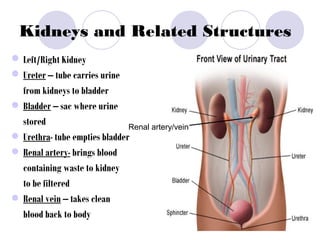
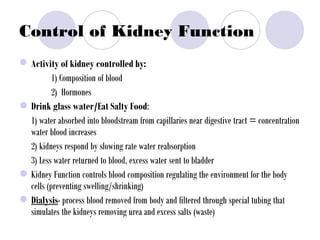
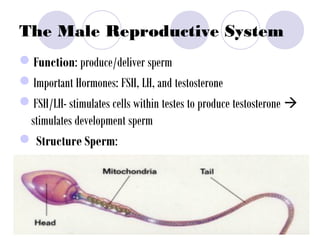
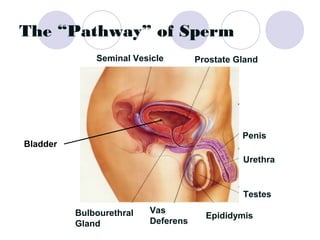
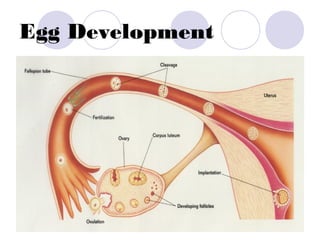
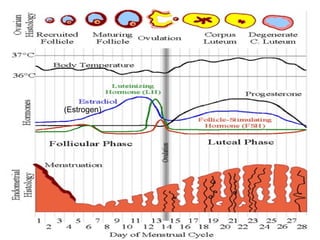
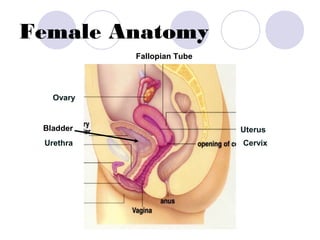
The document summarizes the urogenital system, which includes both the excretory (urinary) and reproductive systems. It describes the key functions and organs of the excretory system, including filtration and waste removal by the kidneys, as well as hormone regulation of kidney function. It then overviews the male and female reproductive systems, describing sperm production and transport in males and the female menstrual cycle and egg development in four phases: follicular, ovulation, luteal, and menstruation.