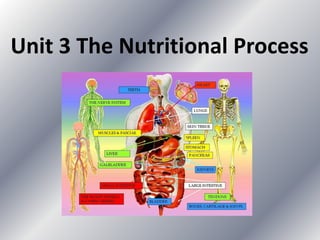
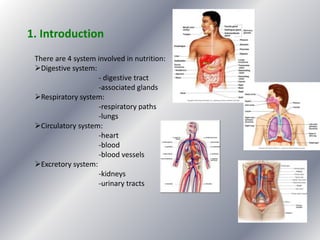
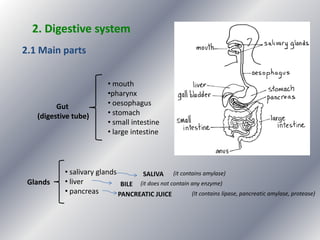
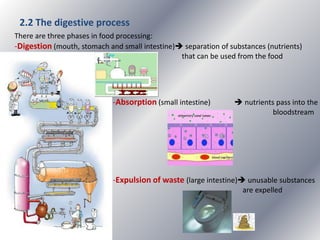
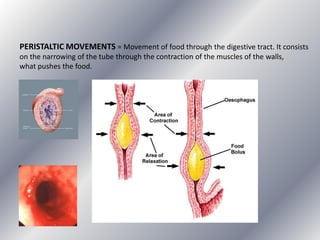
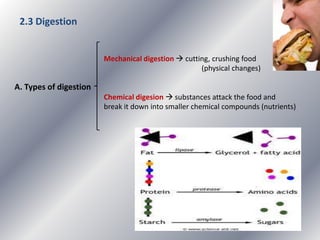
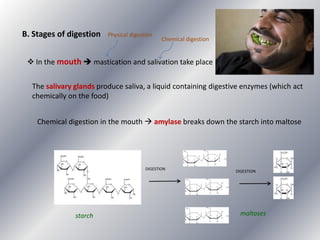
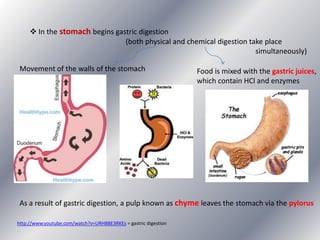
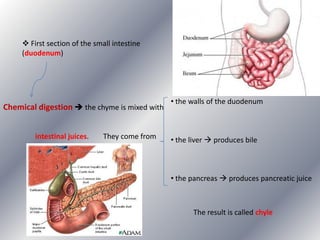
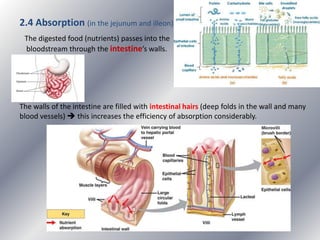
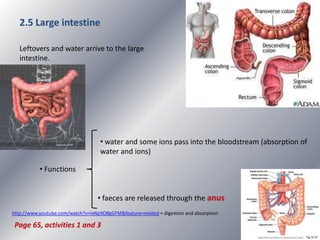
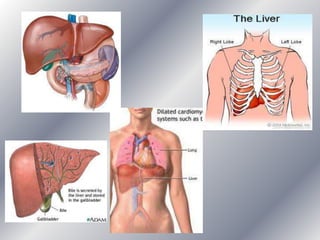
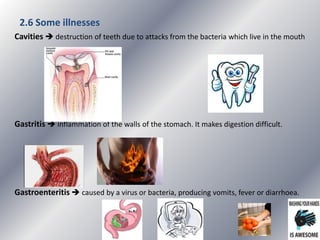
This document summarizes the key systems involved in the nutritional process: digestive, respiratory, circulatory, and excretory. It focuses on the digestive system, including the main parts of the gut and associated glands. The three phases of digestion - digestion, absorption, and expulsion - are described. The stages of digestion that occur in the mouth, stomach, and small intestine involve both physical and chemical breakdown of food. Absorption of nutrients occurs in the small intestine, while waste is expelled through the large intestine and other organs like the lungs and kidneys. Some common digestive illnesses are also briefly mentioned.