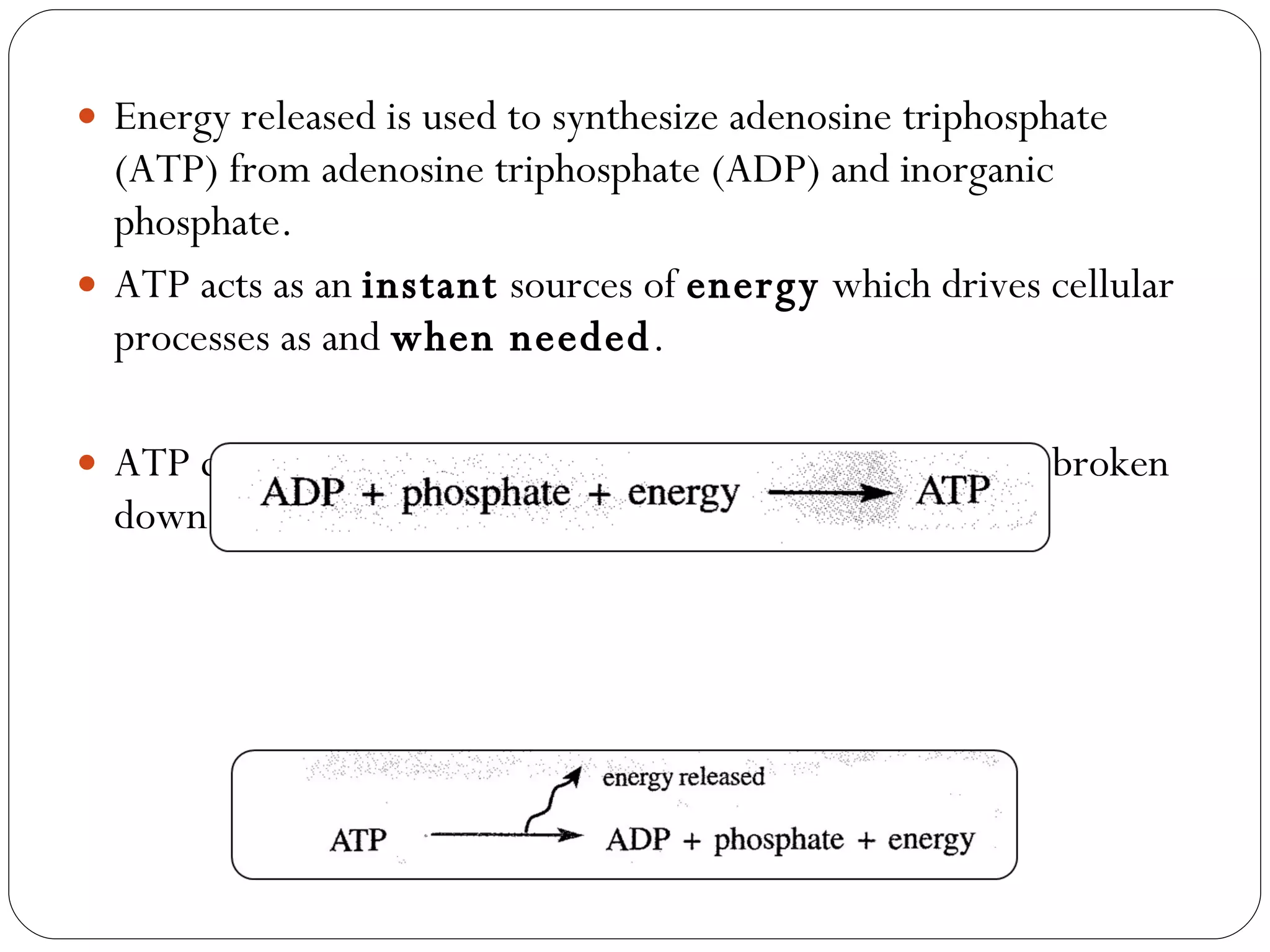
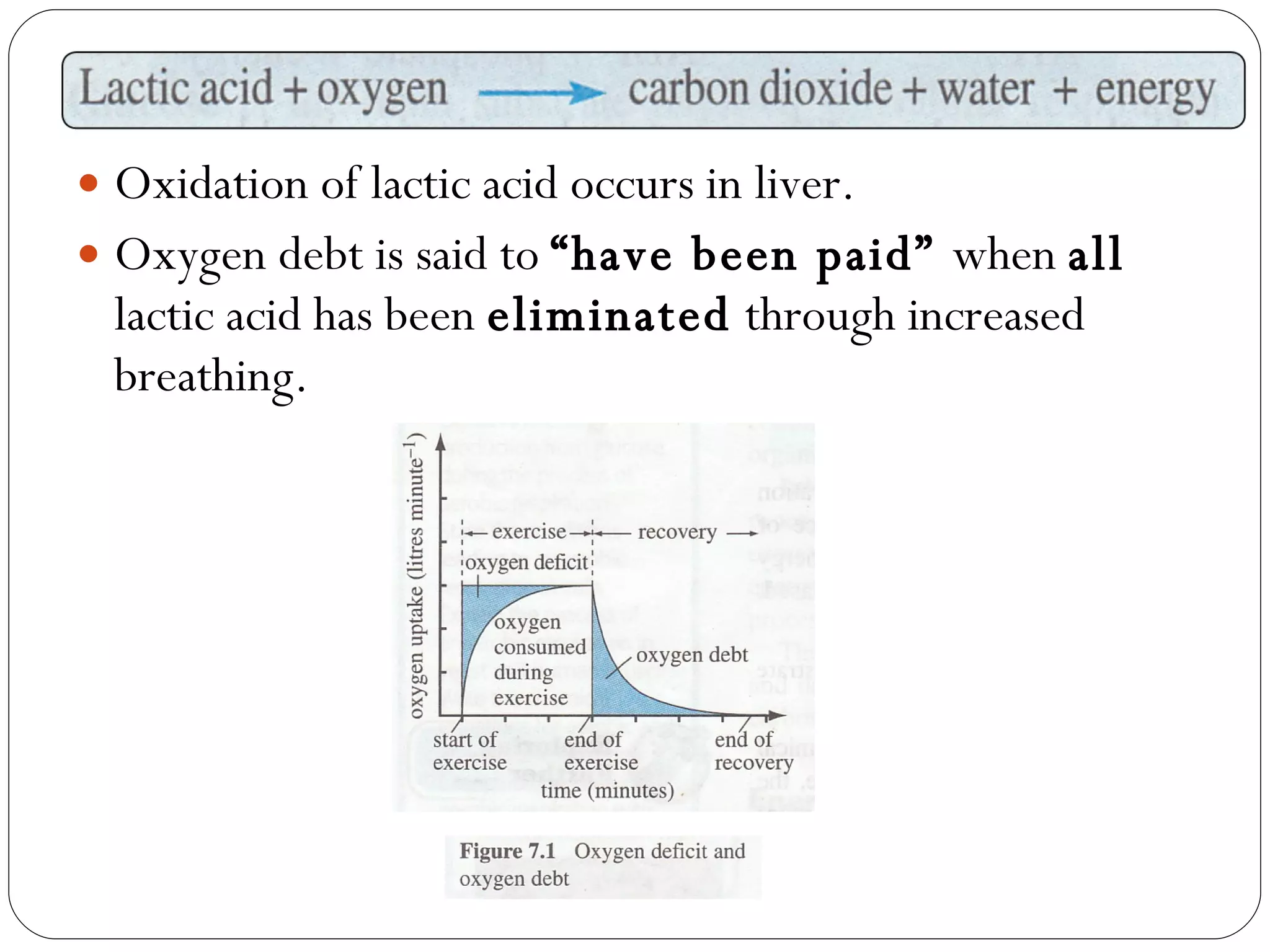
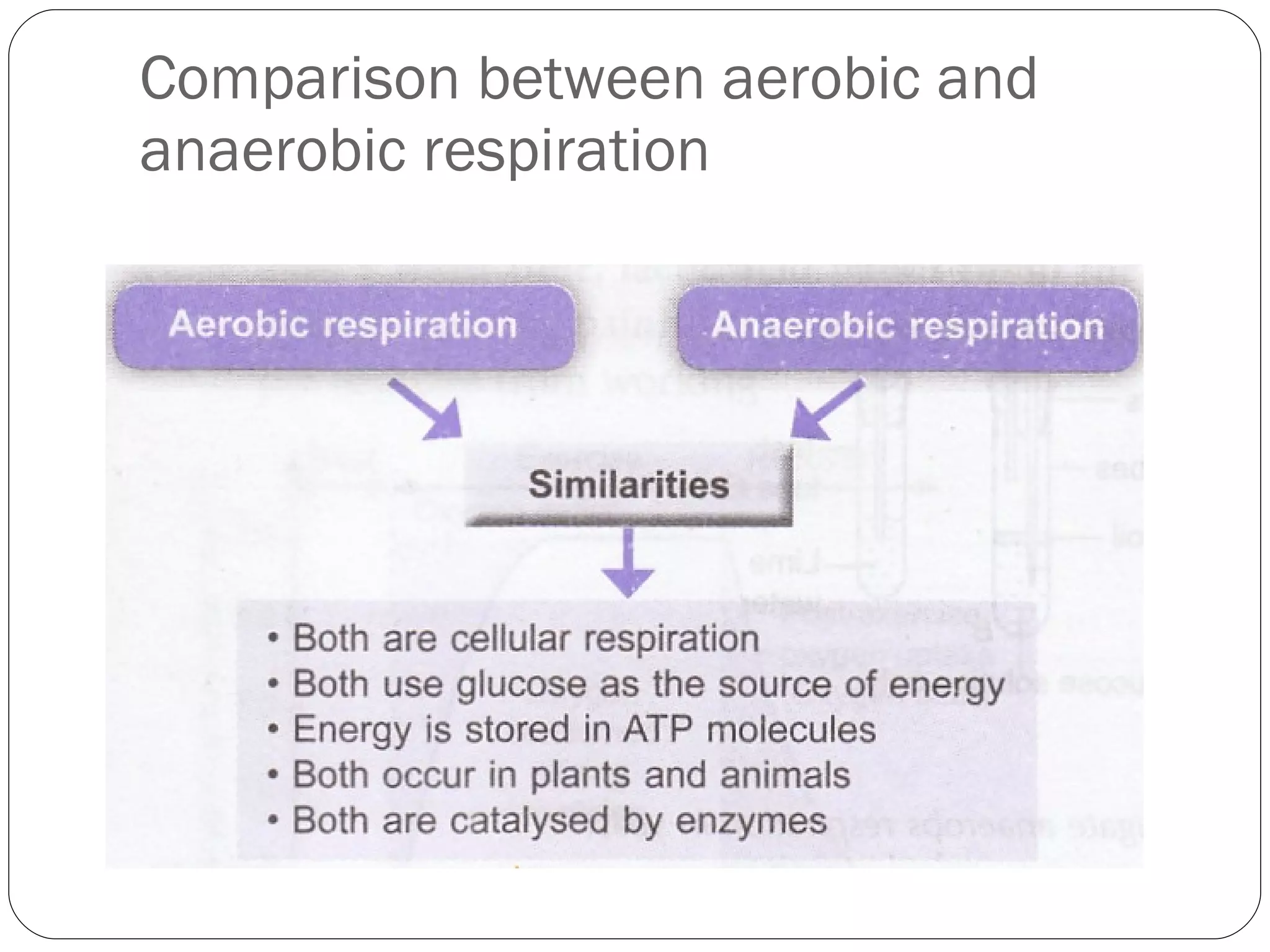
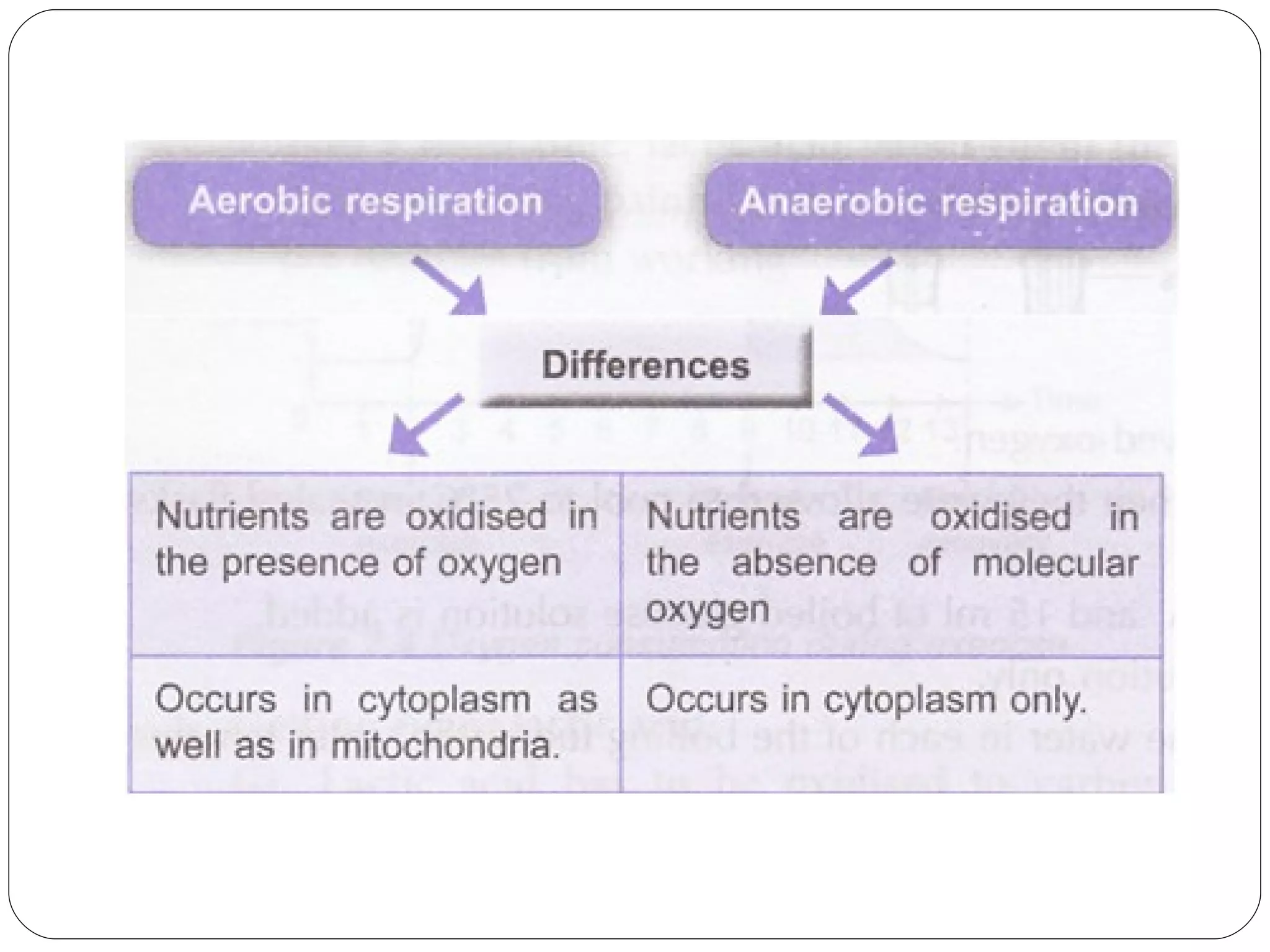
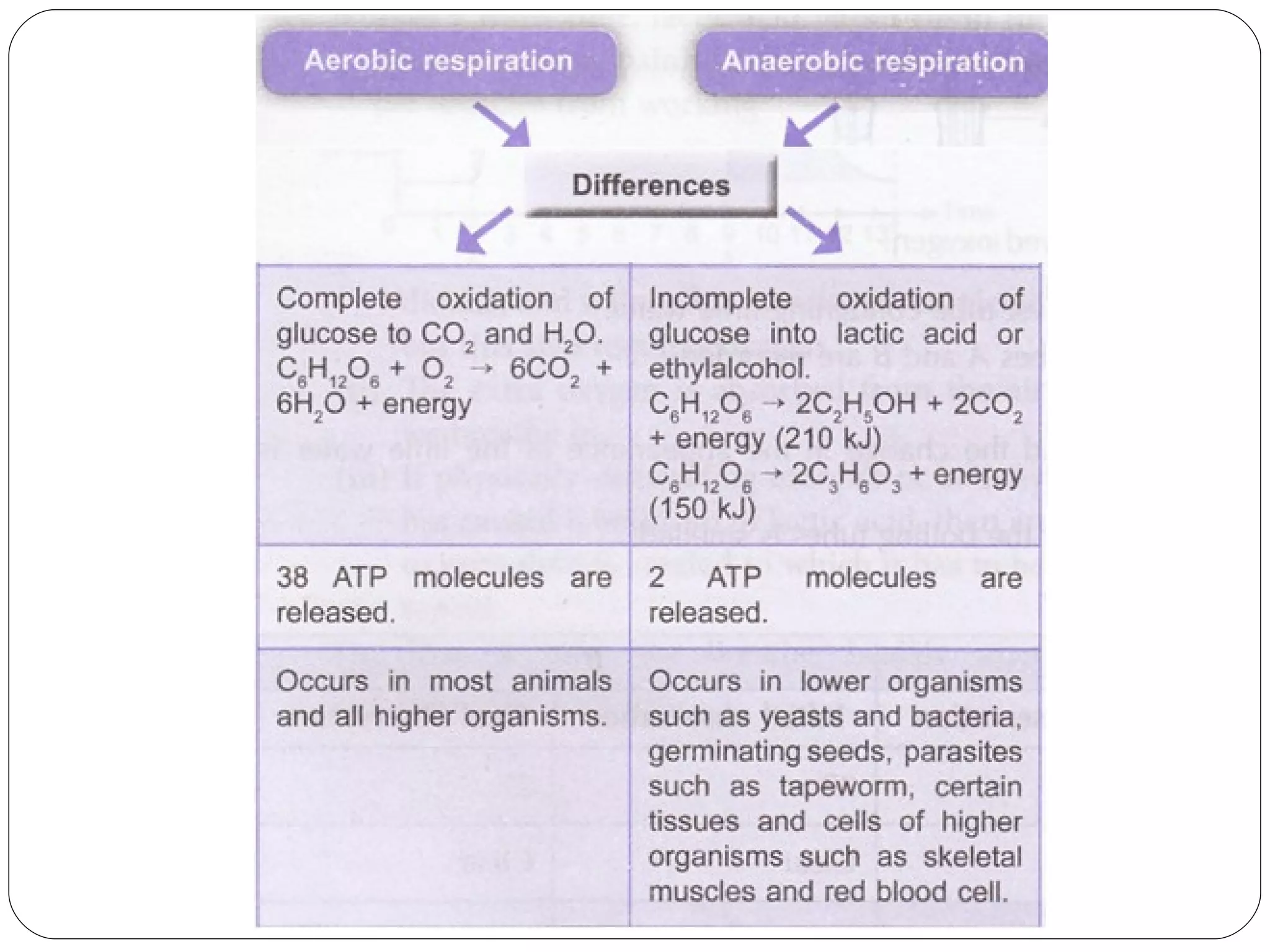
Aerobic respiration requires oxygen and fully breaks down glucose to release more energy in the form of ATP. It occurs in mitochondria. Anaerobic respiration does not require oxygen but produces less ATP. In humans, it occurs in muscles during intense exercise when oxygen demand outstrips supply, breaking glucose down to lactic acid. The lactic acid must later be oxidized to remove oxygen debt after exercise is complete. Anaerobic respiration in yeast produces ethanol through fermentation.