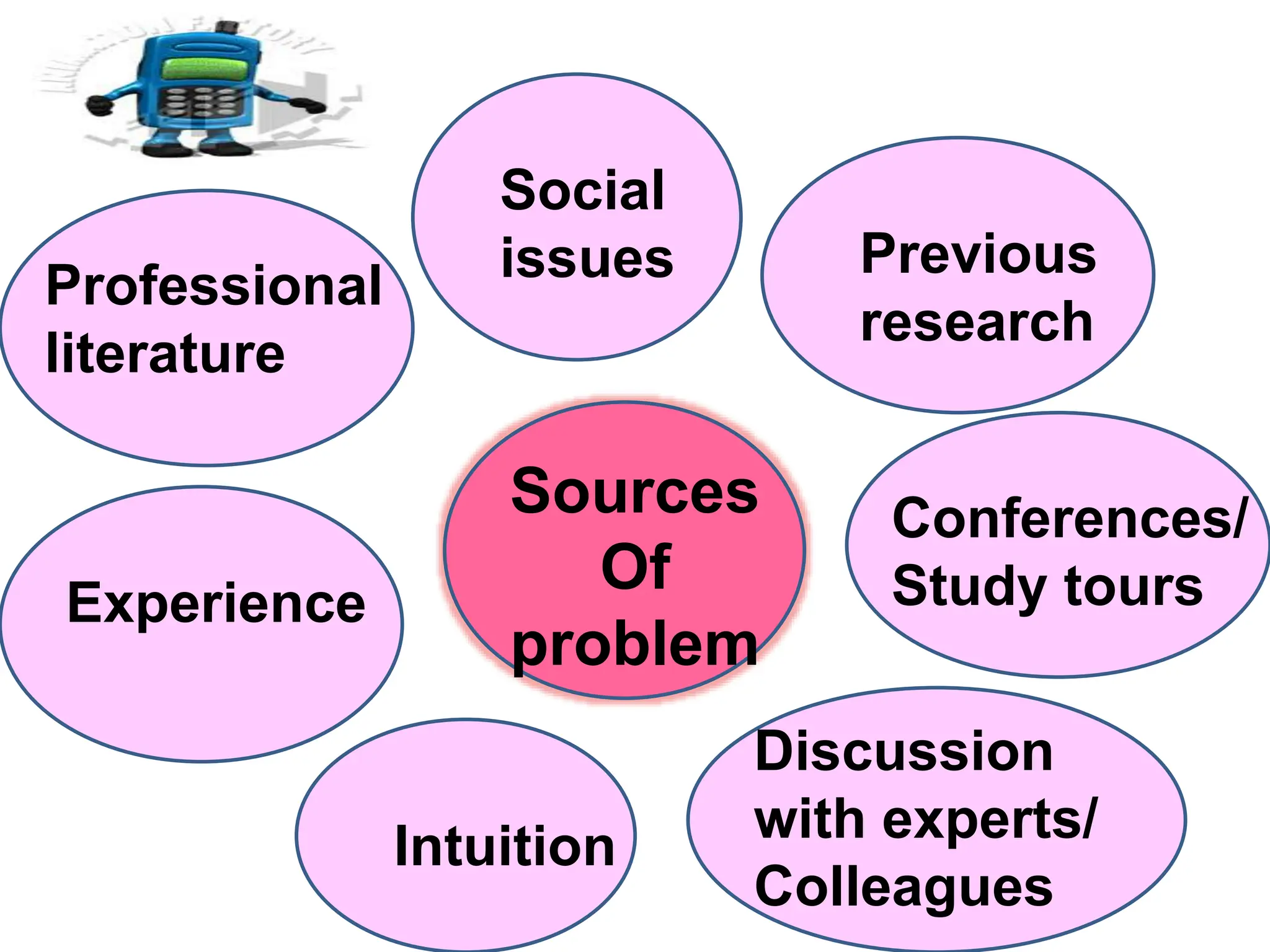
This document discusses identifying research problems in nursing. It defines research as a systematic, organized inquiry aimed at finding answers to specific problems. Nursing research builds the body of nursing knowledge and provides a scientific basis for practice. Some key points made about identifying research problems include that they should be verifiable, needed, important, feasible, and add to nursing knowledge. Well-defined problems specify what will be studied, how it will be studied, who or what will be studied, and where. Sources of research problems include intuition, experience, literature, social issues, and discussions with experts.