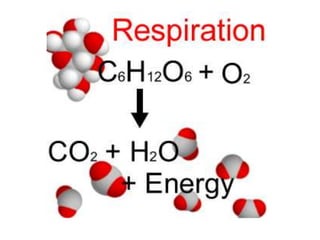
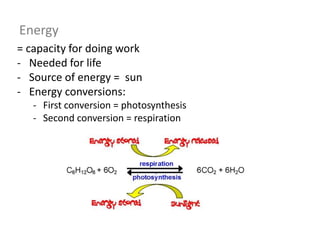
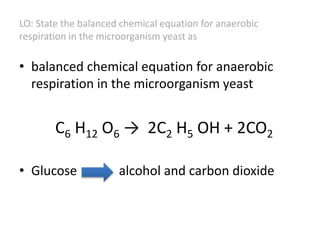
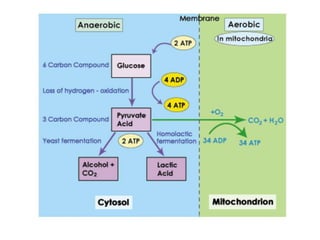
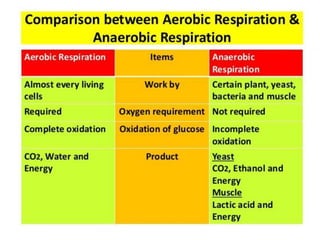
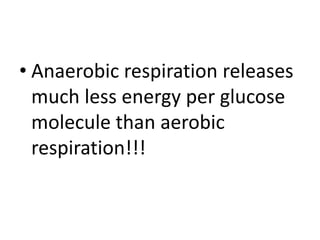Respiration involves the breakdown of nutrients to release energy in cells. It requires oxygen and enzymes. Aerobic respiration uses oxygen to break down glucose, releasing carbon dioxide and water. The chemical equation is C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O. Anaerobic respiration breaks down glucose without oxygen, producing less energy. In yeast, the equation is C6H12O6 → 2C2H5OH + 2CO2. During vigorous exercise, lactic acid builds up and is later removed as the oxygen debt is repaid during recovery.