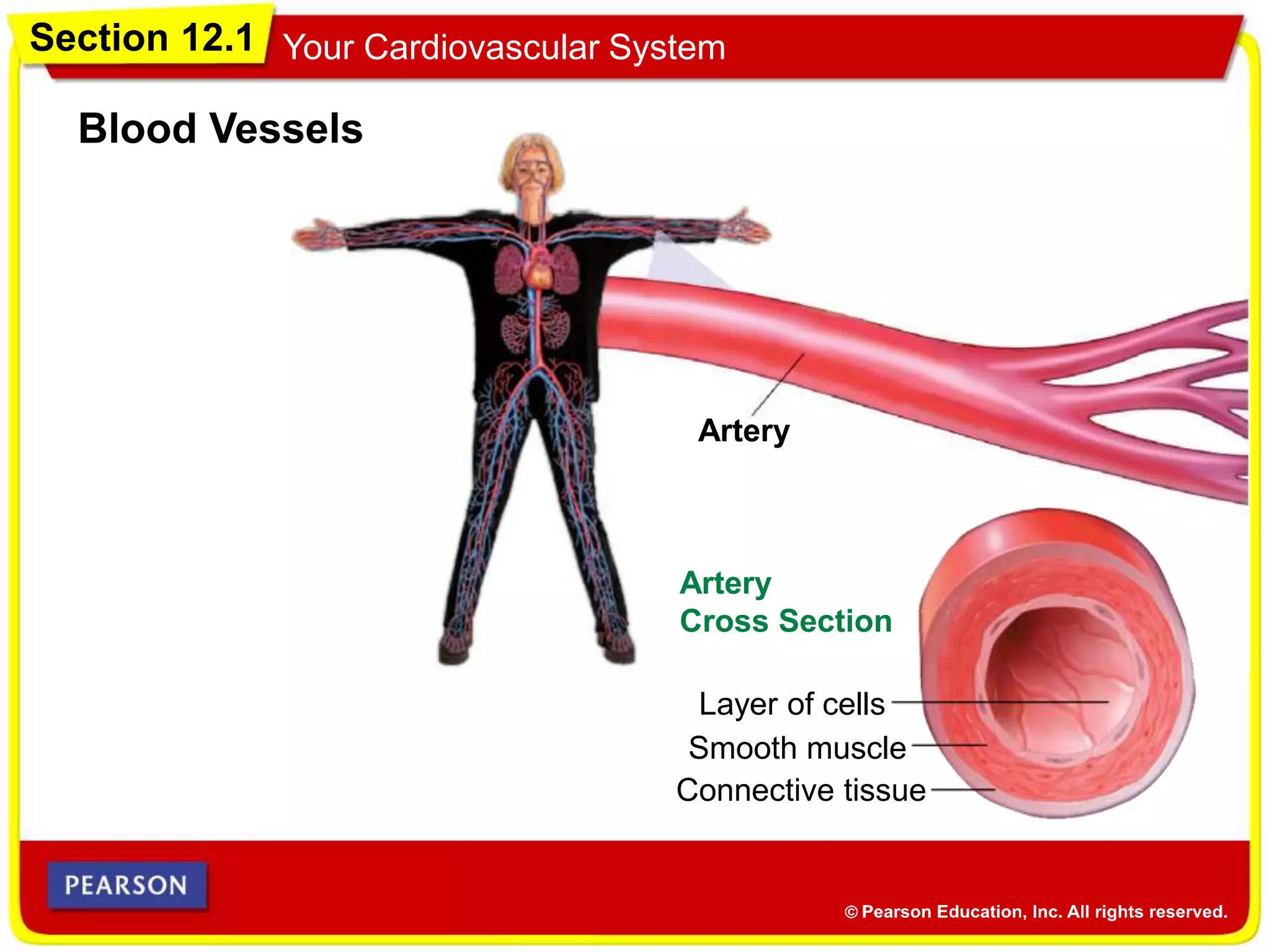
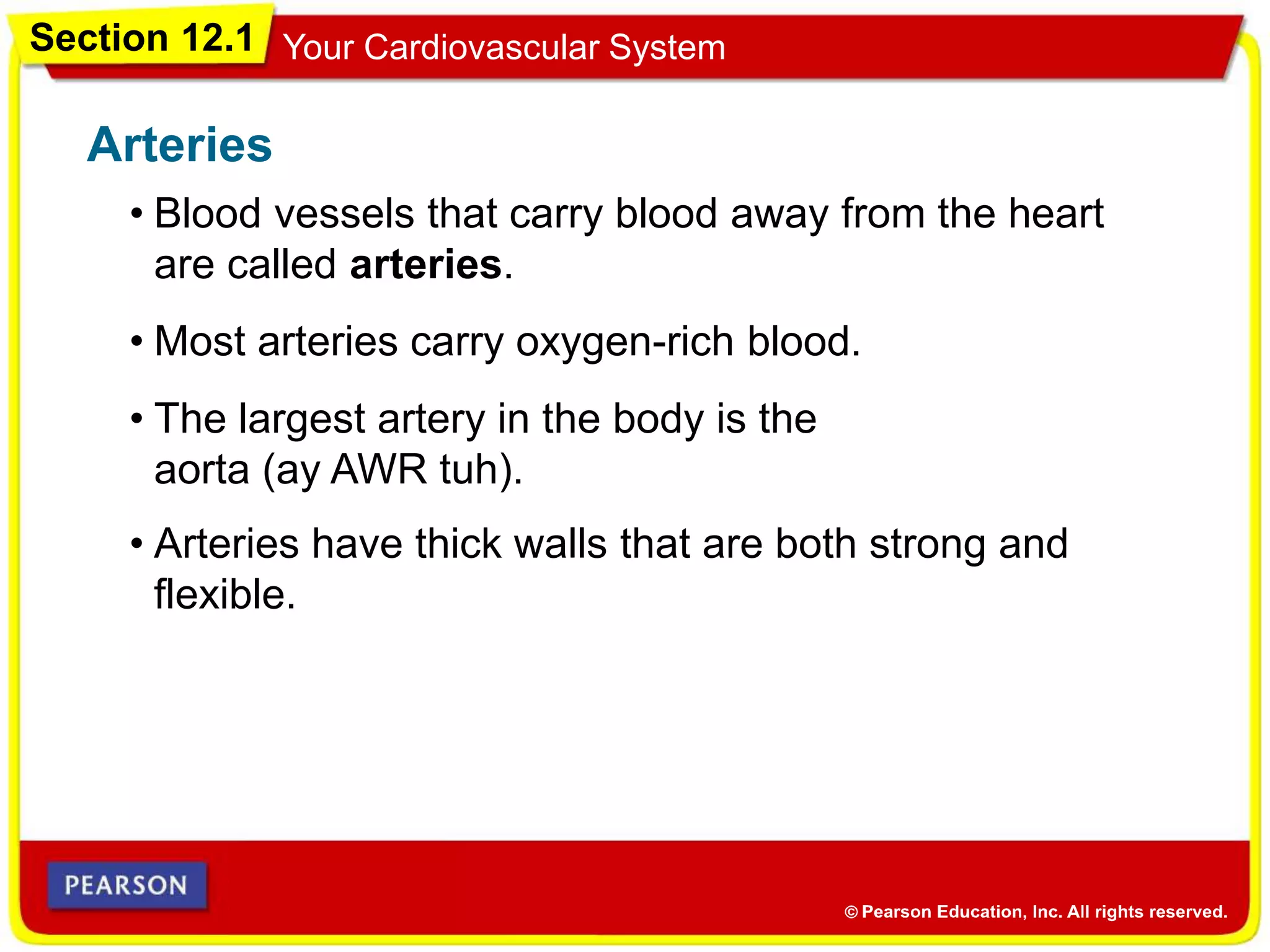
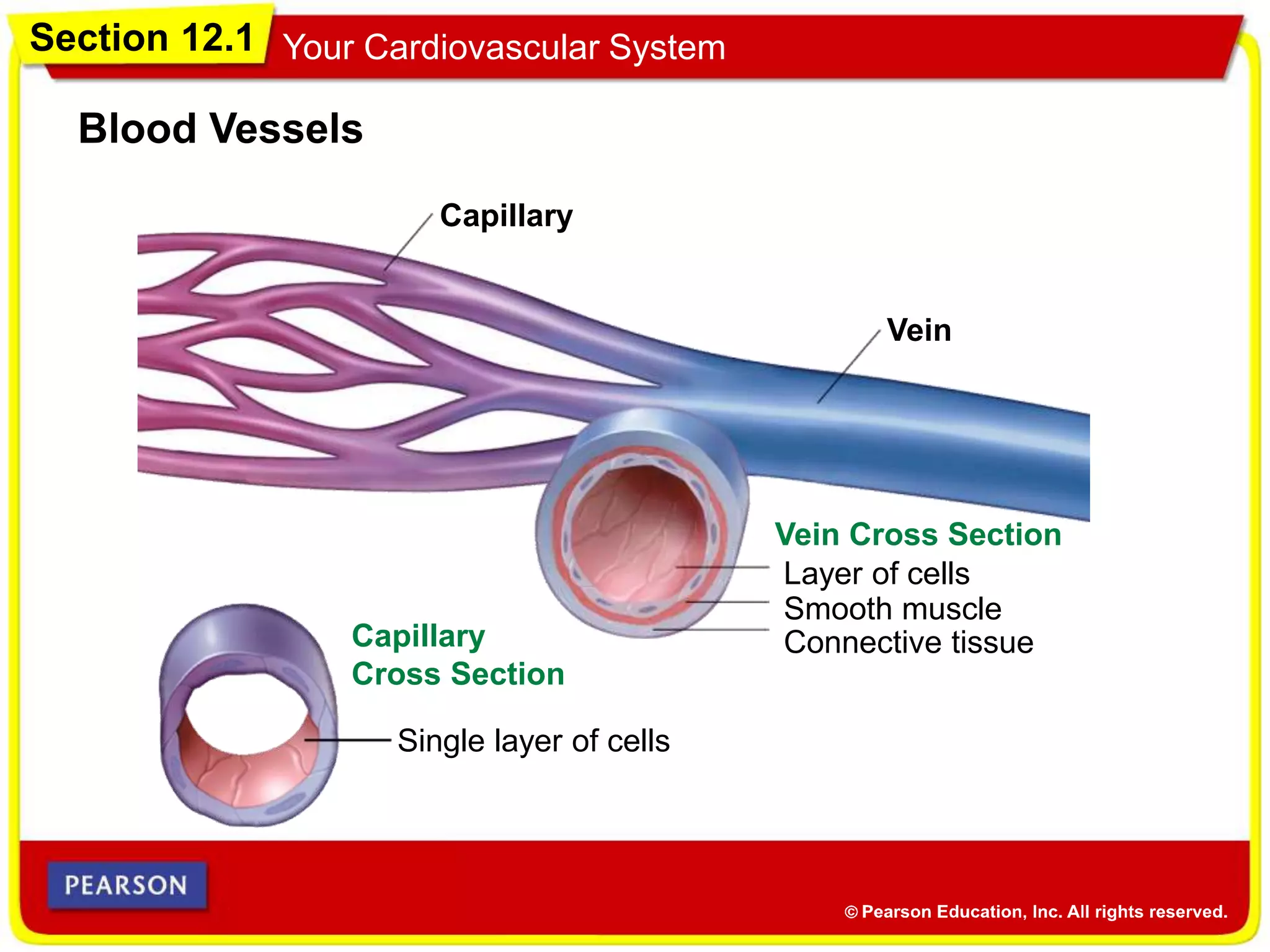
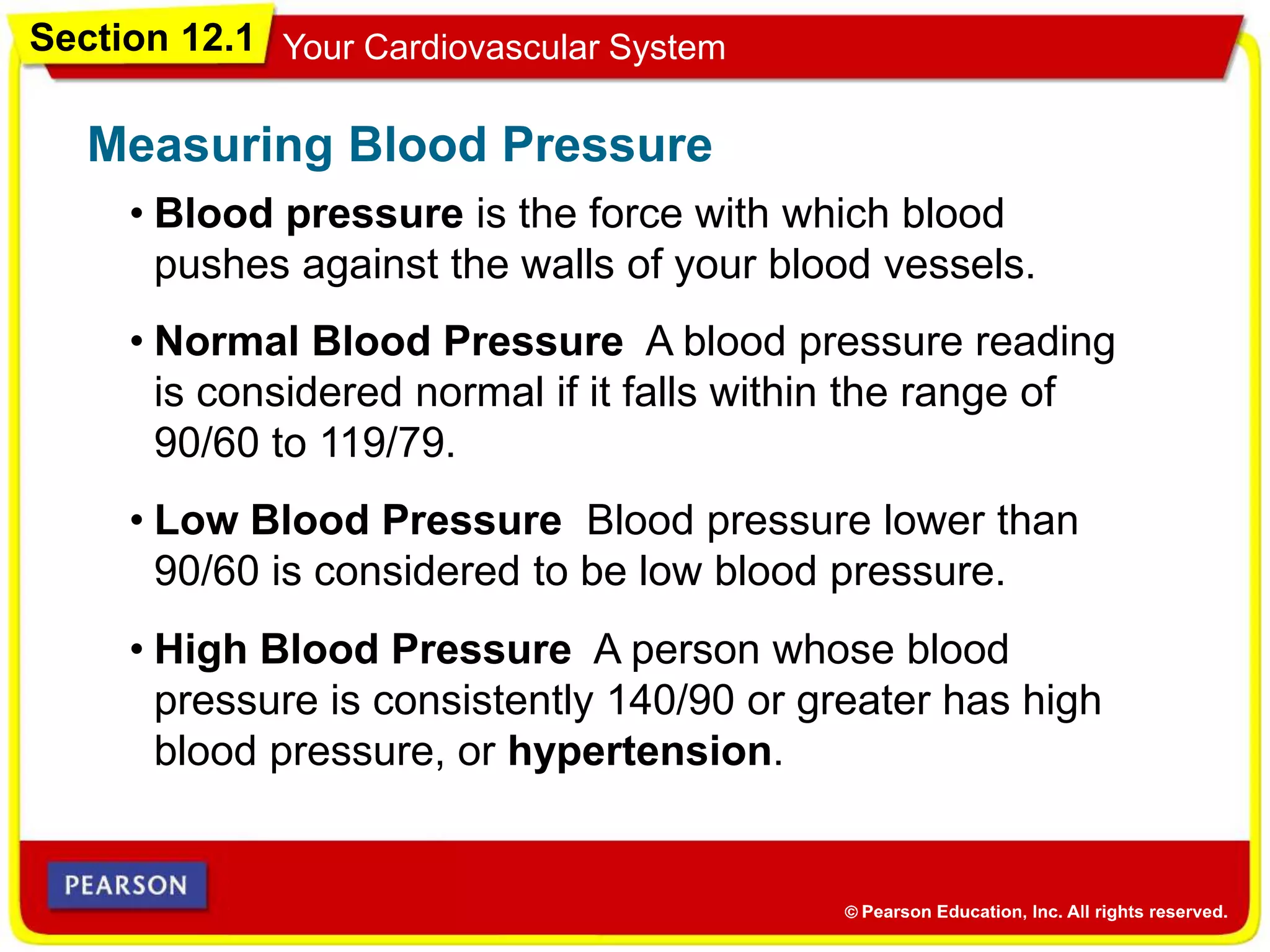
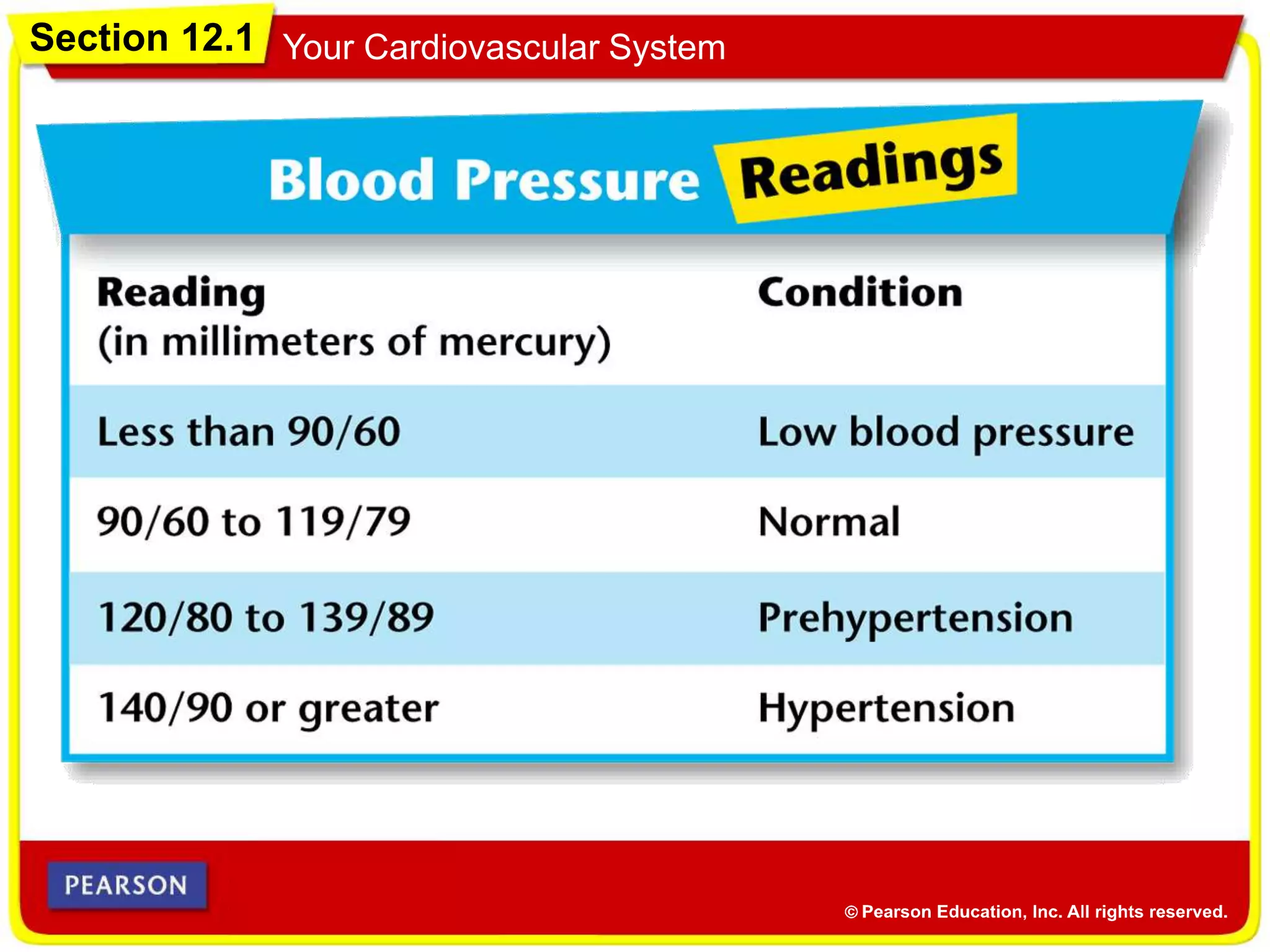
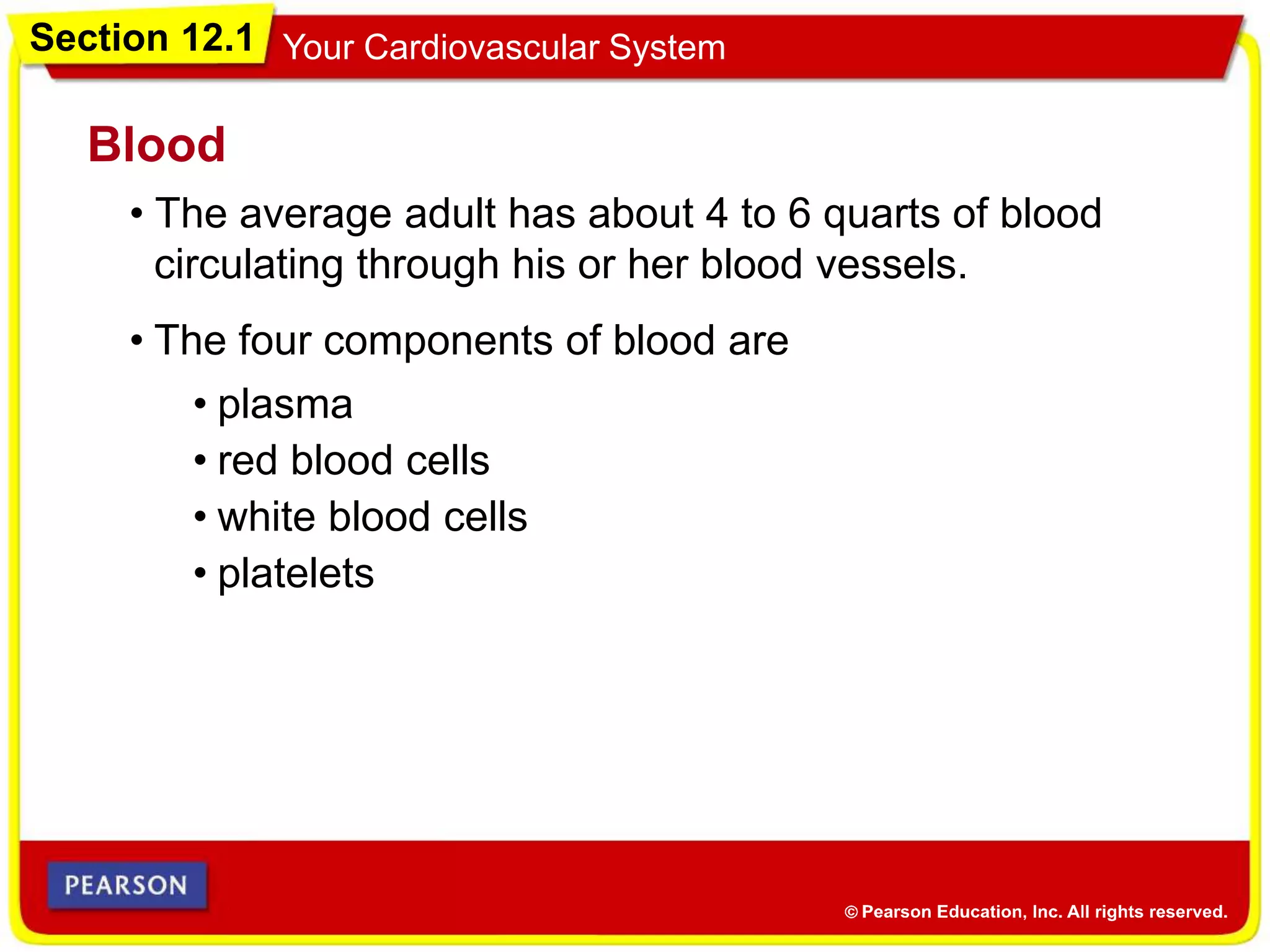
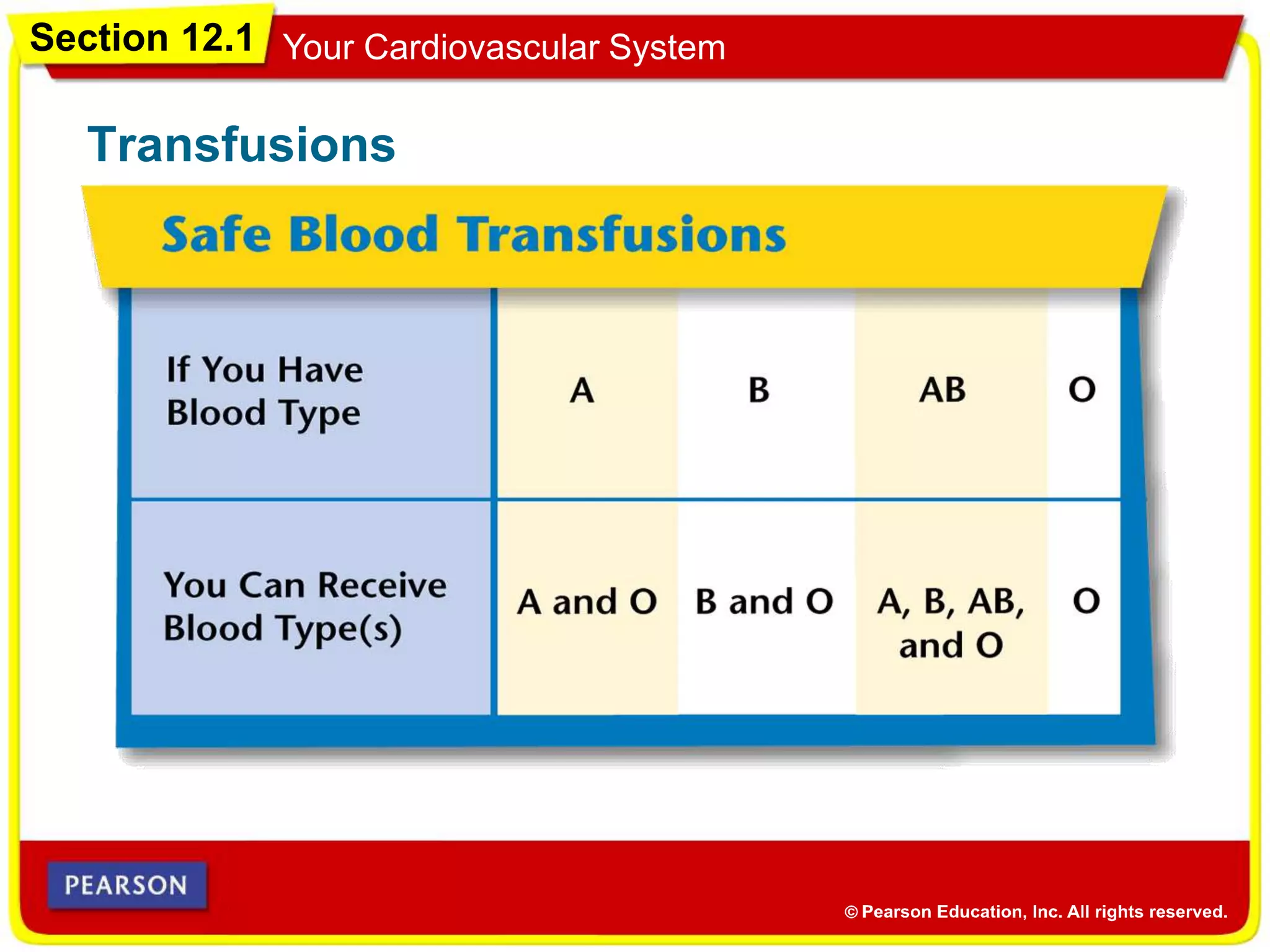
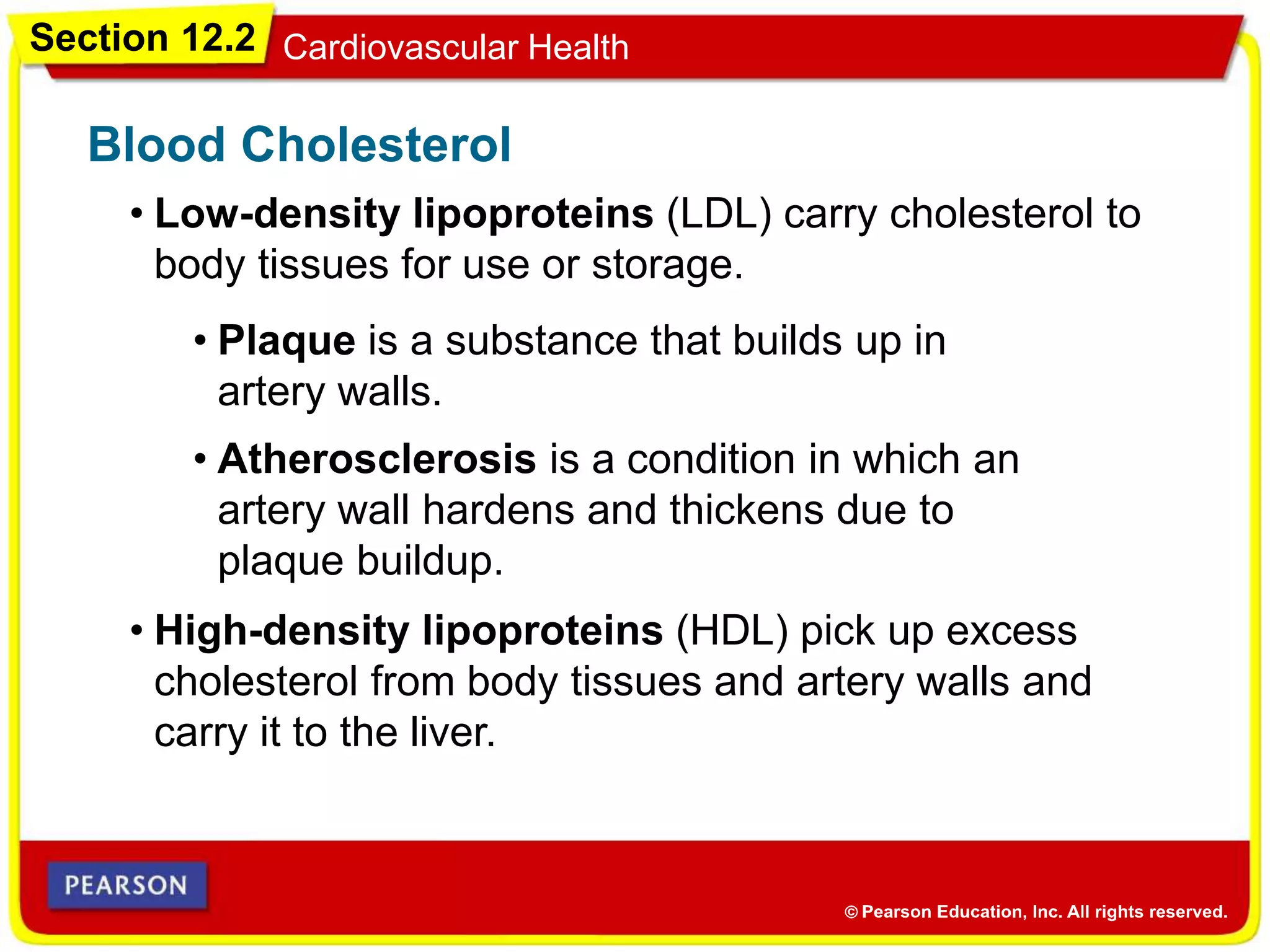
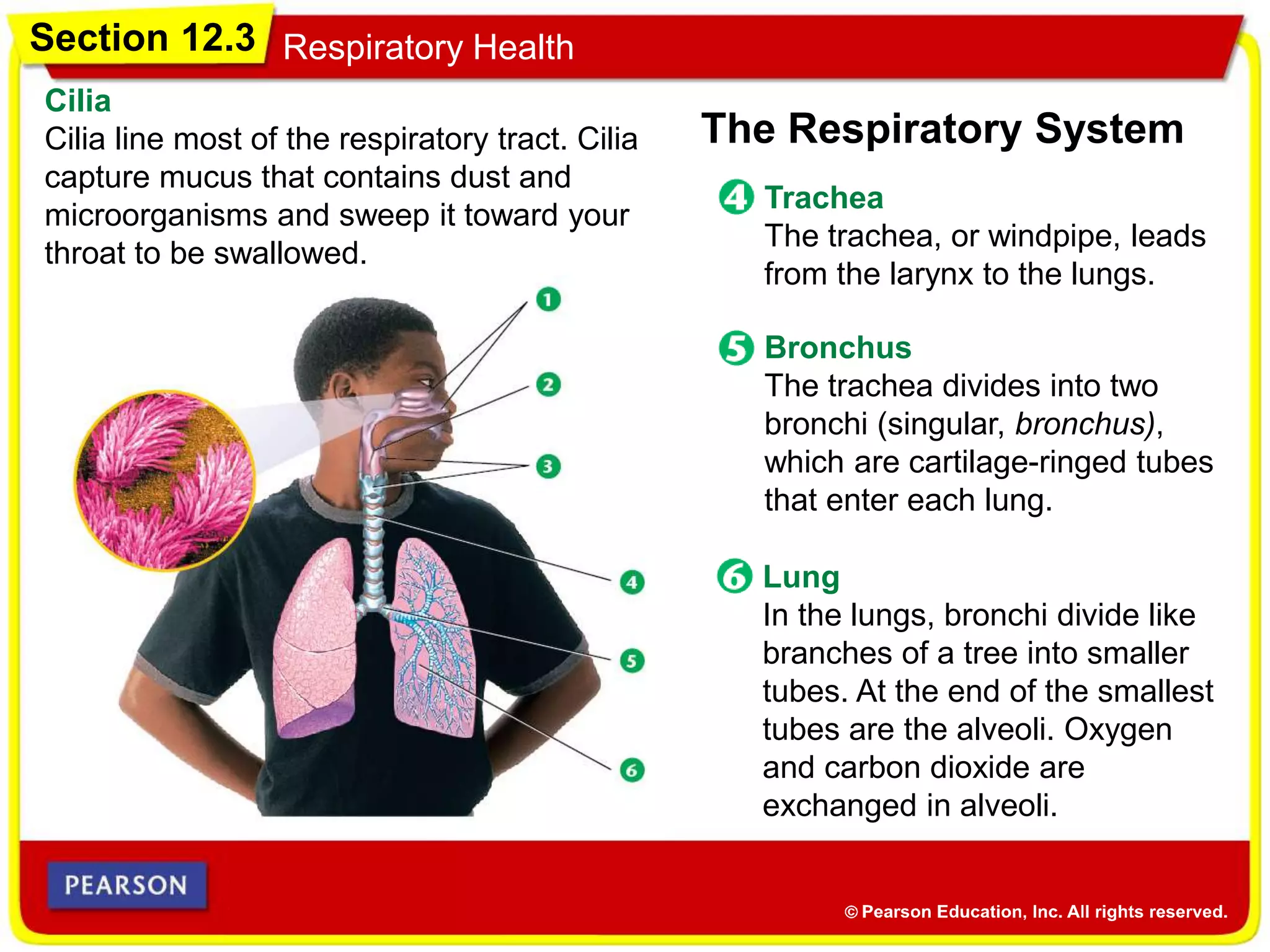
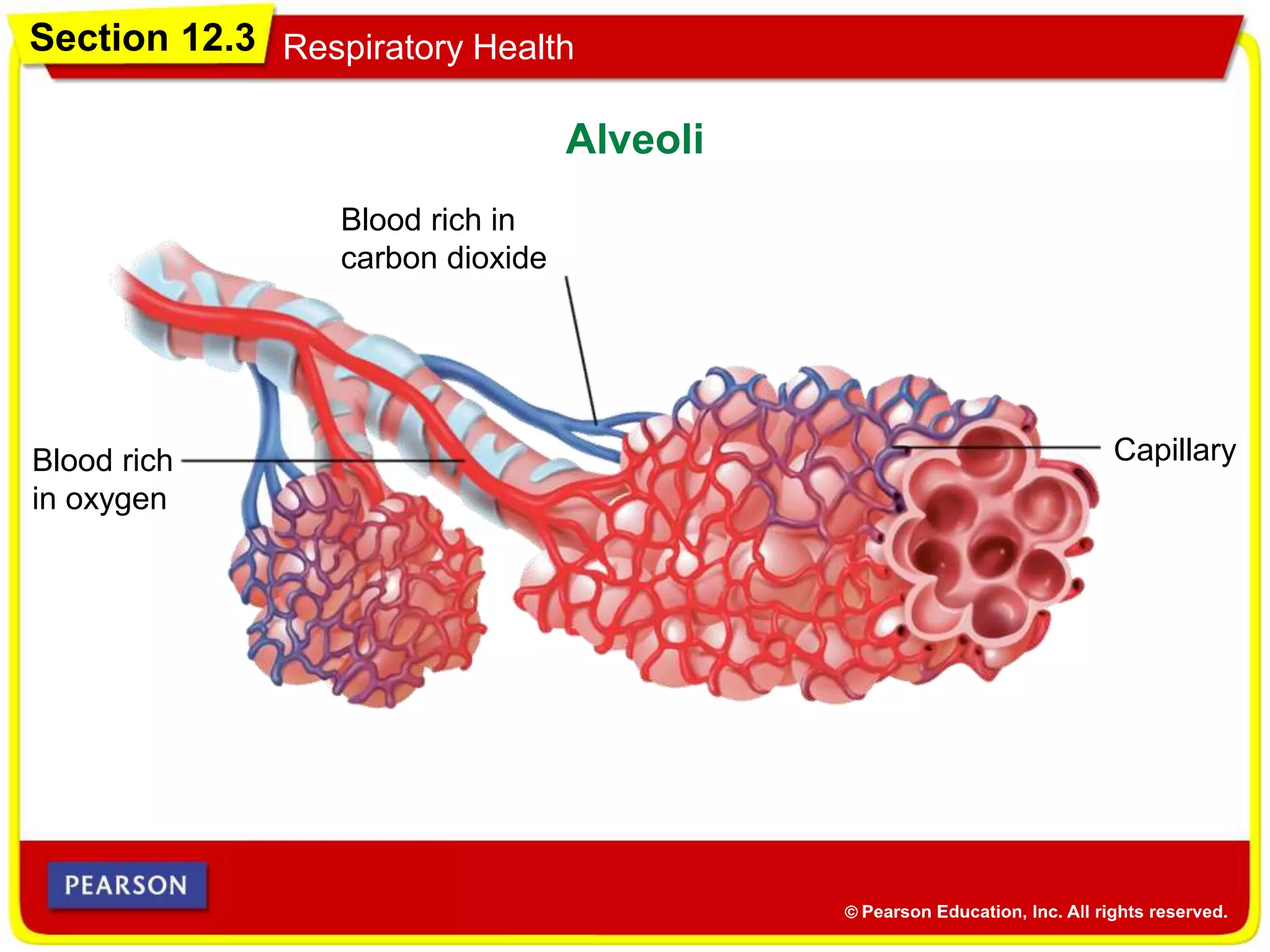
The cardiovascular system consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood, and has three main functions: delivering materials to cells, carrying wastes away, and fighting disease. The heart pumps blood through arteries, capillaries, and veins, delivering oxygen and nutrients to tissues and removing carbon dioxide and other wastes. Blood contains red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and plasma. Maintaining a healthy cardiovascular system involves regular exercise, a balanced diet low in saturated fat, and avoiding smoking.