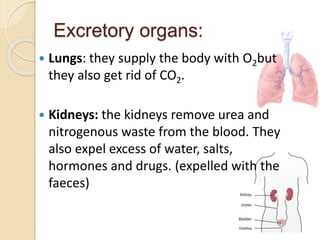
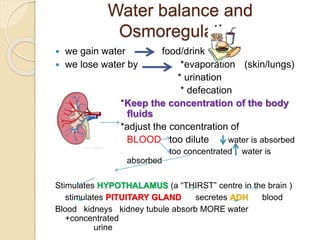
The excretory system removes waste from the body through various organs. The kidneys are the primary organs of excretion, removing nitrogenous wastes such as urea and excess water and salts. The kidneys contain nephrons, which filter the blood to produce urine. Urine passes from the nephrons to the bladder through the ureters for storage and later excretion through the urethra. Homeostasis is maintained as the kidneys regulate water balance and the concentration of substances in the blood and tissues.