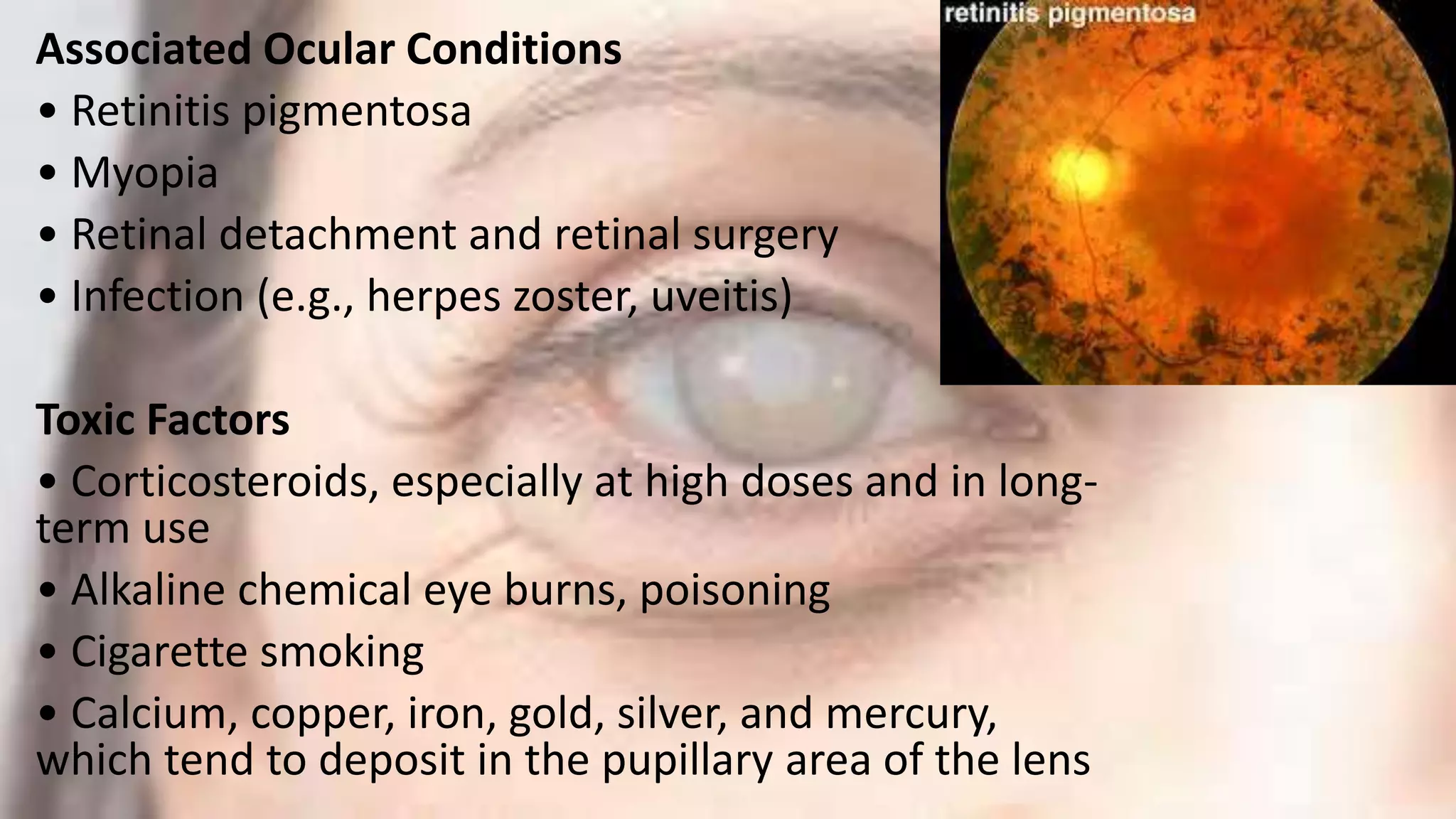
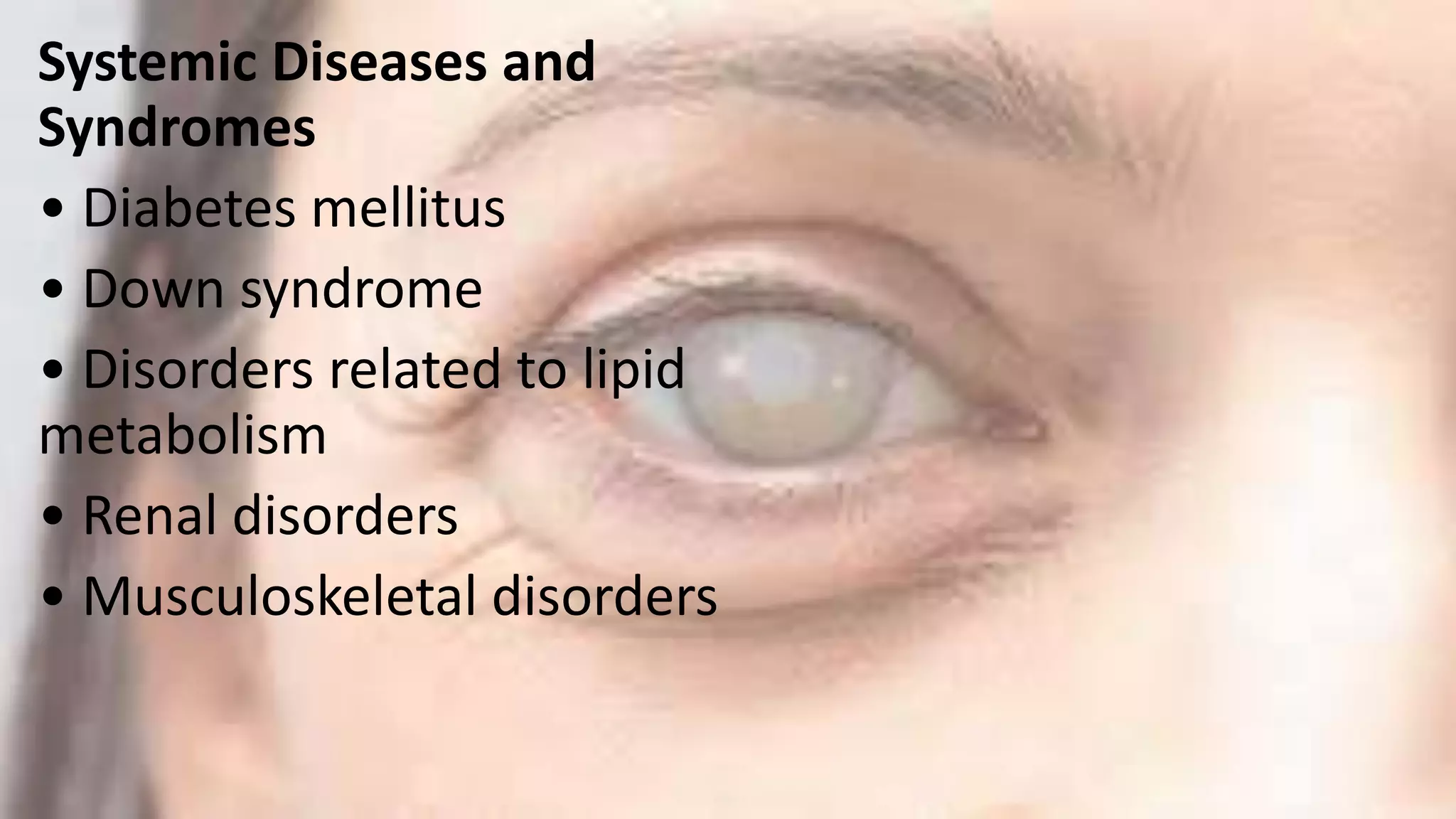
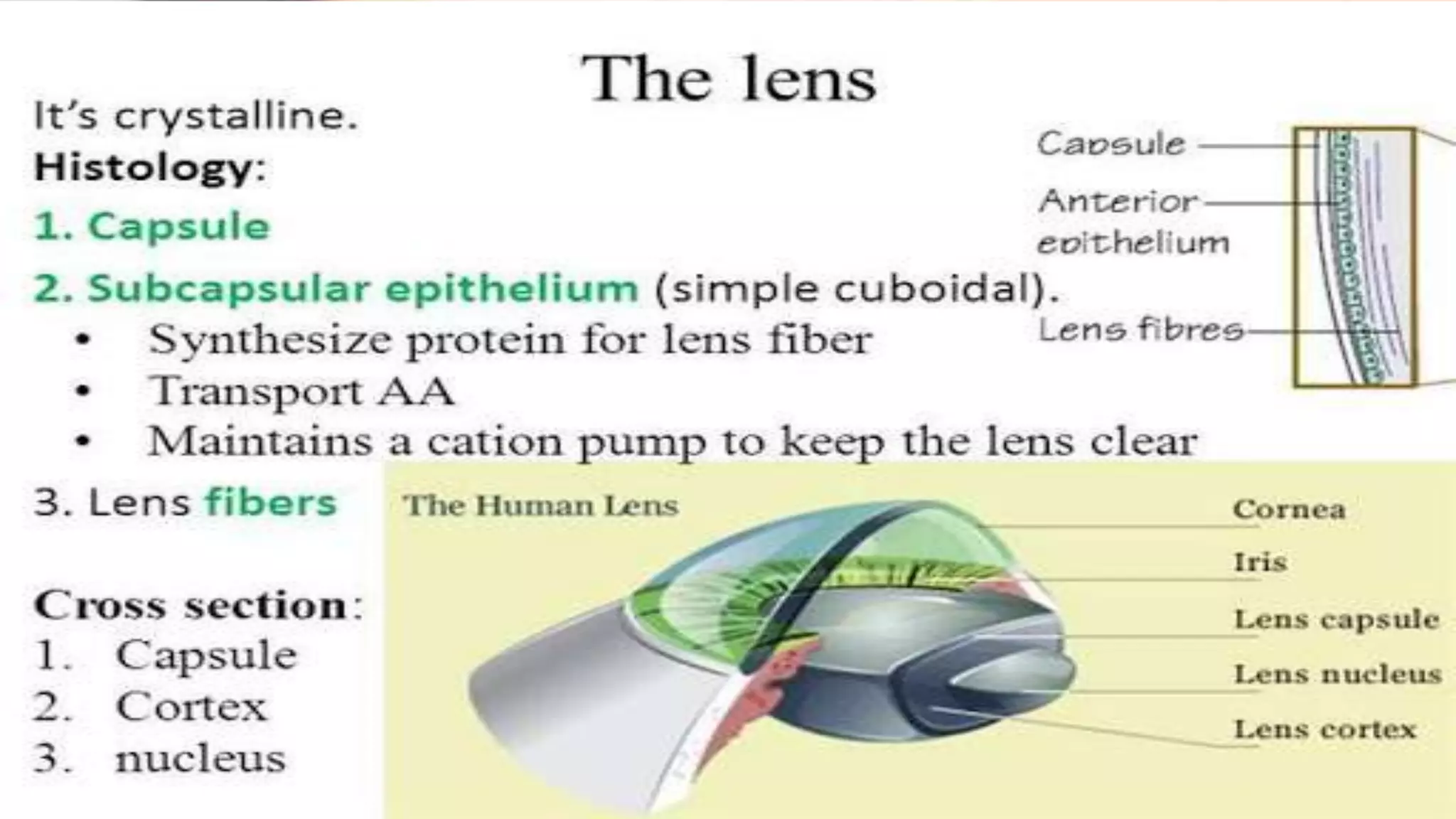
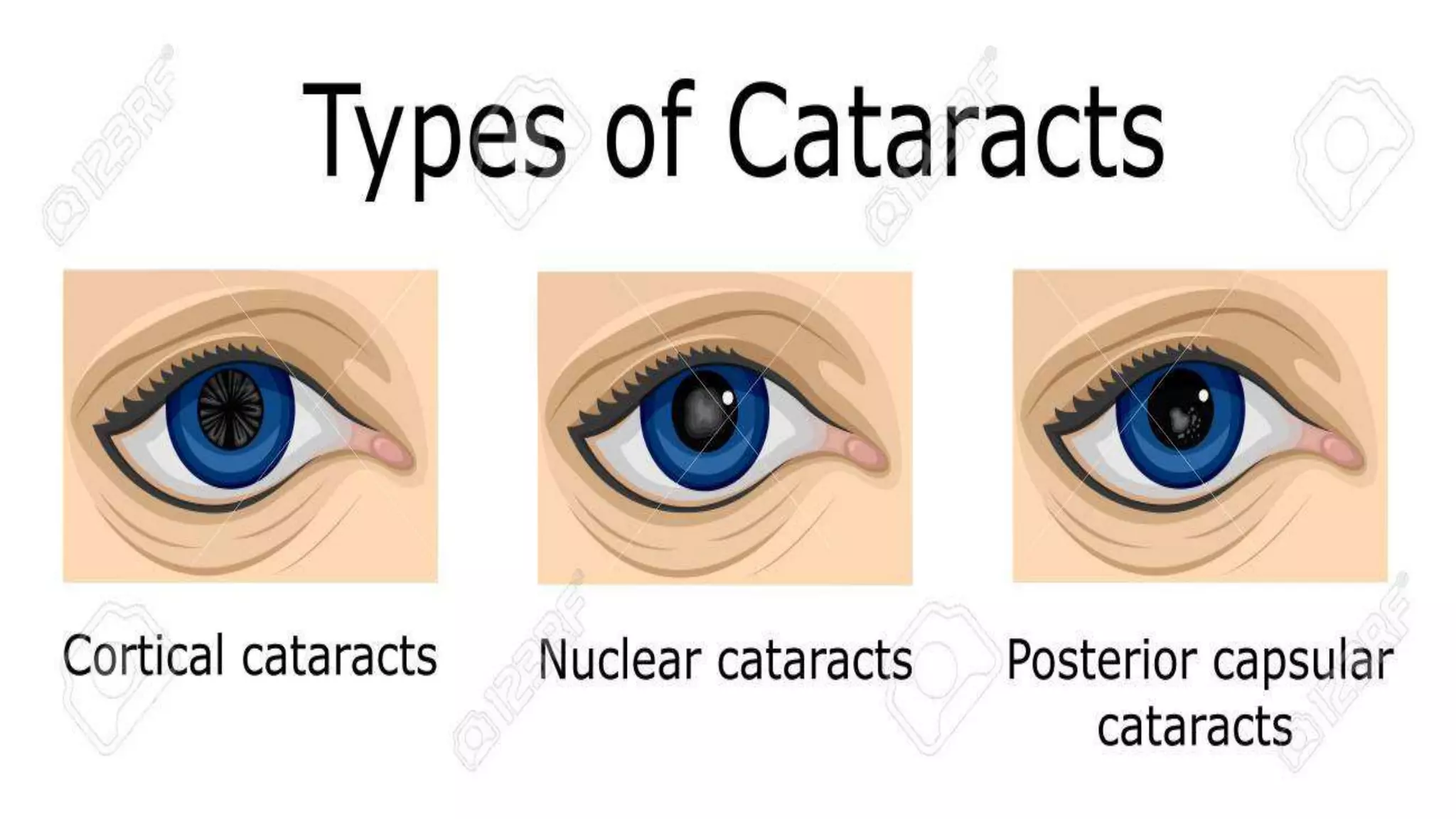
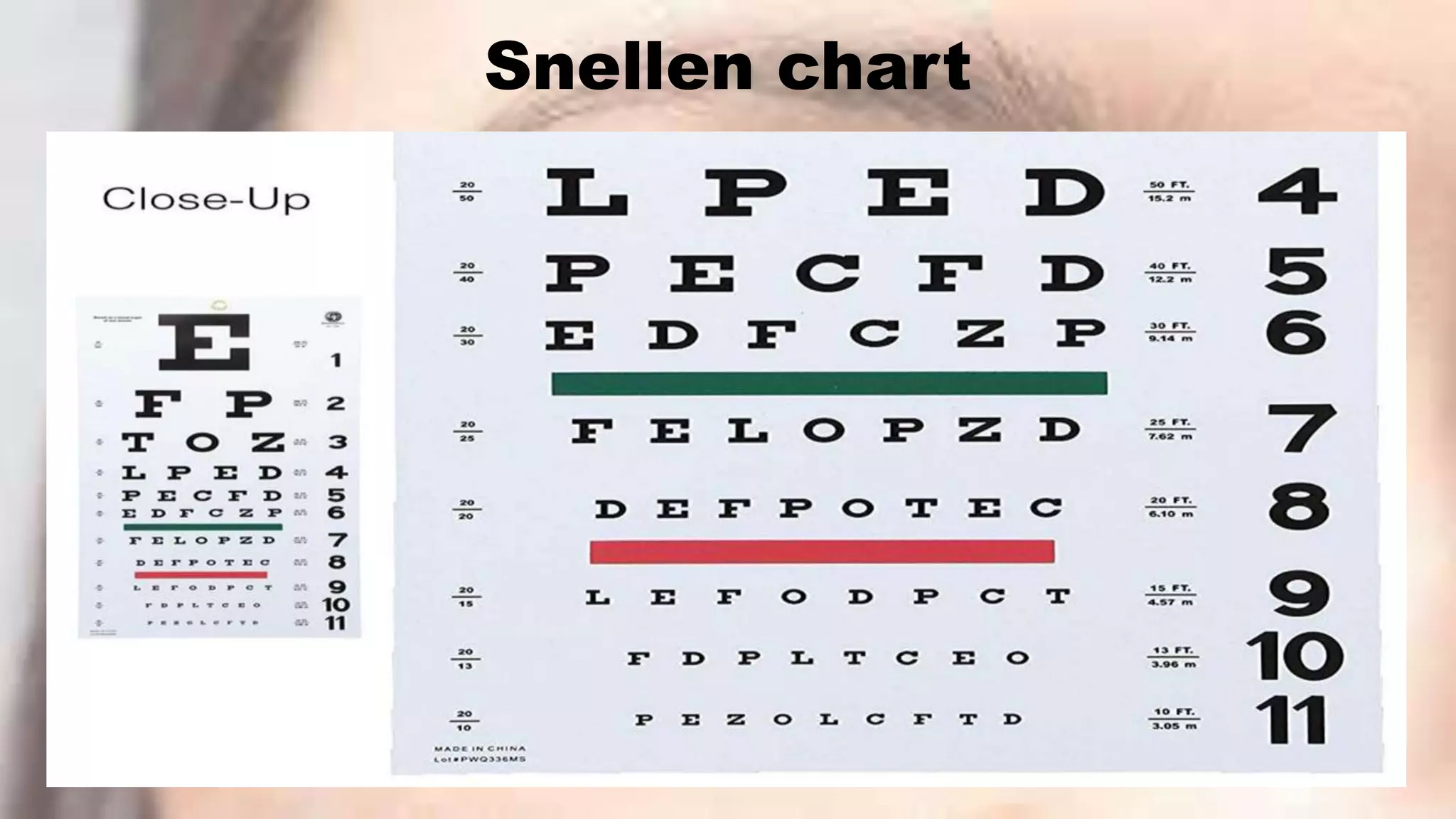
This document provides information about cataracts and their management. It discusses what a cataract is, risk factors for cataract formation such as aging, associated ocular conditions, nutritional and physical factors, and systemic diseases. It describes the clinical manifestations of cataracts and the diagnostic evaluation including various visual acuity tests and examinations. Treatment options discussed include medical management using glasses or surgery. The two main surgical procedures mentioned are extracapsular cataract extraction and phacoemulsification. Postoperative care and potential complications are also outlined. Finally, it provides conclusions and references several research articles on prevalence and risk factors of cataracts.










































![REFERENCES
1. Janice L. Hinkle, Kerry H. Cheever. Brunner and Suddarth’s Textbook of Medical
Surgical Nursing. 2015. New Delhi. Wolters Kluwer.13th Edition. Volume 2. Pg. no.
1761-1764.
2. Lewis. Medical Surgical Nursing Assessment and Management of clinical
problems.2015. New Delhi. Elsevier. 2nd Edition. Volume I. Pg. no. 409-412.
3. World Health Organization. Blindness and vision impairment prevention.
Available from https://www.who.int/blindness/causes/priority/en/index1.html
[cited 7 April 2020]
4. Singh S, Pardhan S, Kulothungan V, Swaminathan G, Ravichandran JS, Ganesan S,
Sharma T, Raman R. The prevalence and risk factors for cataract in rural and urban
India. Indian J Ophthalmol [serial online] 2019 [cited 2020 Apr 7]; 67:477-83.
Available from: http://www.ijo.in/text.asp?2019/67/4/477/254705 [cited 7 April
2020]
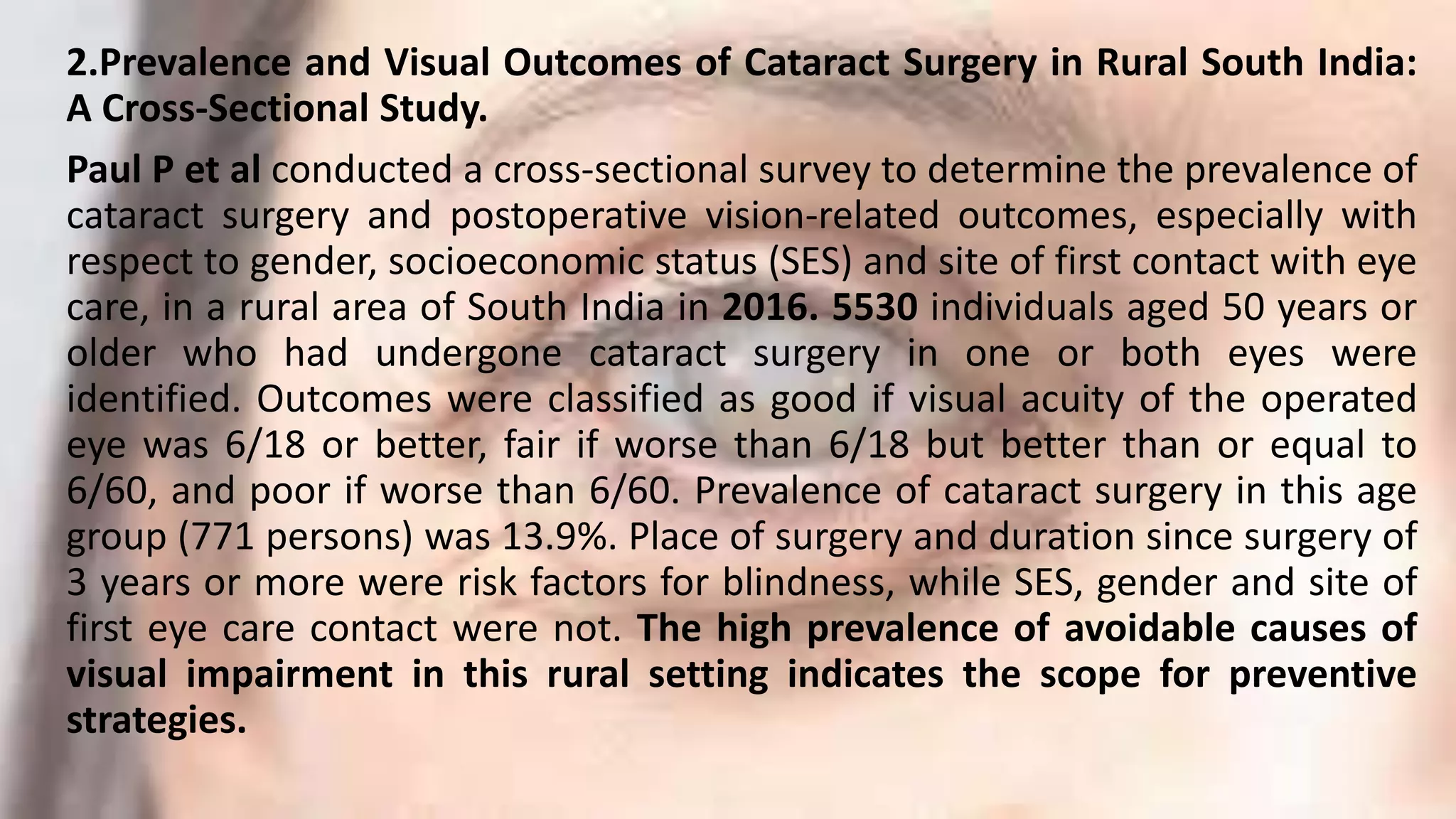
5. PubMed. Prevalence and Visual Outcomes of Cataract Surgery in Rural South
India: A Cross-Sectional Study. Ophthalmic Epidemiol. 2016 Oct;23(5):309-15. doi:
10.1080/09286586.2016.1212991. Epub 2016 Aug 23.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cataract-200605111818/75/Cataract-and-its-management-50-2048.jpg)




