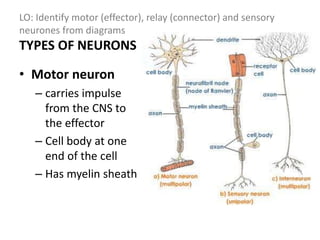
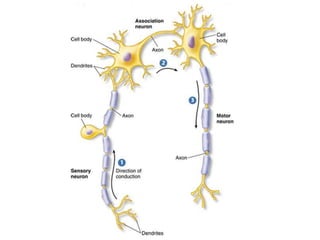
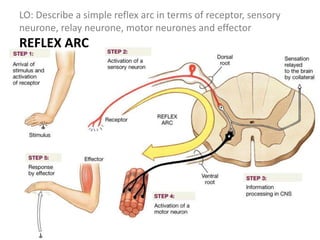
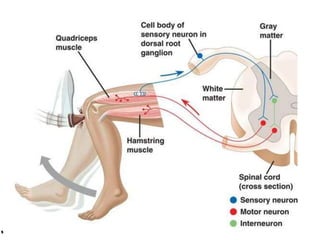
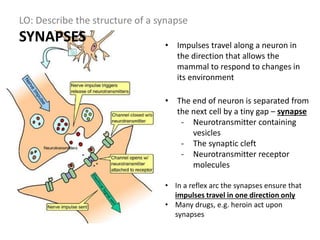
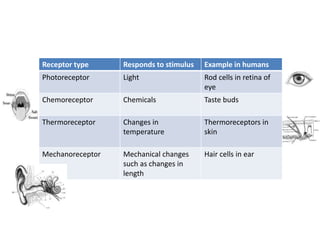
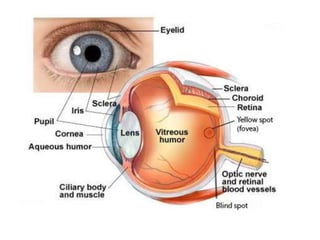
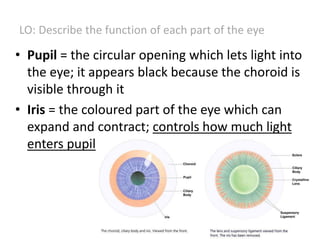
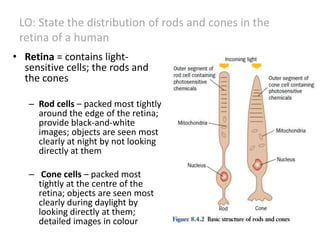
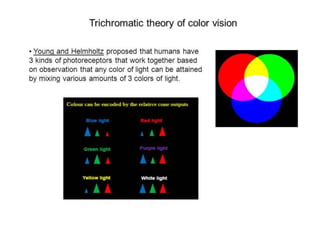
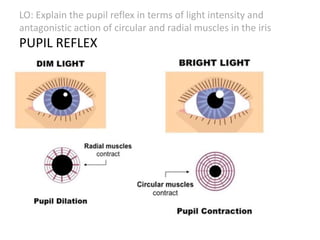
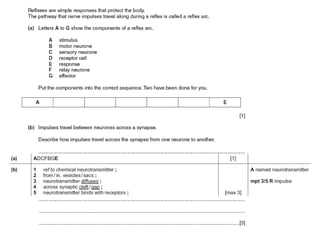
The document describes the human nervous system. It discusses the central nervous system (CNS) which includes the brain and spinal cord for coordination. The peripheral nervous system (PNS) consists of nerves that coordinate and regulate body functions. It distinguishes between voluntary actions initiated by conscious decision and involuntary reflex actions. A nerve impulse is an electrical signal that passes along nerve cells called neurons. A simple reflex arc involves a receptor, sensory neuron, relay neuron, motor neuron, and effector. Synapses allow impulses to travel between neurons via the release of neurotransmitters. Sense organs such as the eye respond to specific stimuli like light. The eye contains structures like the iris, lens, retina and cornea that help focus light and detect